|
Cayo Hueso, Havana
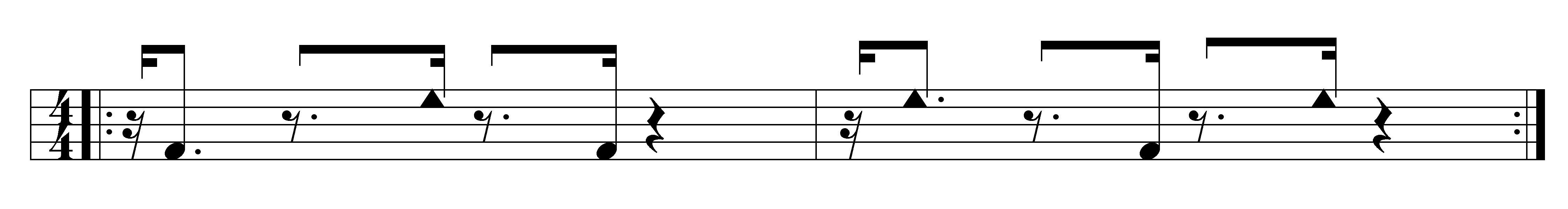
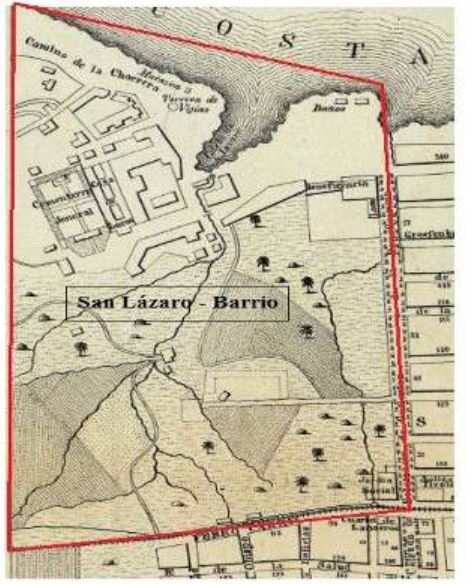
Cayo Hueso is a ''consejo popular'' (ward) in the municipality of Centro Habana, Havana, Cuba. A traditionally working-class neighborhood populated by Afro-Cubans, it is known for its many cultural landmarks such as the ''Callejón de Hamel'', the Fragua Martiana Museum and the ''Parque de los Mártires Universitarios''. Although Cayo Hueso today is considered part of Centro Havana, originally it formed part of Barrio San Lázaro, an area bounded by Calle Infanta to the west, Calle Zanja to the south, Calle Belascoáin to the east and the Gulf of Mexico to the north. Cayo Hueso was declared a ''barrio'' on 26 July 1912, and made part of Centro Habana upon its establishment in 1963. History The earliest settlement in the current area of Cayo Hueso dates back to the second half of the 16th century, following the burning of Havana by French pirate Jacques de Sores. It wasn't until 1912 that the area was officially recognized as the neighbourhood of Cayo Hueso. Its name, which means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ward (country Subdivision)
A ward is a local authority area, typically used for electoral purposes. In some countries, wards are usually named after neighbourhoods, thoroughfares, parishes, landmarks, geographical features and in some cases historical figures connected to the area (e.g. William Morris Ward in the London Borough of Waltham Forest, England). It is common in the United States for wards to simply be numbered. Origins The word “ward”, for an electoral subdivision, appears to have originated in the Wards of the City of London, where gatherings for each ward known as “wardmotes” have taken place since the 12th century. The word was much later applied to divisions of other cities and towns in England and Wales and Ireland. In parts of northern England, a ''ward'' was an administrative subdivision of a historic counties of England, county, very similar to a hundred (country subdivision), hundred in other parts of England. Present day In Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Sri Lanka, South Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920s and 1930s. Through styling and design of the exterior and interior of anything from large structures to small objects, including how people look (clothing, fashion and jewelry), Art Deco has influenced bridges, buildings (from skyscrapers to cinemas), ships, ocean liners, trains, cars, trucks, buses, furniture, and everyday objects like radios and vacuum cleaners. It got its name after the 1925 Exposition internationale des arts décoratifs et industriels modernes (International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts) held in Paris. Art Deco combined modern styles with fine craftsmanship and rich materials. During its heyday, it represented luxury, glamour, exuberance, and faith in socia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedrito Martínez
Pedrito, meaning "little Pedro" or "little Peter" in many Romance languages, may refer to: People * Pedrito (footballer, born 1989), Spanish forward * Pedrito (footballer, born 1996), Spanish midfielder * Pedrito Reyes (fl. 1930s), Filipino writer, co-creator of the ''Kulafu'' comic strip * Pedrito Ríos, semi-mythical " drummer boy of Tacuarí" * Pedrito Sierra (born 1989), Puerto Rican volleyball player * Don Pedro Jaramillo (died 1907), curandero from the Mexico-Texas border region, known as "Don Pedrito" * Pedro Calvo, Cuban popular singer known as "Pedrito" * Pedro Fernández (singer) (born 1969), Mexican recording artist and actor, known as "Pedrito" * Pedro Ruiz Carrilero, a feridor for Circuit Bancaixa 05/06 a Spanish pilota team * Margarita Landi (1918–2004), Spanish journalist Places * Dom Pedrito, a municipality in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil * Nazca (Buenos Aires Metro), a station on the Buenos Aires Metro, known as "San Pedrito" * San Pedrito Point, a headland at Todo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sara González Gómez
Sara González Gómez (Marianao, Cuba; June 13, 1949 or 1951 - La Habana, Cuba; February 1, 2012) was a Cuban singer. In the 1960s, she studied the viola in the Amadeo Roldán Conservatory. She graduated from the National School of Art Instructors where she also taught guitar and solfège. She was one of the founders of the Nueva Trova Movement and one of its main proponents. She belonged to The Cuban Institute of Cinematographic Art and Industry ( ICAIC) Sound Experimentation Group (GES), under the direction of Leo Brouwer, where she studied composition, harmony and orchestration. She produced music for film, television and radio as well as participating in several group albums with other figures from the Nueva Trova Movement and the GES. She was in a relationship with the painter Diana Balboa. Sara González shared the stage with Silvio Rodríguez, Pablo Milanés, Augusto Blanca, Joan Manuel Serrat, Chico Buarque, Mercedes Sosa, Soledad Bravo, Daniel Viglietti, Pete See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omara Portuondo
Omara Portuondo Peláez (born 29 October 1930) is a Cuban singer and dancer. A founding member of the popular vocal group Cuarteto d'Aida, Portuondo has collaborated with many important Cuban musicians during her long career, including Julio Gutiérrez, Juanito Márquez and Chucho Valdés. Although primarily known for her rendition of boleros, she has recorded in a wide range of styles from jazz to son cubano. Since 1996, she has been part of the Buena Vista Social Club project, touring extensively and recording several albums with the ensemble. She won a Latin Grammy Award for Best Contemporary Tropical Album in 2009 and a Latin Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award in 2019, and she received three Grammy Award nominations. Early life and career Born on 29 October 1930 in the Cayo Hueso neighborhood of Havana, Portuondo had three sisters. Her mother, Esperanza Peláez, came from a wealthy family of Spanish ancestry, and had created a scandal by running off with and marrying a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mario Bauzá
Prudencio Mario Bauzá Cárdenas (April 28, 1911 – July 11, 1993) was an Afro-Cuban jazz, Latin, and jazz musician. He was among the first to introduce Cuban music to the United States by bringing Cuban musical styles to the New York City jazz scene. While Cuban bands had had popular jazz tunes in their repertoire for years,Acosta, Leonardo 2003. ''Cubano be, cubano bop: one hundred years of jazz in Cuba''. Smithsonian, Washington, D.C.. Bauzá's composition "Tangá" was the first piece to blend jazz harmony and arranging technique, with jazz soloists and Afro-Cuban rhythms. It is considered the first true Afro-Cuban jazz or Latin jazz tune. Biography As a child he studied clarinet becoming recognized as a child prodigy on the instrument and was featured with the Havana Symphony at the age of 11. Bauzá then performed on clarinet and bass clarinet with pianist Antonio María Romeu's charanga (flute and violins) orchestra. This proved a fateful event as the orchestra visited Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Félix Chappottín
Félix Chappottín (March 31, 1907 – December 21, 1983) was a Cuban trumpeter and bandleader. He was a member of three highly successful Cuban bands: Septeto Habanero, Arsenio Rodríguez's conjunto and Conjunto Chappottín, which he directed. Life and career Early life and ''septeto'' era Félix Chappottín Lage was born on March 31, 1907 in Cayo Hueso, Havana, to tobacconist/musician Julio Chappottín and housewife Natalia Lage. His father was a member of the son group Los Apaches. At 8 years of age, Chappottín began to study cornet under Venancio González; he later took up the tuba, the oboe and the euphonium. At age twelve he joined the local youth band of Guanajuay. In 1924 he joined the Estudiantina Orquídea de Américo González as trumpeter, and in 1927, he joined the Septeto Habanero, previously the Sexteto Habanero, becoming the most famous trumpeter in Cuba. With the Habanero, Chappottín recorded several 78 rpm singles for Victor between February 1928 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
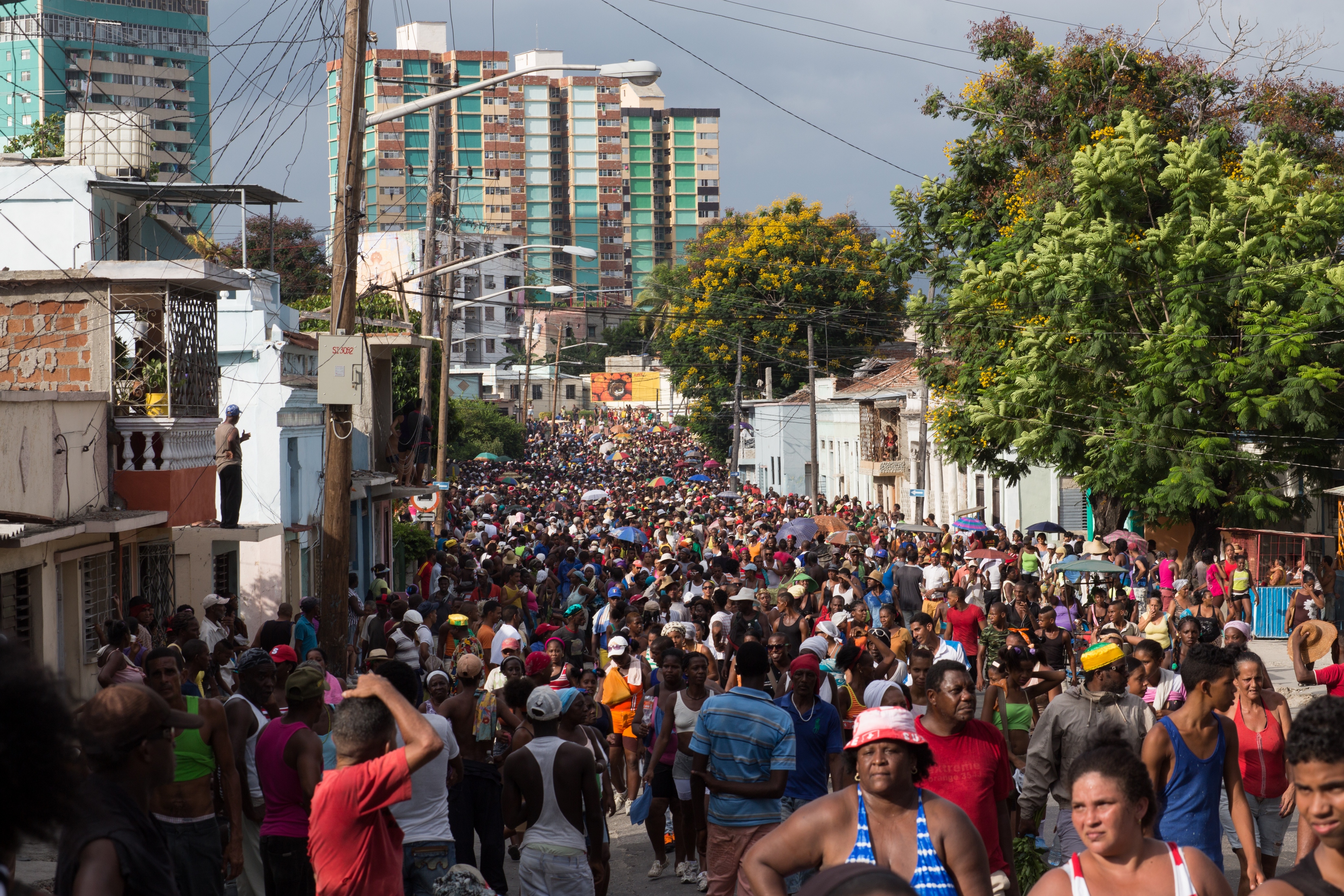
Cuban Carnival
The first African drums were heard in Cuba, since the 16th century, only during the celebration of certain feasts, such as the Día de Reyes (Three Kings Day) and Carnestolendas or Carnival, because their use was restricted to some mutual aid societies, called "Cabildos de nación", where the slaves and their descendants were allowed to gather and practice their cultural and religious traditions. The music and dance of the Cuban Carnival was always very popular in Cuba, and has exerted an important influence in other genres of the Cuban music, such as the "Conga de Salón" and the "Mozambique" rhythm. the Cuban Conga has transcended the national frontiers to become one of the most famous and cherished genres of the Cuban music outside the country, like the well known Congas de Salón from the late 1930s and early 1940s Bim Bam Bum, from Rafael Hernández and Uno, dos y tres, from Rafael Ortiz, which at a later time was known in English as: One, two, three, Kick! Most recently, in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conga (music)
The term conga refers to the music groups within Cuban comparsas and the music they play. Comparsas are large ensembles of musicians, singers and dancers with a specific costume and choreography which perform in the street carnivals of Santiago de Cuba and Havana.Millet, José and Brea Rafael 1989. Del carnival santiaguero: congas y paseos. In Oscar Ruiz Miyares (ed) ''Guía cultural de Santiago de Cuba''. The instrumentation differs between ''congas santiagueras'' and ''congas habaneras''. ''Congas santiagueras'' include the ''corneta china'' (Chinese cornet), which is an adaptation of the Cantonese suona introduced in Oriente in 1915, and its percussion section comprises bocúes (similar to African ashiko drums), the quinto (highest pitched conga drum), galletas and the pilón, as well as brakes which are struck with metal sticks. ''Congas habaneras'' lack the ''corneta china'' but include trumpets, trombones and saxophones, and they have a different set of percussion instrume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Festival Of Youth And Students
The World Festival of Youth and Students is an international event organized by the World Federation of Democratic Youth (WFDY) and the International Union of Students after 1947. History The festival has been held regularly since 1947 as an event of global youth solidarity for democracy and against war and imperialism. The largest festival was the 6th World Festival of Youth and Students, 6th, held in 1957 in Moscow, when 34,000 young people from 131 countries attended the event. This festival also marked the international debut of the song "Moscow Nights", which subsequently went on to become a widely recognized Russian song. There were no festivals between 1962 and 1968, as events proposed in Algeria and then Ghana were cancelled due to coups and political turmoil in both countries. Until the 19th festival in Sochi, Russia in 2017 (with 185 countries participating), the largest festival by number of countries with participants was the 13th, held in 1989 in Pyongyang when 177 co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poetry Reading
A poetry reading is a public oral recitation or performance of poetry. Reading poetry aloud allows the reader to express their own experience through poetry, changing the poem according to their sensibilities. The reader uses pitch and stress, and pauses become apparent. A poetry reading typically takes place on a small stage in a café or bookstore where multiple poets recite their own work. A more prominent poet may be chosen as the " headliner" of such an event and famous poets may also take the stage at a bigger venue such as an amphitheater or college auditorium. How early poems like the ''Illiad'' were transmitted to audiences is not clear. Modern poetry readings only became popular in the last half of the twentieth century, at least in the United States, with stars like Dylan Thomas and Robert Frost. Live poetry reading competitions, called poetry slams and beginning in the 1980s, also remain popular. Background Voice is an active, physical thing in oral poetry. It needs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuban Rumba
Rumba is a secular genre of Cuban music involving dance, percussion, and song. It originated in the northern regions of Cuba, mainly in urban Havana and Matanzas, during the late 19th century. It is based on African music and dance traditions, namely Abakuá and yuka, as well as the Spanish-based ''coros de clave''. According to Argeliers León, rumba is one of the major "genre complexes" of Cuban music, and the term rumba complex is now commonly used by musicologists. This complex encompasses the three traditional forms of rumba (yambú, guaguancó and columbia), as well as their contemporary derivatives and other minor styles. Traditionally performed by poor workers of African descent in streets and ''solares'' (courtyards), rumba remains one of Cuba's most characteristic forms of music and dance. Vocal improvisation, elaborate dancing and polyrhythmic drumming are the key components of all rumba styles. '' Cajones'' (wooden boxes) were used as drums until the early 20th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_interior.jpg)