|
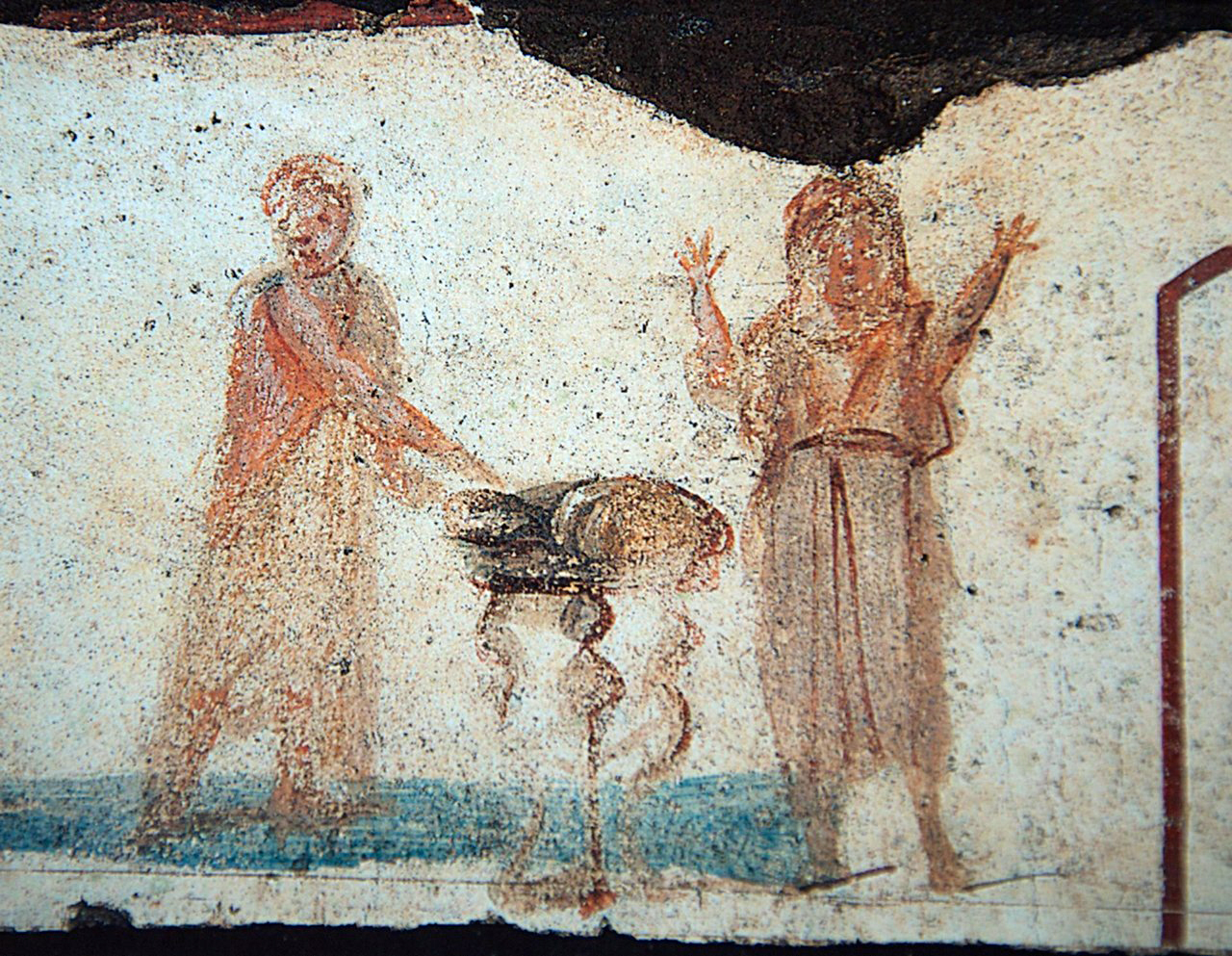
Catacombs Of Saint Gaudiosus
The Catacombs of Saint Gaudiosus are underground paleo-Christian burial sites (4th–5th century AD), located in the northern area of the city of Naples (now Stella district). History The catacombs were probably occupied on a pre-existing Greek-Roman necropolis in the district known nowadays as Rione Sanità, that was uninhabited at that time. According to tradition, it was the burial site of St Gaudiosus, a bishop arrived in Naples from North Africa, due to a shipwreck. His burial took place between 451 and 453 and the place, although was already the tomb of another bishop, St Nostriano, became an object of veneration. The entire area of Rione Sanità was uninhabited throughout the Middle Ages because of the numerous mudslides from the hill of Capodimonte which buried the area. The urbanisation of Rione Sanità began only around the sixteenth century and the catacombs returned to their original burial function. During the seventeenth century, with the construction of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montesarchio
Montesarchio ( nap, Muntesarchio; la, Caudium; grc, Καύδιον, Kaúdion) is a ''comune'' in the Province of Benevento, Campania, southern Italy. It is located south-west of Benevento in the Valle Caudina at the foot of Monte Taburno. The commune was granted the official status of City (''Città'') by a presidential decree of 31 July 1977. History Ancient era Montesarchio is the site of ancient Caudium, an ancient city of Apulia et Calabria, situated on the road from Beneventum (modern Benevento) to Capua. It seems probable that it was in early times a place of importance, and the capital or chief city of the tribe called the Caudini; but it bears only a secondary place in history. It is first mentioned during the Second Samnite War, 321 BCE, when the Samnite army under Gaius Pontius encamped there, previous to the great disaster of the Romans in the neighbouring pass known as the Caudine Forks; and again, a few years later, as the headquarters occupied by the Samnit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catacombs
Catacombs are man-made subterranean passageways for religious practice. Any chamber used as a burial place is a catacomb, although the word is most commonly associated with the Roman Empire. Etymology and history The first place to be referred to as ''catacombs'' was the system of underground tombs between the 2nd and 3rd milestones of the Appian Way in Rome, where the bodies of the apostles Peter and Paul, among others, were said to have been buried. The name of that place in Late Latin was L.L. fem. nom. pl. n. ''catacumbas'' (sing. ''catacumba'') a word of obscure origin, possibly deriving from a proper name or a derivation of the Latin phrase ''catatumbas'', "among the tombs". The word referred originally only to the Roman catacombs, but was extended by 1836 to refer to any subterranean receptacle of the dead, as in the 18th-century Paris catacombs. The ancient Christians carved the first catacombs from soft tufa rock. (ref)" (World Book Encyclopedia, page 296) All Roman ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burial Monuments And Structures
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objects in it, and covering it over. A funeral is a ceremony that accompanies the final disposition. Humans have been burying their dead since shortly after the origin of the species. Burial is often seen as indicating respect for the dead. It has been used to prevent the odor of decay, to give family members closure and prevent them from witnessing the decomposition of their loved ones, and in many cultures it has been seen as a necessary step for the deceased to enter the afterlife or to give back to the cycle of life. Methods of burial may be heavily ritualized and can include natural burial (sometimes called "green burial"); embalming or mummification; and the use of containers for the dead, such as shrouds, coffins, grave liners, and bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Naples
Naples and its immediate surroundings preserve an archaeological heritage of inestimable value and among the best in the world. For example, the archaeological park of the Phlegraean Fields (Cumae, Baiae, the Flavian Amphitheatre and the Pozzuoli forum) is directly connected to the centre of Naples through the Cumana railway, and the nearby sites of Pompeii, Herculaneum, Stabiae and Oplontis are among the World Heritage sites of UNESCO. Despite the ancient city being largely buried by the extensive modern city, remains are preserved in many places. Parthènope, the first settlement founded by the Cumaeans of Naples on the Pizzofalcone hill in the 8th century BC, has left only a few traces, such as the 7th century BC necropolis and the stretch of a wall in the Town Hall square, probably belonging to the port. Much more visible is the 6th c. BC Greek and later Roman city of Neapolis, partly due to the relatively recent underground extension, which includes many archaeological sites a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catacombs Of Rome
The Catacombs of Rome ( it, Catacombe di Roma) are ancient catacombs, underground burial places in and around Rome, of which there are at least forty, some rediscovered only in recent decades. Though most famous for Christian burials, either in separate catacombs or mixed together, Jews and also adherents of a variety of pagan Roman religions were buried in catacombs, beginning in the 2nd century AD,Toynbee: 39–40. occasioned by the ancient Roman ban on burials within a city, and also as a response to overcrowding and shortage of land. The most extensive and perhaps the best known is the Christian Catacomb of Callixtus located near the Park of the Caffarella, but there are other sites, both Christian and not, scattered around the city, some of which are now engulfed by modern urban sprawl. The Christian catacombs are extremely important for the history of Early Christian art, as they contain the great majority of examples from before about 400 AD, in fresco and sculpture, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crypta Neapolitana
The Crypta Neapolitana (Latin for "Neapolitan crypt") is an ancient Roman road tunnel near Naples, Italy. It was built in 37 BC and is over 700 metres long. The tunnel connected Naples with the so-called Phlegrean Fields and the town of Pozzuoli along the road known as the ''via Domiziana''. Geography The eastern entrance (on the Naples side) lies in the Vergiliano park of Piedigrotta ("at the foot of the grotta"); the western end is in the area now called Fuorigrotta ("outside the grotta"). The site is also noteworthy for the presence of the so-called Virgil's tomb, as well as the tomb of the Italian poet Giacomo Leopardi. History Naples and Pozzuoli were separated by a great impenetrable marsh: the first road between the two cities was probably built by the Greeks and was narrow and indirect. The first Roman road connecting Neapolis and the Phlegrean fields, the ''via (Antiniana) per colles'', was built at the beginning of the 1st century BC and followed the easiest rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bourbon Tunnel
The Bourbon Tunnel, Tunnel Borbonico or Bourbon Gallery (Italian: ) is an ancient underground passage, constructed for military purposes to connect the Royal Palace to military barracks in Naples, Italy. The monarchy in the era of King Ferdinand II of Bourbon was fearful of the revolution-prone populace of Naples. Errico Alvino was commissioned to construct a military passage for troops connecting the Royal Palace of Naples to Via Morelli, boring underneath the hill of Pizzofalcone and reaching the quartiere San Ferdinando, but also connecting to other tunnels and aqueducts, including the old Carmignano aqueduct (1627–1629). The monarchy would also not have been ignorant that the Viceroy of Naples in 1647 had nearly been trapped in this urban Royal Palace, and only by luck was able to flee to a nearby convent to escape angry crowds during the Revolt of Masaniello, thus the tunnel could also serve as an escape route for its royal inhabitants. Alvino envisioned a two-lane tunne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catacombs Of San Gennaro
The Catacombs of San Gennaro are underground paleo-Christian burial and worship sites in Naples, Italy, carved out of tuff, a porous stone. They are situated in the northern part of the city, on the slope leading up to , consisting of two levels, San Gennaro Superiore, and San Gennaro Inferiore. The catacombs lie under the Rione Sanità neighborhood of Naples, sometimes called the "Valley of the Dead". The site is now easily identified by the large church of Madre del Buon Consiglio. History Originally, there were three separate cemeteries, dedicated, respectively, to Saint Gaudiosus (''San Gaudioso''), Saint Severus (''San Severo'') and St. Januarius (''San Gennaro''). These catacombs in Naples are different from their Roman counterparts in that they have more spacious passageways along two levels. The lower level is the oldest, going back to the 3rd-4th century and may actually be the site of an earlier pre-Christian cemetery later ceded to the new sect. It apparently be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totò
Antonio Griffo Focas Flavio Angelo Ducas Comneno Porfirogenito Gagliardi de Curtis di Bisanzio (15 February 1898 – 15 April 1967), best known by his stage name Totò (), or simply as Antonio de Curtis, and nicknamed ''il Principe della risata'' ("the Prince of laughter"), was an Italian actor, comedian, screenwriter, dramatist, poet, singer and lyricist. He was commonly referred to as one of the most popular Italian performers of all time. He is best known for his funny and sometimes cynical character as a comedian in theatre and then in many successful films shot from the 1940s to the 1960s, but he also worked with many iconic Italian film directors in dramatic/poetic roles. Early life Totò was born Antonio Vincenzo Stefano Clemente on 15 February 1898 in the Rione Sanità, a poor district of Naples, the illegitimate son of Anna Clemente (1881–1947), a Sicilian woman, and the Neapolitan marquis Giuseppe de Curtis (1873–1944). His father did not legally recognize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
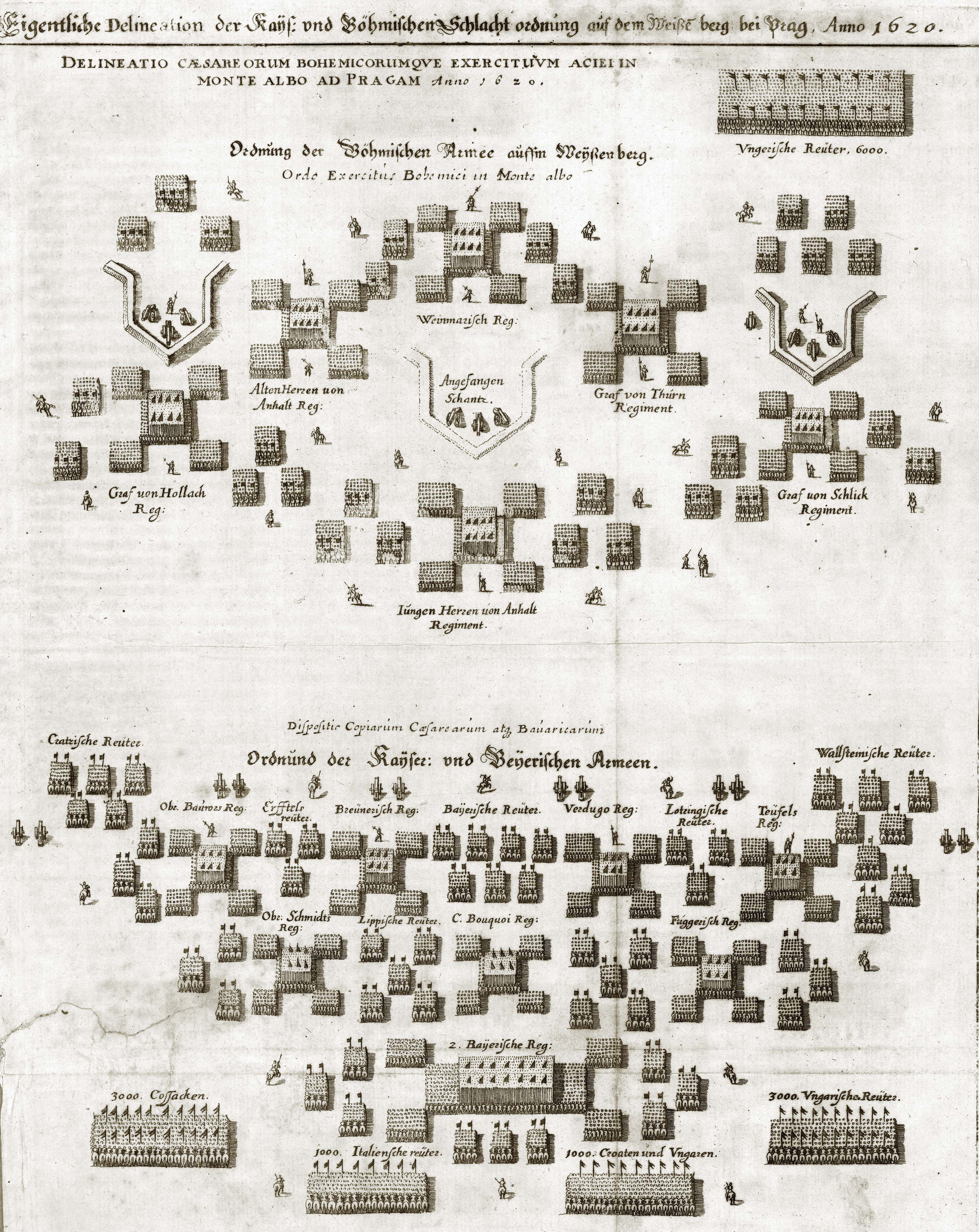
Battle Of White Mountain
), near Prague, Bohemian Confederation(present-day Czech Republic) , coordinates = , territory = , result = Imperial-Spanish victory , status = , combatants_header = , combatant1 = Catholic League , combatant2 = Bohemian Confederation Electoral Palatinate , commander1 = , commander2 = , strength1 = 23,00012 guns , strength2 = 21,00010 guns , casualties1 = 650 killed and wounded , casualties2 = 2,800 killed and wounded , map_type = Czech Republic Prague#Czech Republic , map_mark = Battle icon (crossed swords).svg , map_relief = , map_size = 300px , map_marksize = 30 , map_caption = , map_label = White Mountain The Battle of White Mountain ( cz, Bitva na Bílé hoře; german: Schlacht am Weißen Berg) was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfano
Alfano is a village and small ''comune'' in the province of Salerno in the Campania region of south-western Italy. As of December 31, 2012, the comune had a population of 1082. History There is little reliable evidence on the ancient history of Alfano. However, according to tradition, a large city existed on the slopes of Mount Centaurino, near the present frazione of Roccagloriosa. This would have been destroyed in a catastrophic earthquake, if it had existed. In 1496 the town was given to the Neapolitan noble Giovanni Carafa, Duke of Paliano. Geography Alfano has borders with the municipalities of Laurito, Roccagloriosa and Rofrano. Main sights The main church in Alfano is the Church of Saint Nicholas. The baronial Novelli Palace dates back to the 18th century. It has a grand entrance of stone, leading to a hall. For some time, Novelli Palace served as the Town Hall of Alfano. Palazzo dei Baroni Speranza, another palace, belonged to the Baron Speranza di Laurito. This palace, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)