|
Cayman Ridge
The Cayman Ridge is an undersea mountain range on the northern margin of the Cayman Trough in the Caribbean Sea. It extends from the Sierra Maestra in the east to the Misteriosa Bank in the west, a distance of about . The Cayman Ridge also includes the Cayman Islands. The ridge formed as an island arc when the Cayman Trough was the site of a subduction zone during the Paleocene and Eocene epochs. As the dynamics of the area changed, the subduction zone became a transform fault zone with a pull-apart basin during which time volcanism Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called ... had dwindled along the entire length of the arc. The Cayman Ridge is now an inactive volcanic zone. References Underwater ridges of the Atlantic Ocean Borders of Cuba Geography of the Cayman Isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undersea Mountain Range
Undersea mountain ranges are mountain ranges that are mostly or entirely underwater, and specifically under the surface of an ocean. If originated from current tectonic forces, they are often referred to as a ''mid-ocean ridge''. In contrast, if formed by past above-water volcanism, they are known as a '' seamount chain''. The largest and best known undersea mountain range is a mid-ocean ridge, the Mid-Atlantic Ridge The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge (a divergent or constructive plate boundary) located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. In the North Atlantic, the ridge separates the North .... It has been observed that, "similar to those on land, the undersea mountain ranges are the loci of frequent volcanic and earthquake activity".Martin F. Price, Alton C. Byers, Donald A. Friend, ''Mountain Geography: Physical and Human Dimensions'' (2013), p. 16. References · Coastal and oceanic landforms Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transform Fault
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subduction zone. A transform fault is a special case of a ''strike-slip fault'' that also forms a plate boundary. Most such faults are found in oceanic crust, where they accommodate the lateral offset between segments of divergent boundaries, forming a zigzag pattern. This is a result of oblique seafloor spreading where the direction of motion is not perpendicular to the trend of the overall divergent boundary. A smaller number of such faults are found on land, although these are generally better-known, such as the San Andreas Fault and North Anatolian Fault. Nomenclature Transform boundaries are also known as conservative plate boundaries because they involve no addition or loss of lithosphere at the Earth's surface. Background Geophysicist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Arcs
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle along the subduction zone. They are the principal way by which continental growth is achieved. Island arcs can either be active or inactive based on their seismicity and presence of volcanoes. Active arcs are ridges of recent volcanoes with an associated deep seismic zone. They also possess a distinct curved form, a chain of active or recently extinct volcanoes, a deep-sea trench, and a large negative Bouguer anomaly on the convex side of the volcanic arc. The small positive gravity anomaly associated with volcanic arcs has been interpreted by many authors as due to the presence of dense volcanic rocks beneath the arc. Inactive arcs are a chain of islands which contains older volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks. The curved shape of many vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Cuba
Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean Sea. Cuba's area is 110,860 km² (42,803 sq mi) including coastal and territorial waters with a land area of . This makes it the eighth-largest island country in the world. The main island (Cuba) has of coastline and of land borders—all figures including the U.S. Navy's Guantanamo Bay Naval Base. Cuba lies west of the North Atlantic Ocean, east of the Gulf of Mexico, south of the Straits of Florida, northwest of the Windward Passage, and northeast of the Yucatán Channel. The main island (Cuba), at , makes up most of the land areaStoner, K. Lynn.Cuba ''Encarta Online Encyclopedia''. 2005. 31 October 2009. and is the List of islands by area, 17th-largest island in the world by land area. The island is long and across its widest points and across its narrowest points. The largest island outside the main island is the Isla de la Juventud (Isle of Youth) in the southwest, with an area of . Cuba is an archipelago of islands located i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
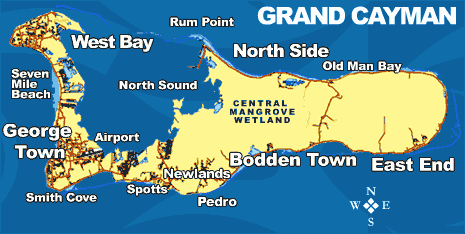
Geography Of The Cayman Islands
