|
Cathédrale Saint-Mammès De Langres
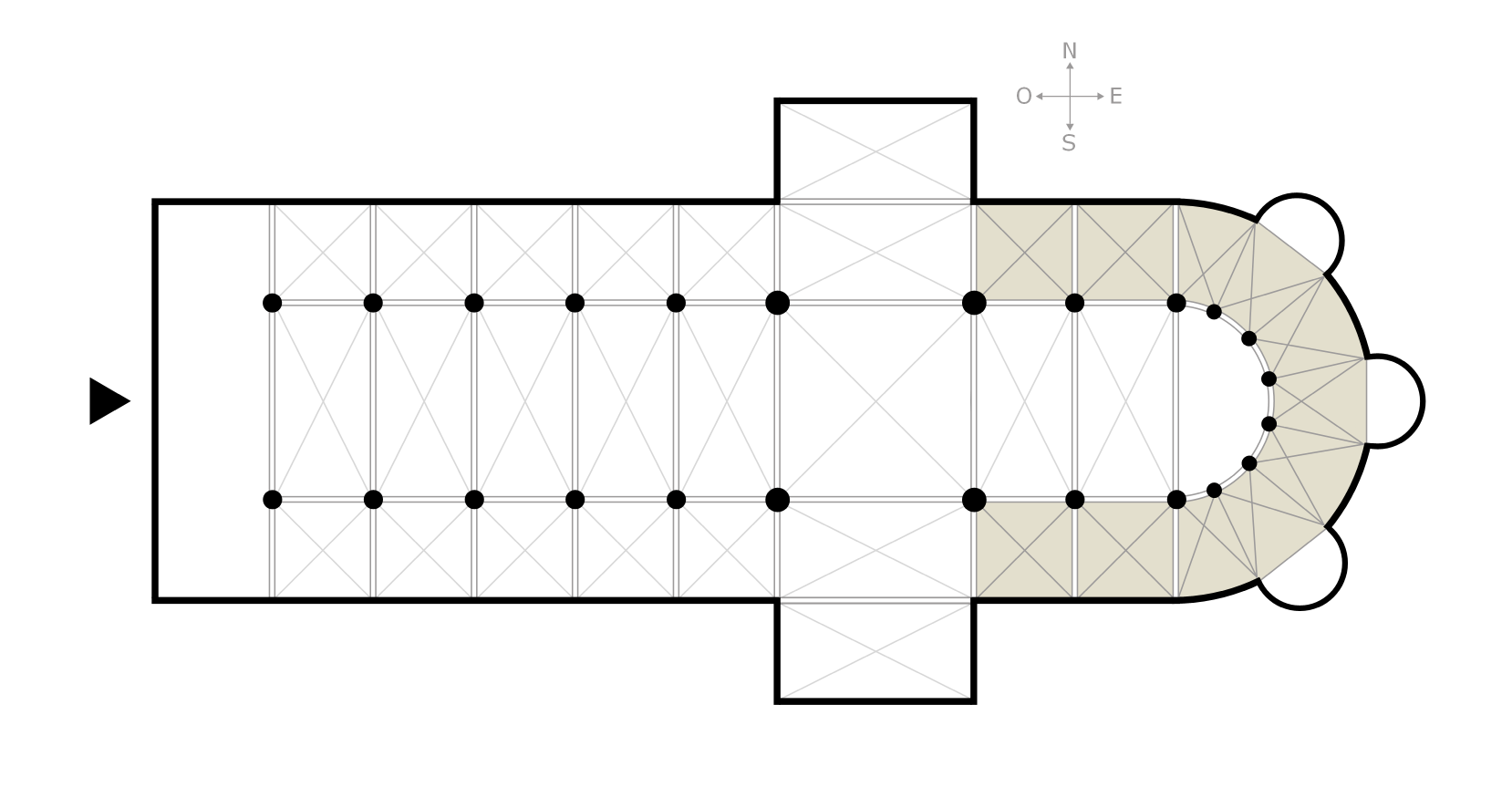
Langres Cathedral (french: Cathédrale Saint-Mammès de Langres) is a Roman Catholic church in Langres, France. It was erected in the twelfth century, and is dedicated to the 3rd-century martyr Mammes of Caesarea. The cathedral is the seat of the Bishop of Langres, and is a national monument. The nave and interior are in the Romanesque and French Gothic style while the later facade is an example of French Neoclassical architecture History Romanesque and Gothic construction At the time that the cathedral was built, the diocese of Langres was considerably larger; it reached further south and included Dijon, which did not become a separate diocese until 1731. Around 1140, bishop Geoffroy de La Roche-Vanneau (1091–1162), a close friend of Saint Bernard of Clairvaux, took the decision to rebuild the cathedral. At that time the cathedral of Saint-Étienne in Sens, the first fully Gothic cathedral, was already under construction. The choir and the ambulatory were constructed firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langres
Langres () is a commune in France, commune in northeastern France. It is a Subprefectures in France, subprefecture of the Departments of France, department of Haute-Marne, in the Regions of France, region of Grand Est. History As the capital of the Romanized Gauls, Gallic tribe known as the Lingones, it was called Andematunnum, then Lingones, and now Langres. A hilltop town, Langres was built on a limestone promontory of the same name. This stronghold was originally occupied by the Lingones. At a later date the Romans fortified the town, which they called Andemantunum, located at a strategic crossroads of twelve Roman roads. The first-century Triumphal Gate and the many artefacts exhibited in the museums are remnants of the town's Gallo-Roman history. After the period of invasions, the town prospered in the Middle Ages, due in part to the growing political influence of its bishops. The diocese covered Champagne (province), Champagne, the Duchy of Burgundy, and Franche-Comté, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the Roman diocese, diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek language, Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into Roman diocese, dioceses based on the Roman diocese, civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the Roman province, provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's State church of the Roman Empire, official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine the Great, Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude De Longwy
Claude de Longwy de Givry (1481–1561) was a French bishop and Cardinal, from an aristocratic background. He was the son of Philippe de Longuy, Seigneur de Givry and Jeanne de Beautremont, Dame de Mirabeau. He had four brothers: Jean de Longuy, Sieur de Givry and Baron de Mirabeau (who married Jeanne d'Orleans, natural sister of King Francis I), Christophe de Longuy, Antoine de Longuy, and Étienne de Longuy. Claude's aunt Jeanne had married Guy de la Baume, Count de Montrevel, and one of their sons was Cardinal Pierre de la Baume (1539-1544), Prince and Bishop of Geneva (1522-1543). Bishop of Macon Claude de Longuy became bishop of Mâcon, in 1510, as successor to his uncle Étienne de Longwy (1488-1510). He attended the schismatic Conciliabulum of Pisa in 1511, no doubt on the command of King Louis XII of France. On 16 March 1516 he made his solemn entry. He served as Bishop of Macon until 1529. On 10 January 1527, the Bishop's niece, Jeanne de Longuy was married to Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Mammes
Saint Mammes (Mamas, Mammas, Mammet) of Caesarea ( el, Μάμας; french: Mammès; it, Mamante; es, Mamés; pt, São Mamede) was a child-martyr of the 3rd century, who was martyred at Caesarea. His parents, Theodotus and Rufina, were also martyred. Life Born in prison to parents who had been jailed for being Christians, Mammes became an orphan when his parents were executed. After their death, Mammes was raised by a rich widow named Ammia, who died when Mammes was 15 years old. According to legend, Mammes was tortured for his faith by the governor of Caesarea and was then sent before the Roman Emperor Aurelian, who tortured him again. The Mammes legend states that an angel then liberated him and ordered him to hide on a mountain near Caesarea. Mammes was later thrown to the lions, but he managed to make the beasts docile by preaching to them. Afterward, a lion remained with him as a companion. Accompanied by the lion, he visited Severus Alexander, who sentenced him t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Alexander III
Pope Alexander III (c. 1100/1105 – 30 August 1181), born Roland ( it, Rolando), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 September 1159 until his death in 1181. A native of Siena, Alexander became pope after a contested election, but had to spend much of his pontificate outside Rome while several rivals, supported by Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa, claimed the papacy. Alexander rejected Byzantine Emperor Manuel I Komnenos' offer to end the East–West Schism, sanctioned the Northern Crusades, and held the Third Council of the Lateran. The city of Alessandria in Piedmont is named after him. Early life and career Rolando was born in Siena. From the 14th century, he was referred to as a member of the aristocratic family of Bandinelli, although this has not been proven. He was long thought to be the 12th-century canon lawyer and theologian Master Roland of Bologna, who composed the "Stroma" or "Summa Rolandi"—one of the earliest comment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying Buttresses
The flying buttress (''arc-boutant'', arch buttress) is a specific form of buttress composed of an arch that extends from the upper portion of a wall to a pier of great mass, in order to convey lateral forces to the ground that are necessary to push a wall outwards. These forces arise from vaulted ceilings of stone and from wind-loading of roofs. The namesake and defining feature of a flying buttress is that it is not in contact with the wall at ground level, unlike a traditional buttress, and so transmits the lateral forces across the span of intervening space between the wall and the pier. To provide lateral support, flying-buttress systems are composed of two parts: (i) a massive pier, a vertical block of masonry situated away from the building wall, and (ii) an arch that bridges the span between the pier and the wall — either a segmental arch or a quadrant arch — the ''flyer'' of the flying buttress. History As a lateral-support system, the flying buttress was developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The capital of Dijon was one of the great European centres of art and science, a place of tremendous wealth and power, and Western Monasticism. In early Modern Europe, Burgundy was a focal point of courtly culture that set the fashion for European royal houses and their court. The Duchy of Burgundy was a key in the transformation of the Middle Ages toward early modern Europe. Upon the 9th-century partitions of the Kingdom of Burgundy, the lands and remnants partitioned to the Kingdom of France were reduced to a ducal rank by King Robert II of France in 1004. The House of Burgundy, a cadet branch of the House of Capet, ruled over a territory that roughly conformed to the borders and territories of the modern administrative region of Burgundy. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanesque Architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe characterized by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque style, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 11th century, this later date being the most commonly held. In the 12th century it developed into the Gothic style, marked by pointed arches. Examples of Romanesque architecture can be found across the continent, making it the first pan-European architectural style since Imperial Roman architecture. The Romanesque style in England and Sicily is traditionally referred to as Norman architecture. Combining features of ancient Roman and Byzantine buildings and other local traditions, Romanesque architecture is known by its massive quality, thick walls, round arches, sturdy pillars, barrel vaults, large towers and decorative arcading. Each building has clearly defined forms, frequently of very regular, symmetrical plan; the overall appearance is one of simplic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluny Abbey
Cluny Abbey (; , formerly also ''Cluni'' or ''Clugny''; ) is a former Benedictine monastery in Cluny, Saône-et-Loire, France. It was dedicated to Saint Peter. The abbey was constructed in the Romanesque architectural style, with three churches built in succession from the 4th to the early 12th centuries. The earliest basilica was the world's largest church until the St. Peter's Basilica construction began in Rome. Cluny was founded by Duke William I of Aquitaine in 910. He nominated Berno as the first abbot of Cluny, subject only to Pope Sergius III. The abbey was notable for its stricter adherence to the Rule of St. Benedict, whereby Cluny became acknowledged as the leader of western monasticism. In 1790 during the French Revolution, the abbey was sacked and mostly destroyed, with only a small part surviving. Starting around 1334, the Abbots of Cluny maintained a townhouse in Paris known as the Hôtel de Cluny, which has been a public museum since 1843. Apart from the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulatory
The ambulatory ( la, ambulatorium, ‘walking place’) is the covered passage around a cloister or the processional way around the east end of a cathedral or large church and behind the high altar. The first ambulatory was in France in the 11th century but by the 13th century ambulatories had been introduced in England and many English cathedrals were extended to provide an ambulatory. The same feature is often found in Indian architecture and Buddhist architecture generally, especially in older periods. Ritual circumambulation or parikrama around a stupa or cult image is important in Buddhism and Hinduism. Often the whole building was circumambulated, often many times. The Buddhist chaitya hall always allowed a path for this, and the Durga temple, Aihole (7th or 8th century) is a famous Hindu example. The term is also used to describe a garden feature in the grounds of a country house. A typical example is the one shown, which stands in the grounds of Horton Court in Gloucest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sens
Sens () is a Communes of France, commune in the Yonne Departments of France, department in Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in north-central France, 120 km from Paris. Sens is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture and the second city of the department, the sixth in the region. It is crossed by the Yonne (river), Yonne and the Vanne (river), Vanne, which empties into the Yonne here. History The city is said to have been one of the oppidum, oppida of the Senones, one of the oldest Celtic tribes living in Gaul. It is mentioned as Agedincum by Julius Caesar several times in his ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico''. The Roman city was built during the first century BC and surrounded by walls during the third (notable parts of the walls still remain, with alterations along the centuries). It still retains today the skeleton of its Roman street plan. The site was referred to by Ammianus Marcellinus as ''Senones'' (''oppidum Senonas''), where the future emperor Julian (emperor), Julian f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)