|
Catalina Macaw
The Catalina macaw, sometimes known as the rainbow macaw is a first generation hybrid between the blue-and-gold macaw and scarlet macaw. As catalina macaws are hybrids, they do not have a true scientific name. The best way to represent these birds in taxonomy is by the expression ''Ara ararauna'' × ''Ara macao''. Origin The Catalina macaw is named after Catalina Bird Park, formerly located on Santa Catalina Island, California, at which this hybrid was first produced in captivity, in 1940. It is a first-generation hybrid between the blue-and-yellow macaw and scarlet macaw. As Catalina macaws are hybrids, they do not have a proper scientific name. The best way to represent these birds in taxonomy is by the expression ''Ara ararauna × Ara macao''. There is speculation that the first hybrid macaw was the Catalina macaw. Hybridization of macaws can occur naturally or in captivity. However, most Catalina macaws are the result of selective breeding. Therefore, they rarely occur in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Macaw
Hybrid macaws are the product of cross breeding of more than one species of macaw, resulting in a hybrid. They are often characterized and bred for their unique and distinct coloring, and for this reason, are highly sought after and valued in the exotic pet trade. Macaws are native to tropical North and South America. Hybridization of macaws occurs both in nature and captivity, being one of the few species that can produce viable, fertile offspring unlike many other hybrids produced from crossing different species resulting in sterile hybrids with factors that limit their success of survival (e.g. the liger and mule). Hybrid macaws do not hold any scientific names, and are often labeled by the two macaw species they are produced from (e.g. scarlet macaw × green winged macaw) There are 19 species of macaw, many of which can produce up to three generations (potentially more) of hybrids. Generation F1, being the most common, has the widest variety of hybrids and are the most popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (music)
Pitch is a perceptual property of sounds that allows their ordering on a frequency-related scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies. Pitch is a major auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration, loudness, and timbre. Pitch may be quantified as a frequency, but pitch is not a purely objective physical property; it is a subjective psychoacoustical attribute of sound. Historically, the study of pitch and pitch perception has been a central problem in psychoacoustics, and has been instrumental in forming and testing theories of sound representation, processing, and perception in the auditory system. Perception Pitch and frequency Pitch is an auditory sensation in which a listener assigns musical tones to relative positions on a musical scale based primarily on their perception of the frequency of vibration. Pitch is closely related to frequency, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
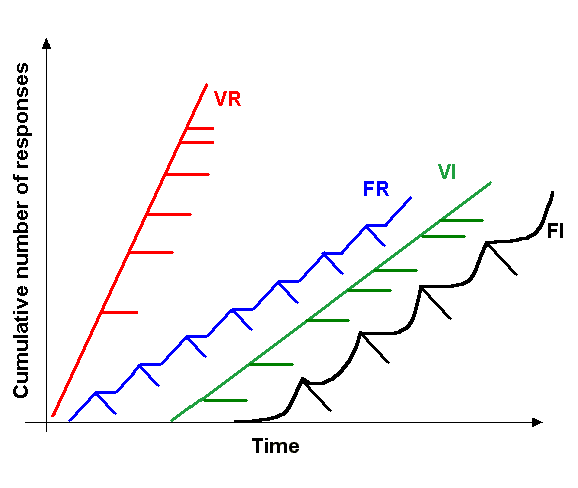
Reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Negati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nervous System
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue first arose in wormlike organisms about 550 to 600 million years ago. In vertebrates it consists of two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are enclosed bundles of the long fibers or axons, that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. Nerves that transmit signals from the brain are called motor nerves or '' efferent'' nerves, while those nerves that transmit information from the body to the CNS are called sensory nerves or '' afferent''. Spinal nerves are mixed nerves that serve both fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ Failure
Organ dysfunction is a condition where an organ does not perform its expected function. Organ failure is organ dysfunction to such a degree that normal homeostasis cannot be maintained without external clinical intervention. It is not a diagnosis. It can be classified by the cause, but when the cause is not known, it can also be classified by whether the onset is chronic or acute. Multiple organ failure can be associated with sepsis Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ... and is often fatal. Countries such as Spain, have shown a rise in mortality risk, due to a large elderly population there. However, there are tools physicians use when diagnosing multiple organ failure and when prognosing the outcome. The Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score uses early la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
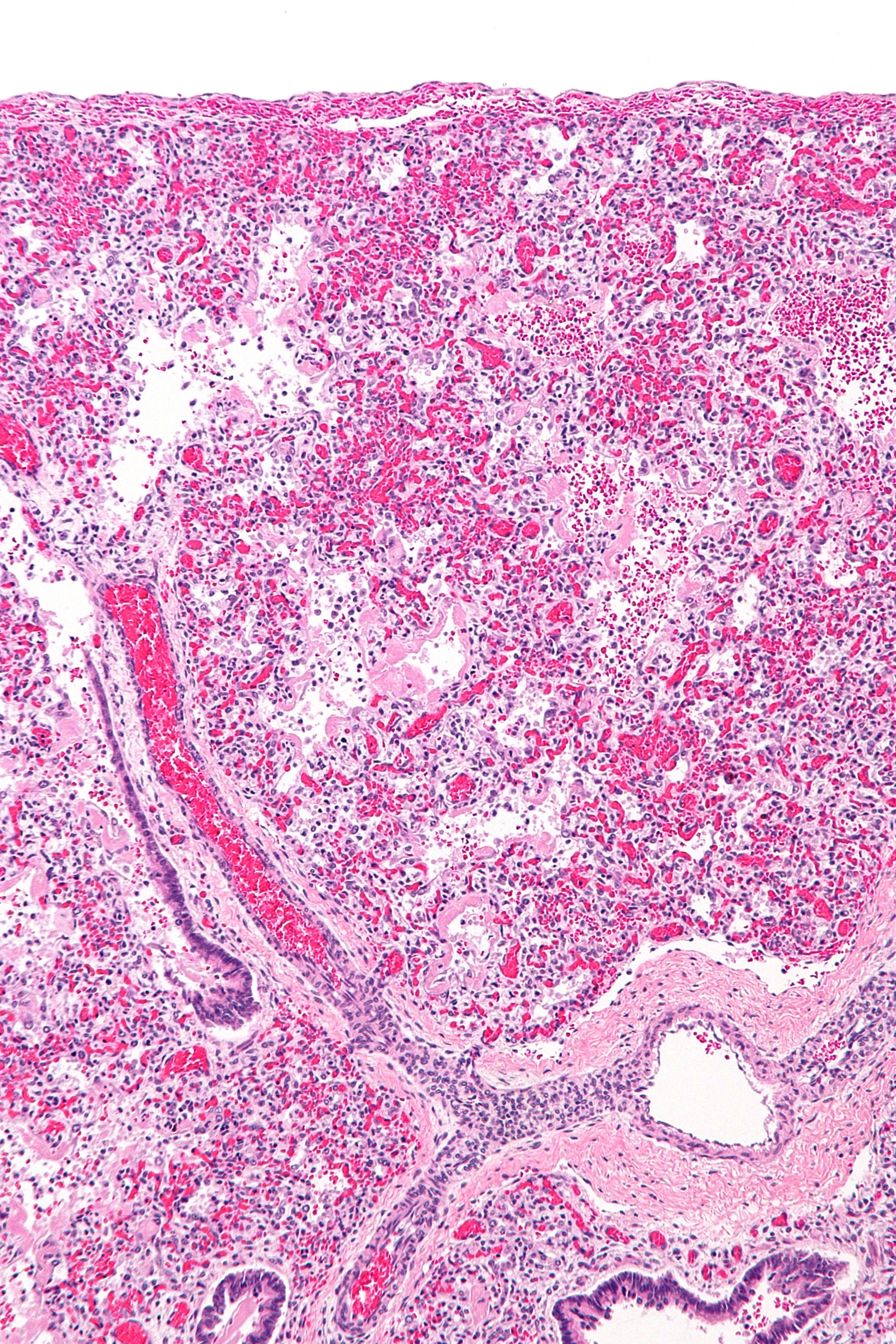
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin coloration (cyanosis). For those who survive, a decreased quality of life is common. Causes may include sepsis, pancreatitis, trauma, pneumonia, and aspiration. The underlying mechanism involves diffuse injury to cells which form the barrier of the microscopic air sacs of the lungs, surfactant dysfunction, activation of the immune system, and dysfunction of the body's regulation of blood clotting. In effect, ARDS impairs the lungs' ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Adult diagnosis is based on a PaO2/FiO2 ratio (ratio of partial pressure arterial oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen) of less than 300 mm Hg despite a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of more than 5 cm H2O. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Hepatitis is ''acute'' if it resolves within six months, and '' chronic'' if it lasts longer than six months. Acute hepatitis can resolve on its own, progress to chronic hepatitis, or (rarely) result in acute liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may progress to scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), liver failure, and liver cancer. Hepatitis is most commonly caused by the virus ''hepatovirus A'', '' B'', '' C'', '' D'', and '' E''. Other viruses can also cause liver inflammation, including cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus, and yellow fever virus. Other common causes of hepatitis include heavy alcohol use, certain medications, toxins, other infections, autoimmune diseases, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Hepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocarditis
Myocarditis, also known as inflammatory cardiomyopathy, is an acquired cardiomyopathy due to inflammation of the heart muscle. Symptoms can include shortness of breath, chest pain, decreased ability to exercise, and an irregular heartbeat. The duration of problems can vary from hours to months. Complications may include heart failure due to dilated cardiomyopathy or cardiac arrest. Myocarditis is most often due to a viral infection. Other causes include bacterial infections, certain medications, toxins and autoimmune disorders. A diagnosis may be supported by an electrocardiogram (ECG), increased troponin, heart MRI, and occasionally a heart biopsy. An ultrasound of the heart is important to rule out other potential causes such as heart valve problems. Treatment depends on both the severity and the cause. Medications such as ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and diuretics are often used. A period of no exercise is typically recommended during recovery. Corticosteroids or int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psittacine Beak And Feather Disease
Psittacine beak and feather disease (PBFD) is a viral disease affecting all Old World and New World parrots. The causative virus—''beak and feather disease virus'' (BFDV)—belongs to the taxonomic genus ''Circovirus'', family ''Circoviridae''. It attacks the feather follicles and the beak and claw matrices of the bird, causing progressive feather, claw and beak malformation and necrosis. In later stages of the disease, feather shaft constriction occurs, hampering development until eventually all feather growth stops. It occurs in an acutely fatal form and a chronic form. Cracking and peeling of the outer layers of the claws and beak make tissues vulnerable to secondary infection. Because the virus also affects the thymus and Bursa of Fabricius, slowing lymphocyte production, immunosuppression occurs and the bird becomes more vulnerable to secondary infections. Beak fractures and necrosis of the hard palate can prevent the bird from eating.Pyne, MPsittacine Beak and Feather D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psittacosis
Psittacosis—also known as parrot fever, and ornithosis—is a zoonotic infectious disease in humans caused by a bacterium called ''Chlamydia psittaci'' and contracted from infected parrots, such as macaws, cockatiels, and budgerigars, and from pigeons, sparrows, ducks, hens, gulls and many other species of birds. The incidence of infection in canaries and finches is believed to be lower than in psittacine birds. In certain contexts, the word is used when the disease is carried by any species of birds belonging to the family Psittacidae, whereas ornithosis is used when other birds carry the disease. In humans Signs and symptoms In humans, after an incubation period of 5–19 days, the symptoms of the disease range from inapparent illness to systemic illness with severe pneumonia. It presents chiefly as an atypical pneumonia. In the first week of psittacosis, the symptoms mimic typhoid fever, prostrating high fevers, joint pains, diarrhea, conjunctivitis, nose bleeds, and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allergy
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include red eyes, an itchy rash, sneezing, coughing, a runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Note: food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions. Common allergens include pollen and certain foods. Metals and other substances may also cause such problems. Food, insect stings, and medications are common causes of severe reactions. Their development is due to both genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves immunoglobulin E antibodies (IgE), part of the body's immune system, binding to an allergen and then to a receptor on mast cells or basophils where it triggers the release of inflammatory chemicals such as histamine. Diagnosis is ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)