The Cayman Islands are a British dependency and island country. It is a three-island archipelago in the Caribbean Sea, consisting of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac, and Little Cayman. Georgetown, the capital of the Cayman Islands is south of Havana, Cuba, and northwest of Kingston, Jamaica, northeast of Costa Rica, north of Panama and are between Cuba and Central America. Georgetown's geographic coordinates are 19.300° north, 81.383° west. The Cayman Islands have a land area of approximately 1.5 times the size of Washington, D.C. and just larger than Saint Kitts and Nevis. The Cayman Islands have a coastline of . The Cayman Islands make a maritime claim of a exclusive fishing zone and a territorial sea of . Geology The islands are located on the Cayman Rise which forms the northern margin of the Cayman Trough. The trough is the deepest point in the Caribbean Sea and forms part of the tectonic boundary between the North American Plate and the Caribbean Plate. The Cayman Rise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borders Of Cuba
A border is a geographical boundary. Border, borders, The Border or The Borders may also refer to: Arts, entertainment and media Film and television * ''Border'' (1997 film), an Indian Hindi-language war film * ''Border'' (2018 Swedish film), a fantasy film * ''Border'' (2018 Bhojpuri film), a war film * ''The Border'' (1982 film), an American drama * ''The Border'' (1996 film), an Italian war drama * ''The Border'' (2007 film), a Finnish-Russian war drama * ''The Border'' (2009 film), a Slovak documentary * ''The Border'' (TV series) a 2008–10 Canadian drama series Literature * "The Border", a 2004 short story by Richard Harland * "The Border", a 2019 novel by Don Winslow Music * "Border" (song), by Years & Years, 2015 * "Borders" (Feeder song), 2012 * "Borders" (M.I.A. song), 2015 * "Borders" (The Sunshine Underground song), 2007 * ''The Border'', soundtrack to the 1982 film, by Ry Cooder * "The Border" (America song), 1983 * "The Border" (Mr. Mister song), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a vent. It includes all phenomena resulting from and causing magma within the crust or mantle of the body, to rise through the crust and form volcanic rocks on the surface. Magmas, that reach the surface and solidify, form extrusive landforms. Volcanic processes Magma from the mantle or lower crust rises through the crust towards the surface. If magma reaches the surface, its behavior depends on the viscosity of the molten constituent rock. Viscous (thick) magma produces volcanoes characterised by explosive eruptions, while non-viscous (runny) magma produce volcanoes characterised by effusive eruptions pouring large amounts of lava onto the surface. In some cases, rising magma can cool and solidify without reaching the surface. Inste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pull-apart Basin
In geology, a basin is a region where subsidence generates accommodation space for the deposition of sediments. A pull-apart basin is a structural basin where two overlapping (en echelon) strike-slip faults or a fault bend creates an area of crustal extension undergoing tension, which causes the basin to sink down. Frequently, the basins are rhombic or sigmoidal in shape. Dimensionally, basins are limited to the distance between the faults and the length of overlap.Frisch, Wolfgang, Martin Meschede, and Ronald C. Blakey. ''Plate tectonics: Continental drift and mountain building''. Springer, 2010. Pull-apart basins are also referred to as overlapping-tension-zones (OTZ). Mechanics and fault configuration The inhomogeneity and structural complexity of continental crust causes faults to deviate from a straight course and frequently causes bends or step-overs in fault paths. Bends and step-overs of adjacent faults become favorable locations for extensional and compressional str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoch (geology)
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely define gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cayman Trough
__NOTOC__ The Cayman Trough (also known as the Cayman Trench, Bartlett Deep and Bartlett Trough) is a complex transform fault zone pull-apart basin which contains a small spreading ridge, the Mid-Cayman Rise, on the floor of the western Caribbean Sea between Jamaica and the Cayman Islands. It is the deepest point in the Caribbean Sea and forms part of the tectonic boundary between the North American Plate and the Caribbean Plate. It extends from the Windward Passage, going south of the Sierra Maestra of Cuba toward Guatemala. The transform fault continues onshore as the Polochic-Motagua fault system, which consists of the Polochic and Motagua faults. This system continues on until the Chiapas massif where it is part of the diffuse triple junction of the North American, Caribbean and Cocos plates. The relatively narrow trough trends east-northeast to west-southwest and has a maximum depth of . Within the trough is a slowly spreading north–south ridge which may be the result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope Carbon-13, 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope Carbon-12, 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Popigai impact structure, Siberia and in what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |