|
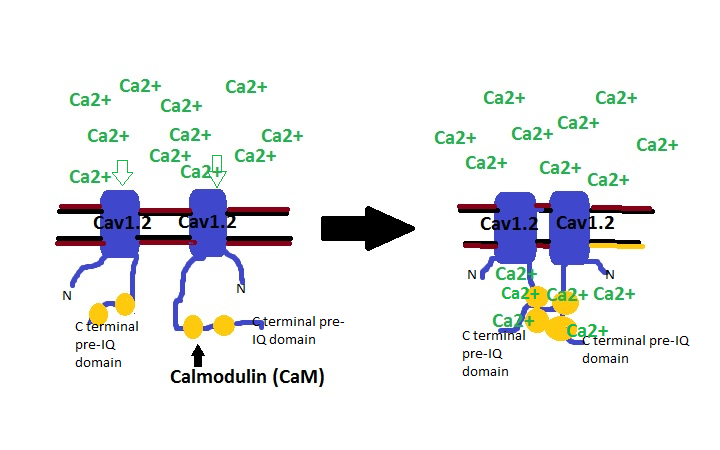
Cav1.2
Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1C subunit (also known as Cav1.2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CACNA1C'' gene. Cav1.2 is a subunit of L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel. Structure and function This gene encodes an alpha-1 subunit of a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Calcium channels mediate the influx of calcium ions (Ca2+) into the cell upon membrane polarization (see membrane potential and calcium in biology). The alpha-1 subunit consists of 24 transmembrane segments and forms the pore through which ions pass into the cell. The calcium channel consists of a complex of alpha-1, alpha-2/delta and beta subunits in a 1:1:1 ratio. The S3-S4 linkers of Cav1.2 determine the gating phenotype and modulated gating kinetics of the channel. Cav1.2 is widely expressed in the smooth muscle, pancreatic cells, fibroblasts, and neurons. However, it is particularly important and well known for its expression in the heart where it mediates L-type c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timothy's Syndrome
Timothy syndrome is a rare autosomal-dominant disorder characterized by physical malformations, as well as neurological and developmental defects, including heart QT-prolongation, heart arrhythmias, structural heart defects, syndactyly (webbing of fingers and toes), and autism spectrum disorders. Timothy syndrome represents one clinical manifestation of a range of disorders associated with mutations in ''CACNA1C'', the gene encoding the calcium channel Cav1.2 α subunit. Signs and symptoms The most striking sign of Timothy syndrome type 1 is the co-occurrence of both syndactyly (about 0.03% of births) and long QT syndrome (1% per year) in a single patient. Other common symptoms include cardiac arrhythmia (94%), heart malformations (59%), and autism or an autism spectrum disorder (80% who survive long enough for evaluation). Facial dysmorphologies such as flattened noses also occur in about half of patients. Children with this disorder have small teeth, which is due to poor ena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
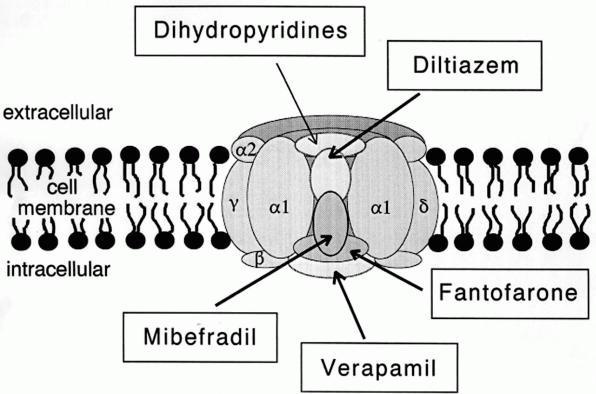
L-type Calcium Channel
The L-type calcium channel (also known as the dihydropyridine channel, or DHP channel) is part of the high-voltage activated family of voltage-dependent calcium channel. "L" stands for long-lasting referring to the length of activation. This channel has four isoforms: Cav1.1, Cav1.2, Cav1.3, and Cav1.4. L-type calcium channels are responsible for the excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal, smooth, cardiac muscle, and for aldosterone secretion in endocrine cells of the adrenal cortex. They are also found in neurons, and with the help of L-type calcium channels in endocrine cells, they regulate neurohormones and neurotransmitters. They have also been seen to play a role in gene expression, mRNA stability, neuronal survival, ischemic-induced axonal injury, synaptic efficacy, and both activation and deactivation of other ion channels. In cardiac myocytes, the L-type calcium channel passes inward Ca2+ current (ICaL) and triggers calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-dependent Calcium Channel
Voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), also known as voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs), are a group of voltage-gated ion channels found in the membrane of excitable cells (''e.g.'', muscle, glial cells, neurons, etc.) with a permeability to the calcium ion Ca2+. These channels are slightly permeable to sodium ions, so they are also called Ca2+-Na+ channels, but their permeability to calcium is about 1000-fold greater than to sodium under normal physiological conditions. At physiologic or resting membrane potential, VGCCs are normally closed. They are activated (''i.e.'': opened) at depolarized membrane potentials and this is the source of the "voltage-gated" epithet. The concentration of calcium (Ca2+ ions) is normally several thousand times higher outside the cell than inside. Activation of particular VGCCs allows a Ca2+ influx into the cell, which, depending on the cell type, results in activation of calcium-sensitive potassium channels, muscular contraction, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long QT Syndrome
Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a condition affecting repolarization (relaxing) of the heart after a heartbeat, giving rise to an abnormally lengthy QT interval. It results in an increased risk of an irregular heartbeat which can result in fainting, drowning, seizures, or sudden death. These episodes can be triggered by exercise or stress. Some rare forms of LQTS are associated with other symptoms and signs including deafness and periods of muscle weakness. Long QT syndrome may be present at birth or develop later in life. The inherited form may occur by itself or as part of larger genetic disorder. Onset later in life may result from certain medications, low blood potassium, low blood calcium, or heart failure. Medications that are implicated include certain antiarrhythmics, antibiotics, and antipsychotics. LQTS can be diagnosed using an electrocardiogram (EKG) if a corrected QT interval of greater than 480–500 milliseconds is found, but clinical findings, other EKG features, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Channel Associated Transcriptional Regulator
Calcium channel associated transcriptional regulator (CCAT) is a transcription factor In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The fu ... found in mammalian cells. Generation In neuronal cells, CCAT is generated upon activation of a cryptic promoter in exon 46 of ''CACNA1C'', the gene that encodes the voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.2. References Genes Transcription factors {{gene-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Channel
A calcium channel is an ion channel which shows selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel, although there are also ligand-gated calcium channels. Comparison tables The following tables explain gating, gene, location and function of different types of calcium channels, both voltage and ligand-gated. Voltage-gated Ligand-gated *the ''receptor-operated calcium channels'' (in vasoconstriction) **P2X receptors Page 479 Pharmacology L-type calcium channel blockers are used to treat hypertension. In most areas of the body, depolarization is mediated by sodium influx into a cell; changing the calcium permeability has little effect on action potentials. However, in many smooth muscle tissues, depolarization is mediated primarily by calcium influx into the cell. L-type calcium channel blockers selectively inhibit these action potentials in smooth muscle which leads to dilation of blood vessels; this in turn corrects hypert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brugada Syndrome
Brugada syndrome (BrS) is a genetic disorder in which the electrical activity of the heart is abnormal due to channelopathy. It increases the risk of abnormal heart rhythms and sudden cardiac death. Those affected may have episodes of syncope. The abnormal heart rhythms seen in those with Brugada syndrome often occur at rest. They may be triggered by a fever. About a quarter of those with Brugada syndrome have a family member who also has the condition. Some cases may be due to a new genetic mutation or certain medications. The most commonly involved gene is SCN5A which encodes the cardiac sodium channel. Diagnosis is typically by electrocardiogram (ECG), however, the abnormalities may not be consistently present. Medications such as ajmaline may be used to reveal the ECG changes. Similar ECG patterns may be seen in certain electrolyte disturbances or when the blood supply to the heart has been reduced. There is no cure for Brugada syndrome. Those at higher risk of sudden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CACNA1C-related Disorders
''CACNA1C''-related disorders are a group of rare diseases caused by variants in the ''CACNA1C'' gene, which encodes a subunit of the L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel. Genomic sequencing has linked a number of heterogenous phenotypes to pathogenic variants in the ''CACNA1C'' gene: * Timothy syndrome, which may or may not occur with syndactyly * Short QT syndrome or Brugada syndrome * Long QT syndrome or other arrhythmia without additional symptoms. ''CACNA1C''-related disorders are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Symptoms of ''CACNA1C''-related disorders are primarily neurological and may include developmental delay, autism or autistic features, and seizures. Facial dysmorphism A dysmorphic feature is an abnormal difference in body structure. It can be an isolated finding in an otherwise normal individual, or it can be related to a congenital disorder, genetic syndrome or birth defect. Dysmorphology is the study of dysm ... may also be present. Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a protein complex that controls transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found in almost all animal cell types and is involved in cellular responses to stimuli such as stress, cytokines, free radicals, heavy metals, ultraviolet irradiation, oxidized LDL, and bacterial or viral antigens. NF-κB plays a key role in regulating the immune response to infection. Incorrect regulation of NF-κB has been linked to cancer, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, septic shock, viral infection, and improper immune development. NF-κB has also been implicated in processes of synaptic plasticity and memory. Discovery NF-κB was discovered by Ranjan Sen in the lab of Nobel laureate David Baltimore via its interaction with an 11-base pair sequence in the immunoglobulin light-chain enhancer in B cells. Later work by Alexander Poltorak and Bruno Lemaitre in mice and ''Drosophila'' frui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdrawal, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically develop gradually, begin during young adulthood, and in many cases never become resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month (ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially substance use disorders, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifetime. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
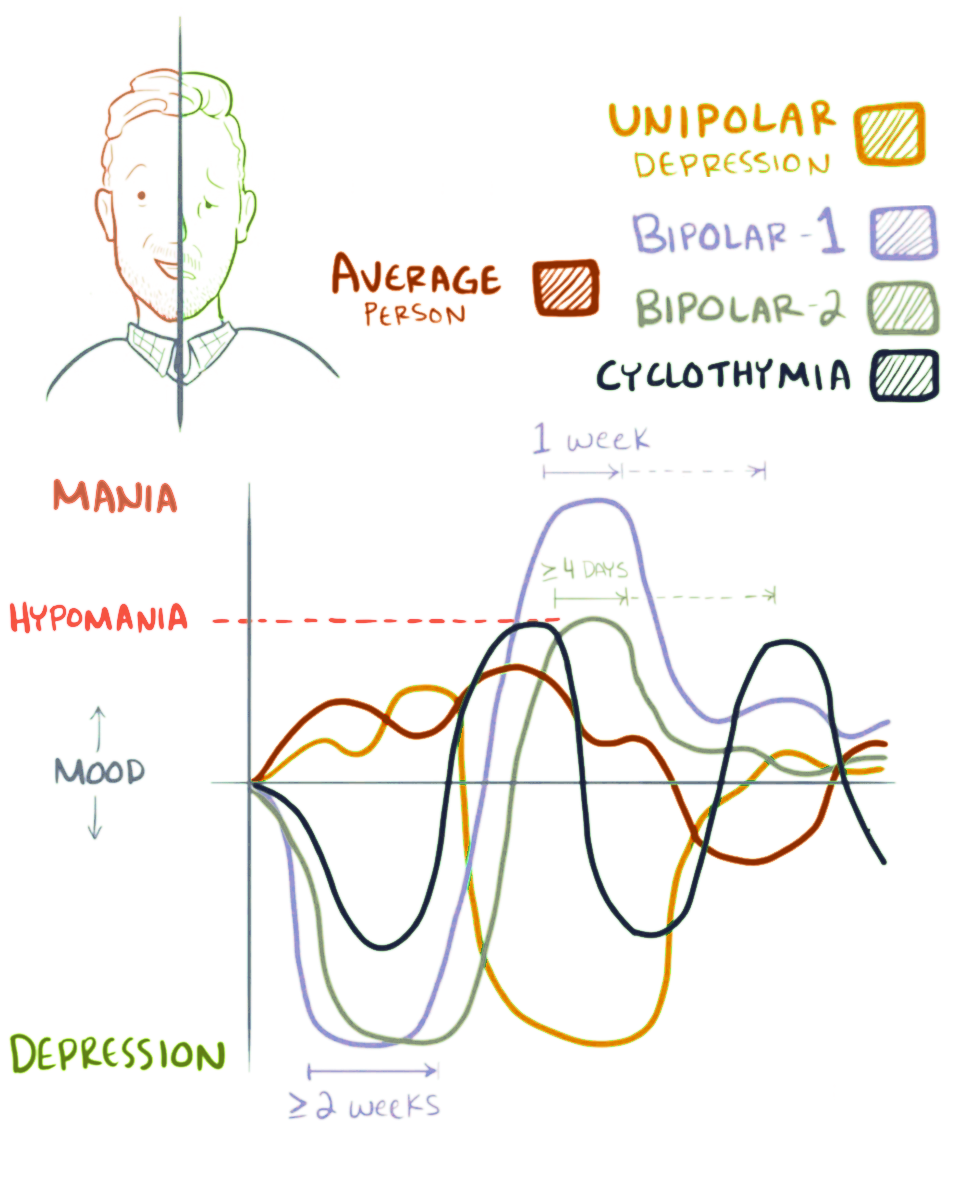
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually also a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying and have a negative outlook on life and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high; over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, while 30–40% engaged in self-harm. Other mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, are commonly associated with bipolar disorder. While the causes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)