|
Casualist Artists
In ethics, casuistry ( ) is a process of reasoning that seeks to resolve moral problems by extracting or extending theoretical rules from a particular case, and reapplying those rules to new instances. This method occurs in applied ethics and jurisprudence. The term is also commonly used as a pejorative to criticize the use of clever but unsound reasoning, especially in relation to moral questions (as in sophistry). It is the " udy of cases of conscience and a method of solving conflicts of obligations by applying general principles of ethics, religion, and moral theology to particular and concrete cases of human conduct. This frequently demands an extensive knowledge of natural law and equity, civil law, ecclesiastical precepts, and an exceptional skill in interpreting these various norms of conduct." It remains a common tool for applied ethics. Etymology According to the Online Etymological Dictionary, the term and its agent noun "casuist", appearing from about 1600, derive f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change. History One of the earliest known mathematicians were Thales of Miletus (c. 624–c.546 BC); he has been hailed as the first true mathematician and the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed. He is credited with the first use of deductive reasoning applied to geometry, by deriving four corollaries to Thales' Theorem. The number of known mathematicians grew when Pythagoras of Samos (c. 582–c. 507 BC) established the Pythagorean School, whose doctrine it was that mathematics ruled the universe and whose motto was "All is number". It was the Pythagoreans who coined the term "mathematics", and with whom the study of mathematics for its own sake begins. The first woman mathematician recorded by history was Hypati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Sanchez
Tomás Sánchez (1550 – 19 May 1610) was a 16th-century Spanish Jesuit and famous casuist. Life In 1567 he entered the Society of Jesus. He was at first refused admittance on account of an impediment in his speech; however, after imploring delivery from this impediment before a picture of Mary at Córdoba, Spain, his application was granted. For a time he was the Master of Novices at Granada. The remainder of his life was devoted to the composition of his works. He died of pneumonia. His contemporaries bear testimony to the energy and perseverance with which he laboured towards self-perfection from his novitiate until his death. His penitential zeal rivalled that of the early anchorites, and, according to his spiritual director, he carried his baptismal innocence to the grave. Luis de la Puente, then rector of the college of Granada and later declared "venerable", attests the holiness of Sanchez in his letter to Francisco Suárez, a translation of which may be found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio Escobar Y Mendoza
Antonio Escobar y Mendoza (15894 July 1669) was the leading ethicist of his time. Biography Born at Valladolid in Castile, he was educated by Jesuits before entering this order, aged fifteen. He soon became a famous preacher, and his facility was so great that for fifty years he preached daily, and sometimes twice a day. Above all he was a prodigious writer: his collected works comprise eighty-three volumes. Escobar's first literary efforts were Latin verses in praise of Ignatius Loyola (1613) and Mary (1618), but his principal works focus on exegesis and moral theology. Of the latter the best-known are ''Summula casuum conscientiae'' (1627), ''Liber theologiae moralis'' (1644) and ''Universae theologiae moralis problemata'' (1652–1666). He used to employ the most popular ethical method called casuistry, analyzing real situations rather than strict rules. Escobar's '' Summula'' received criticism, especially in the Jansenist Blaise Pascal's ''Provincial Letters''. Pascal coin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pragmatism
Pragmatism is a philosophical tradition that considers words and thought as tools and instruments for prediction, problem solving, and action, and rejects the idea that the function of thought is to describe, represent, or mirror reality. Pragmatists contend that most philosophical topics—such as the nature of knowledge, language, concepts, meaning, belief, and science—are all best viewed in terms of their practical uses and successes. Pragmatism began in the United States in the 1870s. Its origins are often attributed to the philosophers Charles Sanders Peirce, William James, and John Dewey. In 1878, Peirce described it in his pragmatic maxim: "Consider the practical effects of the objects of your conception. Then, your conception of those effects is the whole of your conception of the object."Peirce, C.S. (1878), " How to Make Our Ideas Clear", ''Popular Science Monthly'', v. 12, 286–302. Reprinted often, including ''Collected Papers'' v. 5, paragraphs 388–410 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preference Utilitarianism
Preference utilitarianism (also known as preferentialism) is a form of utilitarianism in contemporary philosophy. It is distinct from original utilitarianism in that it values actions that fulfill the most ''personal interests'', as opposed to actions that generate the most pleasure. Overview Unlike classical utilitarianism, in which right actions are defined as those that maximize pleasure and minimize pain, preference utilitarianism entails promoting actions that fulfil the interests (preferences) of those beings involved.Peter Singer, ''Practical Ethics'', 2011, p. 13 The beings may be rational, that is to say, their interests may be carefully selected based on future projections, but this is not compulsory; here "beings" extends to all sentient beings, even those living solely in the present (that is, those without the intellectual capacity to contemplate long-term needs or consequences). Since what is good and right depends solely on individual preferences, there can be noth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utilitarianism
In ethical philosophy, utilitarianism is a family of normative ethical theories that prescribe actions that maximize happiness and well-being for all affected individuals. Although different varieties of utilitarianism admit different characterizations, the basic idea behind all of them is, in some sense, to maximize utility, which is often defined in terms of well-being or related concepts. For instance, Jeremy Bentham, the founder of utilitarianism, described ''utility'' as: That property in any object, whereby it tends to produce benefit, advantage, pleasure, good, or happiness ... rto prevent the happening of mischief, pain, evil, or unhappiness to the party whose interest is considered. Utilitarianism is a version of consequentialism, which states that the consequences of any action are the only standard of right and wrong. Unlike other forms of consequentialism, such as egoism and altruism, utilitarianism considers the interests of all sentient beings equally. Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moral Relativism
Moral relativism or ethical relativism (often reformulated as relativist ethics or relativist morality) is used to describe several philosophical positions concerned with the differences in moral judgments across different peoples and cultures. An advocate of such ideas is often referred to as a relativist for short. ''Descriptive'' moral relativism holds only that people do, in fact, disagree fundamentally about what is moral, with no judgment being expressed on the desirability of this. ''Meta-ethical'' moral relativism holds that in such disagreements, nobody is objectively right or wrong. ''Normative'' moral relativism holds that because nobody is right or wrong, everyone ought to tolerate the behavior of others even when large disagreements about morality exist. Said concepts of the different intellectual movements involve considerable nuance and aren't absolute descriptions. Descriptive relativists do not necessarily adopt meta-ethical relativism. Moreover, not all meta-e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moral Absolutism
Moral absolutism is an ethical view that some (potentially all) actions are intrinsically right or wrong. Stealing, for instance, might be considered to be always immoral, even if done for the well-being of others (e.g., stealing food to feed a starving family), and even if it does in the end promote such a good. Moral absolutism stands in contrast to other categories of normative ethical theories such as consequentialism, which holds that the morality (in the wide sense) of an act depends on the consequences or the context of the act. Comparison with other ethical theories Moral absolutism is not the same as moral universalism. Universalism holds merely that what is right or wrong is independent of custom or opinion (as opposed to moral relativism), but not necessarily that what is right or wrong is independent of context or consequences (as in absolutism). Moral universalism is compatible with moral absolutism, but also positions such as consequentialism. Louis Pojman gives th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
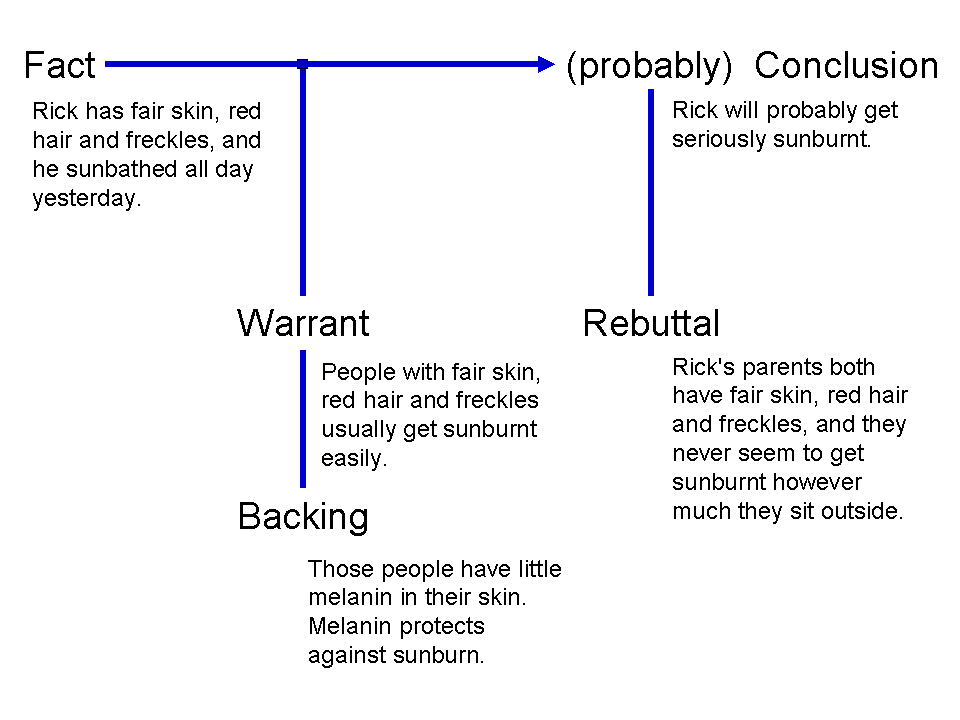
Stephen Toulmin
Stephen Edelston Toulmin (; 25 March 1922 – 4 December 2009) was a British philosopher, author, and educator. Influenced by Ludwig Wittgenstein, Toulmin devoted his works to the analysis of moral reasoning. Throughout his writings, he sought to develop practical arguments which can be used effectively in evaluating the ethics behind moral issues. His works were later found useful in the field of rhetoric for analyzing rhetorical arguments. The Toulmin model of argumentation, a diagram containing six interrelated components used for analyzing arguments, and published in his 1958 book ''The Uses of Argument'', was considered his most influential work, particularly in the field of rhetoric and communication, and in computer science. Biography Stephen Toulmin was born in London, UK, on 25 March 1922 to Geoffrey Edelson Toulmin and Doris Holman Toulmin. He earned his Bachelor of Arts degree from King's College, Cambridge in 1943, where he was a Cambridge Apostle. Soon after, Toulmin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
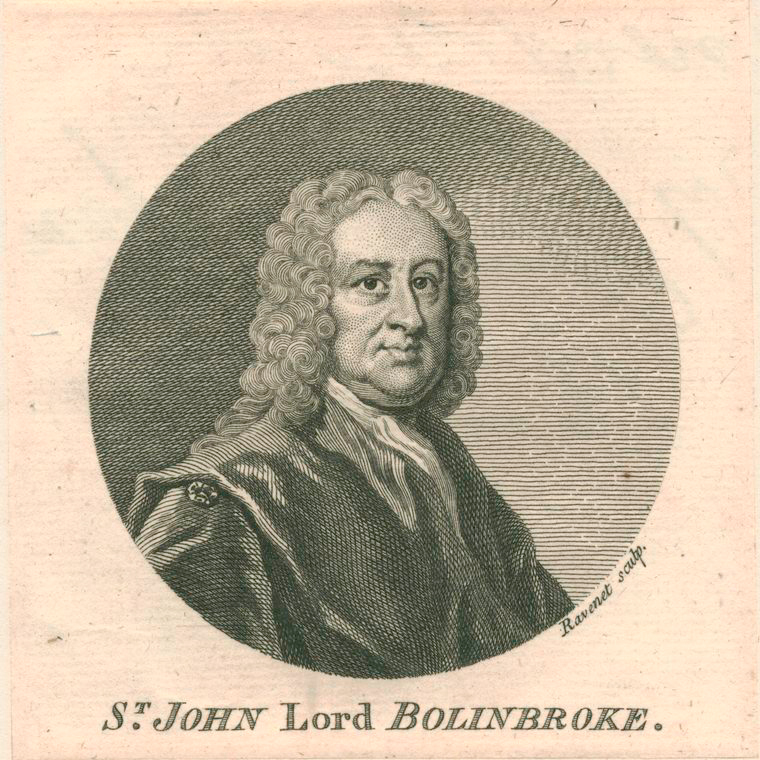
Henry St John, 1st Viscount Bolingbroke
Henry St John, 1st Viscount Bolingbroke (; 16 September 1678 – 12 December 1751) was an English politician, government official and political philosopher. He was a leader of the Tories, and supported the Church of England politically despite his antireligious views and opposition to theology.See e.g., Henry St. John Viscount Bolingbroke, "Letters or Essays Addressed to Alexander Pope: Introduction"''The Works of Lord Bolingbroke: With a Life, Prepared Expressly for This Edition, Containing Additional Information Relative to His Personal and Public Character,'' (Philadelphia: Carey and Hart, 1841) Vol 3, pp. 40–64. Also available on Project Gutenberg as "Letter to Alexander Pope" i ''Letters to Sir William Windham and Mr. Pope''D'Holbach, Baronparagraph 206 He supported the Jacobite rebellion of 1715 which sought to overthrow the new king George I. Escaping to France he became foreign minister for the Pretender. He was attainted for treason, but reversed course and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)