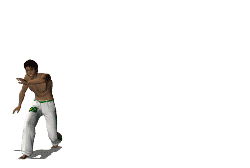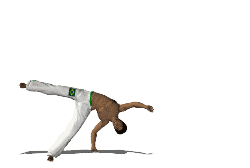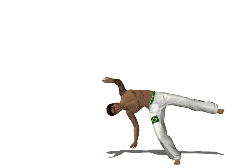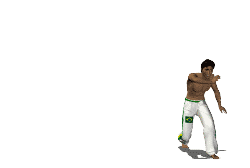|
Cebrennus Rechenbergi
''Cebrennus rechenbergi'', also known as the Moroccan flic-flac spider and cartwheeling spider, is a species of huntsman spider indigenous to the sand dunes of the Erg Chebbi desert in Morocco. If provoked or threatened it can escape by doubling its normal walking speed using forward or backward flips similar to acrobatic flic-flac movements used by gymnasts. ''C. rechenbergi'' is the only spider known to use this unique form of rolling locomotion. The discovery of the Moroccan flic-flac spider has influenced biomimetic robot research, resulting in the development of an experimental robot based on the spider's motion.King, R.S. (2013). ''BiLBIQ: A Biologically Inspired Robot with Walking and Rolling Locomotion''. Biosystems and Biorobotics. 2. Springer, Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg. Etymology The spider is named after its discoverer, Ingo Rechenberg, bionics professor at the Technische Universität Berlin. Rechenberg may have first encountered the spider on a trip to Mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cebrennus Villosus
''Cebrennus'' is a genus of huntsman spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1880. It is considered a senior synonym of ''Cerbalopsis''. The Moroccan flic-flac spider (''C. rechenbergi''), that uses a flic-flac motion to escape threats, was first described in 2014. Species it contains nineteen species, found in Africa, Asia, on Malta, and in Spain: *''Cebrennus aethiopicus'' Simon, 1880 – Egypt, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Sudan, Djibouti, Saudi Arabia *''Cebrennus atlas'' Peter Jäger, Jäger, 2014 – Morocco *''Cebrennus castaneitarsis'' Simon, 1880 – Algeria to Israel *''Cebrennus concolor'' (Denis, 1947) – Egypt *''Cebrennus cultrifer'' Fage, 1921 – Algeria *''Cebrennus flagellatus'' Jäger, 2014 – Afghanistan *''Cebrennus intermedius'' Jäger, 2000 – Saudi Arabia *''Cebrennus kochi'' (Octavius Pickard-Cambridge, O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1872) – Syria, Israel *''Cebrennus laurae'' Jäger, 2014 – Canary Is. *''Cebrennus logunovi'' Jäger, 2000 – T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cebrennus
''Cebrennus'' is a genus of huntsman spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1880. It is considered a senior synonym of ''Cerbalopsis''. The Moroccan flic-flac spider (''C. rechenbergi''), that uses a flic-flac motion to escape threats, was first described in 2014. Species it contains nineteen species, found in Africa, Asia, on Malta, and in Spain: *''Cebrennus aethiopicus'' Simon, 1880 – Egypt, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Sudan, Djibouti, Saudi Arabia *''Cebrennus atlas'' Jäger, 2014 – Morocco *''Cebrennus castaneitarsis'' Simon, 1880 – Algeria to Israel *''Cebrennus concolor'' (Denis, 1947) – Egypt *''Cebrennus cultrifer'' Fage, 1921 – Algeria *''Cebrennus flagellatus'' Jäger, 2014 – Afghanistan *''Cebrennus intermedius'' Jäger, 2000 – Saudi Arabia *''Cebrennus kochi'' (O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1872) – Syria, Israel *''Cebrennus laurae'' Jäger, 2014 – Canary Is. *''Cebrennus logunovi'' Jäger, 2000 – Turkmenistan *'' Cebrennus mayri'' Jäger, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Jäger
Peter Jäger is a German people, German arachnologist, and current Head of Arachnology at the Naturmuseum Senckenberg, Senckenberg Research Institute and Natural History Museum in Frankfurt, Germany. He has named several spiders after celebrities; in 2008, he named ''Heteropoda davidbowie'' after British singer David Bowie, and ''Heteropoda ninahagen'' after German singer Nina Hagen. In 2013, he named ''Bowie monaghani, Ctenus monaghani'' (currently in the genus ''Bowie (spider), Bowie'') after actor Dominic Monaghan, to honor his work in the documentary series ''Wild Things with Dominic Monaghan''. In 2020, Jäger named a new genus and species of huntsman spiders from Madagascar after Greta Thunberg. The new spider is named ''Thunberga greta''. In 2022, he named 54 species of huntsman spiders from across Asia under the new genus ''Bowie (spider), Bowie'' in commemoration of the musician David Bowie 75th's birthday, the second time the musician's name was honored. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cebrennus Rechenbergi
''Cebrennus rechenbergi'', also known as the Moroccan flic-flac spider and cartwheeling spider, is a species of huntsman spider indigenous to the sand dunes of the Erg Chebbi desert in Morocco. If provoked or threatened it can escape by doubling its normal walking speed using forward or backward flips similar to acrobatic flic-flac movements used by gymnasts. ''C. rechenbergi'' is the only spider known to use this unique form of rolling locomotion. The discovery of the Moroccan flic-flac spider has influenced biomimetic robot research, resulting in the development of an experimental robot based on the spider's motion.King, R.S. (2013). ''BiLBIQ: A Biologically Inspired Robot with Walking and Rolling Locomotion''. Biosystems and Biorobotics. 2. Springer, Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg. Etymology The spider is named after its discoverer, Ingo Rechenberg, bionics professor at the Technische Universität Berlin. Rechenberg may have first encountered the spider on a trip to Mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiders Described In 2014
Spiders ( order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 50,356 spider species in 132 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical pedicel, however, as there is currently neither paleontological nor embryological evidence that spiders ever had a separate t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiders Of Africa
Spiders ( order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 50,356 spider species in 132 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical pedicel, however, as there is currently neither paleontological nor embryological evidence that spiders ever had a separate t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparassidae
Huntsman spiders, members of the family Sparassidae (formerly Heteropodidae), are known by this name because of their speed and mode of hunting. They are also called giant crab spiders because of their size and appearance. Larger species sometimes are referred to as wood spiders, because of their preference for woody places (forests, mine shafts, woodpiles, wooden shacks). In southern Africa the genus ''Palystes'' are known as rain spiders or lizard-eating spiders. Commonly, they are confused with baboon spiders from the Mygalomorphae infraorder, which are not closely related. More than a thousand Sparassidae species occur in most warm temperate to tropical regions of the world, including much of Australasia, Africa, Asia, the Mediterranean Basin, and the Americas. Several species of huntsman spider can use an unusual form of locomotion. The wheel spider (''Carparachne aureoflava'') from the Namib uses a cartwheeling motion which gives it its name, while ''Cebrennus rechenbergi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berber Languages
The Berber languages, also known as the Amazigh languages or Tamazight,, ber, label=Tuareg Tifinagh, ⵜⵎⵣⵗⵜ, ) are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They comprise a group of closely related languages spoken by Berber communities, who are indigenous to North Africa.Hayward, Richard J., chapter ''Afroasiatic'' in Heine, Bernd & Nurse, Derek, editors, ''African Languages: An Introduction'' Cambridge 2000. . The languages were traditionally written with the ancient Libyco-Berber script, which now exists in the form of Tifinagh. Today, they may also be written in the Berber Latin alphabet or the Arabic script, with Latin being the most pervasive. Berber languages are spoken by large populations of Morocco, Algeria and Libya, by smaller populations of Tunisia, northern Mali, western and northern Niger, northern Burkina Faso and Mauritania and in the Siwa Oasis of Egypt. Large Berber-speaking migrant communities, today numbering about 4 million, have been livin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartwheeling
A cartwheel is a sideways rotary movement of the body. It is performed by bringing the hands to the floor one at a time while the body inverts. The legs travel over the body trunk while one or both hands are on the floor, and then the feet return to the floor one at a time, ending with the athlete standing upright. It is performed in a variety of athletic activities, including performance dance and some types of Indian dance, in gymnastics and cheer, and in the martial arts of capoeira. It is called a ''cartwheel'' because the performer's arms and legs move in a fashion similar to the spokes of a turning (cart) wheel. In classical Indian Karana dance, it is called ''talavilasitam'', and in capoeira is called ''aú''. Its first use has been recorded in 1925 by Matthew Douglass, the leader of a popular circus based in Gosforth, Newcastle, who used the trick when dodging flaming spears Technique To perform a cartwheel, one moves sideways in a straight line, keeping the back stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namib Desert
The Namib ( ; pt, Namibe) is a coastal desert in Southern Africa. The name is of Khoekhoegowab origin and means "vast place". According to the broadest definition, the Namib stretches for more than along the Atlantic coasts of Angola, Namibia, and South Africa, extending southward from the Carunjamba River in Angola, through Namibia and to the Olifants River (Western Cape), Olifants River in Western Cape, South Africa. The Namib's northernmost portion, which extends from the Angola-Namibia border, is known as Moçâmedes Desert, while its southern portion approaches the neighboring Kalahari Desert. From the Atlantic coast eastward, the Namib gradually ascends in elevation, reaching up to inland to the foot of the Great Escarpment, Southern Africa, Great Escarpment. Annual precipitation ranges from in the most arid regions to at the escarpment, making the Namib the only true desert in southern Africa. Having endured Desert climate, arid or Semi-arid climate, semi-arid cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carparachne Aureoflava
The wheel spider or golden wheel spider (''Carparachne aureoflava''), is a huntsman spider native to the Namib Desert of Southern Africa. This spider should not be confused with '' Leucorchestris arenicola'', a spider sharing the same common name as well as the same locale. The spider escapes parasitic pompilid wasps by flipping onto its side and cartwheeling down sand dune A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, f ...s at speeds of up to 44 turns per second. Characteristics Wheel spiders are up to 20 mm in size, with males and females the same size. The wheel spider is a nocturnal, free-ranging hunter, coming out at night to prey on insects and other small invertebrates. Its bite is mildly venomous, but the spider is not known to be harmful to humans. The wheel spider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |