|
Castlereagh (County Down Townland)
Castlereagh () is a townland and former hamlet in the civil parish of Knockbreda, barony of Castlereagh Lower, in County Down, Northern Ireland. It is southeast of Belfast and now at the fringe of the city's suburbs. The townland has an area of . History About 1350, at the site of a '' ráth'' in the Castlereagh Hills, Aodh Flann O’Neill is said to have built the castle from which the townland was named. Aodh was of the Clandeboye, a branch of the O'Neill dynasty who colonised the area from the west. Con MacShane O'Neill raided Belfast from the castle after Christmas 1602, leading to retributions from the Elizabethan settlers there. In 1615, he was reduced to selling the manor comprising the castle and grounds to Moyses Hill, ancestor of the Marquesses of Downshire, who still exercised jurisdiction there in the 1840s. The castle was ruined by the 1750s. Castlereagh Presbyterian Church was founded in 1650, with a building on Church Road from 1720, and the present one built i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
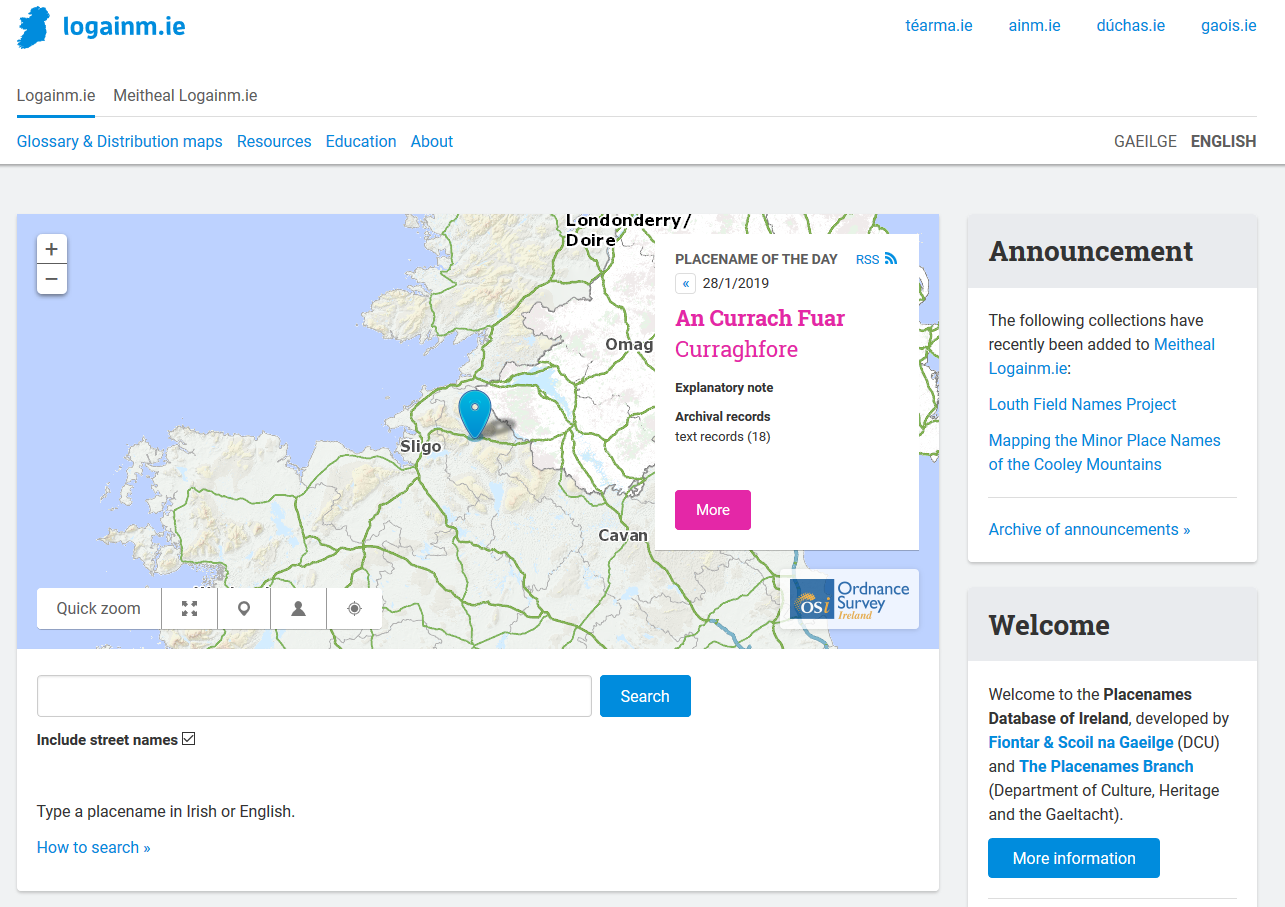
Placenames Database Of Ireland
The Placenames Database of Ireland ( ga, Bunachar Logainmneacha na hÉireann), also known as , is a database and archive of place names in Ireland. It was created by Fiontar, Dublin City University in collaboration with the Placenames Branch of the Department of Tourism, Culture, Arts, Gaeltacht, Sport and Media. The website is a public resource primarily aimed at journalists and translators, students and teachers, historians and researchers in genealogy. Placenames Commission and Placenames Branch The Placenames Commission ( ga, an Coimisiún Logainmneacha) was established by the Department of Finance in 1946 to advise Ordnance Survey Ireland and the government of what the Irish name of places should be. Although both the 1922 Constitution of the Irish Free State and the current constitution adopted in 1937 recognised Irish as the national language, the law in regard to placenames was carried over from the 19th-century UK statutes which established the Ordnance Survey an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquess Of Londonderry
Marquess of Londonderry, of the County of Londonderry ( ), is a title in the Peerage of Ireland. History The title was created in 1816 for Robert Stewart, 1st Earl of Londonderry. He had earlier represented County Down in the Irish House of Commons. Stewart had already been created Baron Londonderry in 1789, Viscount Castlereagh, of Castlereagh in the County of Down, in 1795 and Earl of Londonderry, of the County of Londonderry, in 1796. These titles are also in the Peerage of Ireland. He was the son of Alexander Stewart, who had married Mary Cowan, sister and heiress of Robert Cowan, who gained great wealth as Governor of Bombay from 1729 to 1737. Alexander was from Ballylawn, a townland at the south-west corner of Inishowen in the north of County Donegal, a county located in the west of Ulster in the northern part of Ireland. However, much of the Stewart family's wealth was based on the estates which came into the family through this marriage. The 1st Marquess wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castlereagh (borough)
Castlereagh ( ) was a local government district with the status of borough in Northern Ireland. It merged with Lisburn City Council in May 2015 under local government reorganisation in Northern Ireland to become Lisburn and Castlereagh City Council, with a small amount being transferred to Belfast City Council. It was a mainly urban borough consisting mostly of suburbs of Belfast in the Castlereagh Hills (to the south-east of the city) with a small rural area in the south of the borough. Unusually, it had no natural borough centre. The main centres of population are Carryduff, 6 miles (9.6 km) south of Belfast city centre and Dundonald, 5 miles (8 km) east of it. Castlereagh was named after the barony of Castlereagh, which in turn was named after the townland of same name (from the Irish ''An Caislean Riabhach'', or Grey Castle, a reference to a stronghold of the Clandeboye O'Neils which stood on a site near what is now an Orange hall on Church Road). Creation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland is divided into 11 districts for local government purposes. In Northern Ireland, local councils do not carry out the same range of functions as those in the rest of the United Kingdom; for example they have no responsibility for education, road-building or housing (although they do nominate members to the advisory Northern Ireland Housing Council). Their functions include planning, waste and recycling services, leisure and community services, building control and local economic and cultural development. The collection of rates is handled centrally by the Land and Property Services agency of the Northern Ireland Executive. Local Government Districts The 11 districts were established in 2015. Basic geographical statistics are shown below; data collected for 'religion or religion brought up in' and 'national identity' by district are listed separately. Previously (between 1972 and 2015) the country was divided into 26 smaller districts. Composition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Government (Boundaries) Act (Northern Ireland) 1971
The Local Government (Boundaries) Act (Northern Ireland) 1971 was an Act of the Parliament of Northern Ireland, passed in 1971 to replace the previous system of local authorities established by the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898. The system was based on the recommendations of the Macrory Report, of June 1970, which presupposed the continued existence of the Government of Northern Ireland to act as a regional-level authority. Northern Ireland was to be divided into twenty-six local government districts, each consisting of a number of wards. The Act did not define the Districts exactly, but provided a list of 26 existing local government areas which would form the basis of the pattern. It then gave the Governor of Northern Ireland the power to appoint a Local Government Boundaries Commissioner who was to report with proposed names and boundaries not later than 30 June 1972. The Commissioner's proposals were put into effect by the Local Government (Boundaries) Order (Norther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District Electoral Division
An electoral division (ED, ) is a legally defined administrative area in the Republic of Ireland, generally comprising multiple townlands, and formerly a subdivision of urban and rural districts. Until 1996, EDs were known as district electoral divisions (DEDs, ) in the 29 county council areas and wards in the five county boroughs. Until 1972, DEDs also existed in Northern Ireland. The predecessor poor law electoral divisions were introduced throughout the island of Ireland in the 1830s. The divisions were used as local-government electoral areas until 1919 in what is now the Republic and until 1972 in Northern Ireland. History until partition Electoral divisions originated under the Poor Relief (Ireland) Act 1838 as "poor law electoral divisions": electoral divisions of a poor law union (PLU) returning one or more members to the PLU's board of guardians. The boundaries of these were drawn by Poor Law Commissioners, with the intention of producing areas roughly equivalent in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rural And Urban Districts In Northern Ireland
The urban districts and rural districts of Northern Ireland had their origin in 1899, when the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898 came into effect. They were based on the system of district councils introduced in England and Wales four years earlier. (See List of Irish local government areas 1898–1921 for a historical list of districts in all of Ireland.) At the time of Northern Ireland's creation in 1921, Ireland as a whole was divided into thirty-three administrative counties and six county boroughs; the administrative counties were in turn subdivided into a number of boroughs, urban districts, and rural districts. Each district was itself divided into a number of district electoral divisions. Northern Ireland received a total of six administrative counties, together with the county boroughs of Belfast and Derry. The six administrative counties all included a number of urban and rural districts in 1921, but no boroughs. Evolution and reform Urban District Councils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898
The Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898 (61 & 62 Vict. c. 37) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland that established a system of local government in Ireland similar to that already created for England, Wales and Scotland by legislation in 1888 and 1889. The Act effectively ended landlord control of local government in Ireland.Gailey 1984 Background From the 1880s the issue of local government reform in Ireland was a major political issue, involving both Irish politicians and the major British political parties. Questions of constitutional reform, land ownership and nationalism all combined to complicate matters, as did splits in both the Liberal Party in 1886 and the Irish Parliamentary Party in 1891. Eventually, the Conservative government of Lord Salisbury found it politically expedient to introduce the measures in 1898. The legislation was seen by the government as solving a number of problems: it softened demands for Home Rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Poor Laws
The Irish Poor Laws were a series of Acts of Parliament intended to address social instability due to widespread and persistent poverty in Ireland. While some legislation had been introduced by the pre-Union Parliament of Ireland prior to the Act of Union, the most radical and comprehensive attempt was the Irish act of 1838, closely modelled on the English Poor Law of 1834. In England, this replaced Elizabethan era legislation which had no equivalent in Ireland. Pre-Union In 1703, the Irish Parliament passed an act for "Providing the erection of a workhouse and for the maintenance and apprenticing out of foundling children". By 1771, there were Houses of Industry in every county and by 1833, the total cost was £32,967. Post-Union Until 1838, the use of 'Houses of industry' was on a much smaller scale than in England and Wales. Poor Law Unions The report of the Royal Commission on the Poorer Classes in Ireland 1833 led to the Irish Poor Law Act of 1838, under which three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castlereagh Upper
Castlereagh Upper (named after the former barony of Castlereagh) is a historic barony in County Down, Northern Ireland. It was created by 1841 with the division of Castlereagh into two. It is bordered by eight other baronies: Castlereagh Lower and Dufferin to the east; Lecale Lower and Kinelarty to the south; Iveagh Lower, Lower Half, Iveagh Lower, Upper Half, and Massereene Upper to the west; and Belfast Upper to the north. List of settlements Below is a list of settlements in Castlereagh Upper: Cities *Belfast *Lisburn Towns *Carryduff Villages * Kilmore *Saintfield Population centres *Ballymacarrett *Newtownbreda List of civil parishes Below is a list of civil parishes in Castlereagh Upper: *Blaris (also partly in baronies of Iveagh Lower, Upper Half and Massereene Upper) *Comber (also partly in barony of Castlereagh Lower) * Drumbeg (also partly in barony of Belfast Upper) *Drumbo * Killaney *Killinchy (also partly in baronies of Castlereagh Lower and Dufferin) *Kill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Rebellion Of 1798
The Irish Rebellion of 1798 ( ga, Éirí Amach 1798; Ulster-Scots: ''The Hurries'') was a major uprising against British rule in Ireland. The main organising force was the Society of United Irishmen, a republican revolutionary group influenced by the ideas of the American and French revolutions: originally formed by Presbyterian radicals angry at being shut out of power by the Anglican establishment, they were joined by many from the majority Catholic population. Following some initial successes, particularly in County Wexford, the uprising was suppressed by government militia and yeomanry forces, reinforced by units of the British Army, with a civilian and combatant death toll estimated between 10,000 and 50,000. A French expeditionary force landed in County Mayo in August in support of the rebels: despite victory at Castlebar, they were also eventually defeated. The aftermath of the Rebellion led to the passing of the Acts of Union 1800, merging the Parliament of Ireland int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |