|
Castlerahan Gaelic Footballers
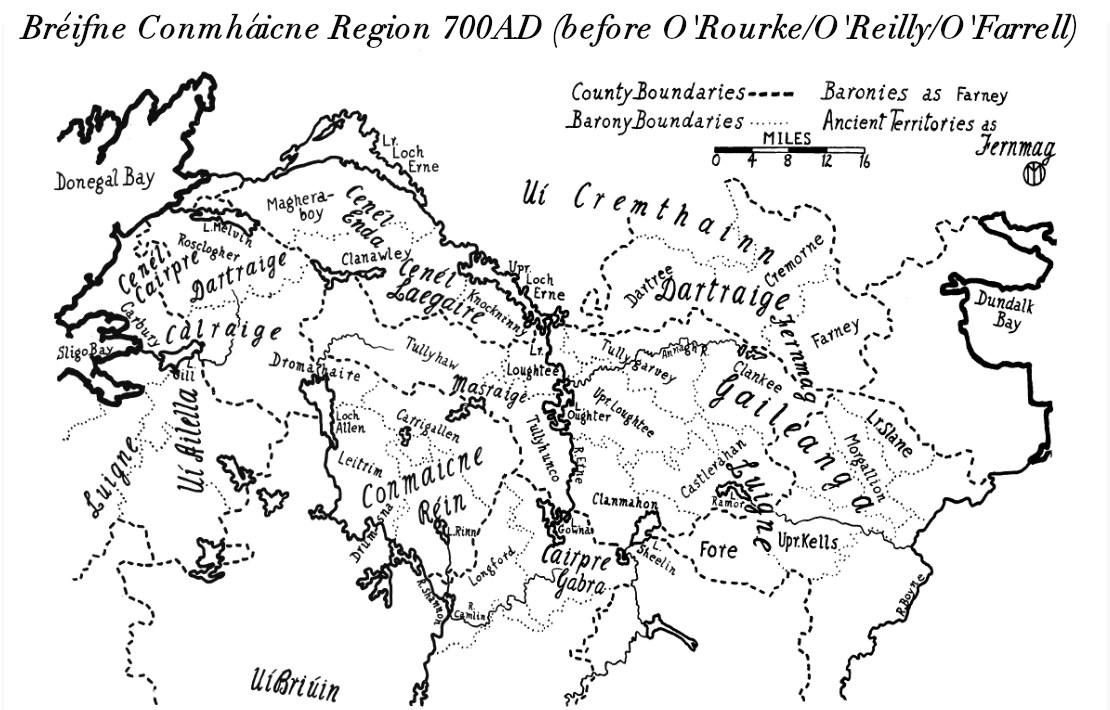
Castlerahan () is a barony in County Cavan, Republic of Ireland. Baronies were mainly cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898. Etymology Castlerahan barony takes its name from Castlerahan townland, from Castlera an, an ancient hillfort located at . The name is derived from Irish ''Caisleán Raithín'', "stone fort of the little ringfort," although other writers link it with ''raithean'', "bracken", or with a Norse Gael leader named Raithin. Geography Castlerahan is located in the southeast of County Cavan, the area surrounding Lough Ramor. History The Luigni tribe lived in the area since the 8th century. It contains the parish of Munterconnaught, named for Cu Connaght Ua Raghallaigh (O'Reilly). The barony of Castlerahan was created by 1609 in the Plantation of Ulster, and was archaically spelled ''Castlerachan''. The baro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish ( Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous to the island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the 19th century, when English gradually became dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century. Irish is still spoken as a first language in a small number of areas of certain counties such as Cork, Donegal, Galway, and Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties Mayo, Meath, and Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second-language speakers. Daily users in Ireland outside the education system number around 73,000 (1.5%), and the total number of persons (aged 3 and over) who claimed they could speak Irish in April 2016 was 1,761,420, representing 39.8% of respondents. For most of recorded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringfort
Ringforts, ring forts or ring fortresses are circular fortified settlements that were mostly built during the Bronze Age up to about the year 1000. They are found in Northern Europe, especially in Ireland. There are also many in South Wales and in Cornwall, where they are called rounds. Ringforts come in many sizes and may be made of stone or earth. Earthen ringforts would have been marked by a circular rampart (a bank and ditch), often with a stakewall. Both stone and earthen ringforts would generally have had at least one building inside. Distribution Ireland In Irish language sources they are known by a number of names: ' (anglicised ''rath'', also Welsh ''rath''), ' (anglicised ''lis''; cognate with Cornish '), ' (anglicised ''cashel''), ' (anglicised ''caher'' or ''cahir''; cognate with Welsh ', Cornish and Breton ') and ' (anglicised ''dun'' or ''doon''; cognate with Welsh and Cornish ').Edwards, Nancy. ''The Archaeology of Early Medieval Ireland''. Routledge, 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mullagh, County Cavan
Mullagh (; ) is a town, civil parish and townland in County Cavan, Ireland. , the town's population was 1,348. It lies in the south-east of the county, at the junction of the R191 and the R194 regional roads near the towns of Virginia and Bailieborough. St Kilian and churches The town has a heritage centre dedicated to St Kilian, who was born in Mullagh c 640 and was martyred in Würzburg in Franconia in northern Bavaria, Germany, in circa 689. The centre also has an exhibition related to ogham script and the development of illuminated manuscripts. The Catholic church, a Victorian neo-Gothic structure located 400m from the village on the Virginia Road (R194), is named in memory of its patron, Saint Kilian. It was built in the late 1850s. Ruins of an earlier church, known as the ''Teampeall Ceallaigh'', remain in what is now part of the Church of Ireland grounds located approximately 600m along the same road. Development Mullagh's population has seen an increase from 679 re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilnaleck
Kilnaleck or Kilnalec () is a small village in County Cavan, Ireland on the R154 regional road. Kilnaleck was once the centre of a mining boom when in 1879 some local businessmen and a school headmaster decided to develop the coal that existed nearby. However, the coal was very deep and hard to extract and the mine was forced to close. The village is part of Crosserlough parish. Transport A number of Cavan Area Rural Transport (CART) routes serve Kilnaleck. Over the decades Kilnaleck was served by CIÉ and from 1987 by Bus Éireann. However in 2009 the remaining service, Bus Éireann route 179, was discontinued. Nowadays the nearest Bus Éireann routes may be accessed at Mountnugent (route 187) or Ballinagh (route 111), 7 km and 10 km distant respectively. Amenities There is a national school in the village. There is also a children's playground, Roman Catholic church, Garda station. Sport Kilnaleck is home to Crosserlough GFC, and Innyvale Athletic Club is based o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crosserlough
Crosserlough, historically known as ''Cros Ar Loch'', is a large civil parish in southern County Cavan, in the province of Ulster, Ireland. It is located between Ballyjamesduff and Lough Sheelin. The parish consists of three areas. Kilnaleck, which is a village, Drumkilly and Crosserlough. The latter is a small settlement at the northern edge of the eponymous townland. Facilities There are three schools in the parish, Kilnaleck, Drumkilly and Crosserlough. There are three Catholic Churches in Crosserlough, St Mary's Church (the Parish Church) in the townland of Cullow, in the Crosserlough area. This church was built in 1888. There is also a Church of Ireland church at Kildrumferton. There are five pubs, three grocery shops, a post office, a pharmacy, two off-licences (attached to pubs), a butcher's shop, a garage, barbers, drapery shop, a number of takeaway restaurants, a hairdresser, beautician, car dealership and approximately 30 houses in Kilnaleck. John Comiskey, a Chica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballyjamesduff
Ballyjamesduff () is a town in County Cavan, Ireland. A former market town, it was the winner of the 1966 and 1967 Irish Tidy Towns Competition. History The first mention of Ballyjamesduff is found in The Registry of Deeds, Kings Inns, Henrietta Street, Dublin, Deed No.12-294-5122, drawn up on 12 May 1714. In ''A Topographical Dictionary of Ireland'', first published by Samuel Lewis in 1837, its entry reads: :''"Ballyjamesduff, an old market town, in county Cavan, and the province of Ulster. The town is situated on the old mail-coach road from Virginia to Cavan. :''The parish was created in 1831, by disuniting nine townlands from the parish of Castleraghan, five from that of Denn, two from Lurgan, and four from the parish of Kildrumferton."'' Demographics The population was 2,661 at the 2016 census. At that census, Ballyjamesduff had a similar population to the County Cavan towns of Bailieborough, Virginia and Kingscourt: each with about 2,500 people. The town's population is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castlerahan GAA
Castlerahan is a Gaelic football club from Ballyjamesduff, County Cavan, Ireland. They take their name from the Castlerahan barony in which Ballyjamesduff is located. History The club was founded in its current state in 1961, Ballyjamesduff and Castlerahan fielding separate teams prior to then. The club reached its first Senior Championship final in 1968, losing to Crosserlough. In 2011, the club reached its first senior final since 1968. They lost the final heavily to Cavan Gaels. It was four years before Castlerahan reached another county final against Kingscourt Stars in 2015. Castlerahan came up one point short on that occasion. Castlerahan lost further finals to neighbours Ramor United after a replay in 2016, and to Cavan Gaels again in 2017. Castlerahan played in their fourth consecutive final in 2018, facing Crosserlough. Having been six points down, they staged a comeback to win by a point and finally win their first senior championship. Castlerahan successfully de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantation Of Ulster
The Plantation of Ulster ( gle, Plandáil Uladh; Ulster-Scots: ''Plantin o Ulstèr'') was the organised colonisation (''plantation'') of Ulstera province of Irelandby people from Great Britain during the reign of King James I. Most of the settlers (or ''planters'') came from southern Scotland and northern England; their culture differed from that of the native Irish. Small privately funded plantations by wealthy landowners began in 1606, while the official plantation began in 1609. Most of the colonised land had been confiscated from the native Gaelic chiefs, several of whom had fled Ireland for mainland Europe in 1607 following the Nine Years' War against English rule. The official plantation comprised an estimated half a million acres (2,000 km2) of arable land in counties Armagh, Cavan, Fermanagh, Tyrone, Donegal, and Londonderry. Land in counties Antrim, Down, and Monaghan was privately colonised with the king's support. Among those involved in planning and ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munterconnaught
, native_name_lang = ga , settlement_type = , image_skyline = Munterconnaught Parish, Church of Ireland - geograph.org.uk - 791537.jpg , imagesize = , image_alt = , image_caption = Parish sign and church in Munterconnaught , pushpin_map = Ireland , pushpin_label_position = , pushpin_map_alt = Location of Munterconnaught within the Republic of Ireland , pushpin_mapsize = , pushpin_map_caption = Location of Munterconnaught within the Republic of Ireland , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Republic of Ireland , subdivision_type1 = Province , subdivision_name1 = Ulster , subdivision_type2 = County , subdivision_name2 = County Cavan , blank_name = Irish grid reference , blank_info N599842, website = , footnotes = Munterconnaught () is a civil and ecclesiastical parish of County Cavan in the Republic of Ireland. It is located between the southern shores of Lough Ramor and the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luighne Connacht
Luighne Connacht was a territory located in north-central Connacht, on the borders of what is now County Mayo and County Sligo, Ireland. Origin The Luighne were a people, originally found in Brega, south of Kells in what is now County Meath. The baronies of Lune in Meath, and Leyney in Sligo, were called after them. According to Lambert McKenna (pp.xvi-xvii): ''"heyprobably acquired their land in Connacht as a reward for military service rendered to the tribes which had victoriously invaded that part of the country. Their migration ... and their settlement in Connacht are constantly referred to in the poems of this book" (see The Book of O'Hara) "and are the chief subject of the story of the Battle of Crionna; it evidently remained a very lively tradition among them even down to late times."'' According to this story, the Luighne accompanied Tadhg mac Cian, who ''"The genealogists brought Tadc and his descendants from Éli in northern Munster, but since we find the Luign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norse Gael
Norse is a demonym for Norsemen, a medieval North Germanic ethnolinguistic group ancestral to modern Scandinavians, defined as speakers of Old Norse from about the 9th to the 13th centuries. Norse may also refer to: Culture and religion * Norse mythology * Norse paganism * Norse art * Norse activity in the British Isles * Vikings Language * Proto-Norse language, the Germanic language predecessor of Old Norse * Old Norse, a North Germanic language spoken in Scandinavia and areas under Scandinavian influence from c. 800 AD to c. 1300 AD ** Old West Norse, the western dialect of Old Norse, spoken in Norway and areas under Norwegian influence *** Greenlandic Norse *** Norn language, an extinct North Germanic language that was spoken in Shetland and Orkney, off the north coast of mainland Scotland, and in Caithness ** Old East Norse, the eastern dialect of Old Norse, spoken in Denmark, Sweden and areas under their influence Location * Norse, Texas, a ghost town founded by Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

%2C_Co_Roscommon%2C_Ireland.jpg)



