|
Castleman's Disease
Castleman disease (CD) describes a group of rare lymphoproliferative disorders that involve enlarged lymph nodes, and a broad range of inflammatory symptoms and laboratory abnormalities. Whether Castleman disease should be considered an autoimmune disease, cancer, or infectious disease is currently unknown. Castleman disease includes at least three distinct subtypes: unicentric Castleman disease (UCD), human herpesvirus 8 associated multicentric Castleman disease (HHV-8-associated MCD), and idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease (iMCD). These are differentiated by the number and location of affected lymph nodes and the presence of human herpesvirus 8, a known causative agent in a portion of cases. Correctly classifying the Castleman disease subtype is important, as the three subtypes vary significantly in symptoms, clinical findings, disease mechanism, treatment approach, and prognosis. All forms involve overproduction of cytokines and other inflammatory proteins by the body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
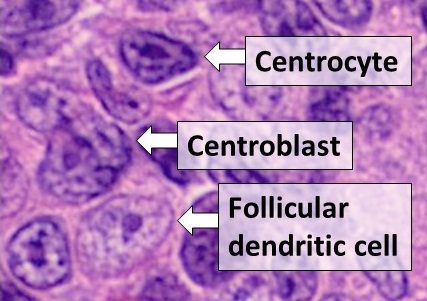
Follicular Dendritic Cells
Follicular dendritic cells (FDC) are cells of the immune system found in primary and secondary lymph follicles (lymph nodes) of the B cell areas of the lymphoid tissue. Unlike dendritic cells (DC), FDCs are not derived from the bone-marrow hematopoietic stem cell, but are of mesenchymal origin. Possible functions of FDC include: organizing lymphoid tissue's cells and microarchitecture, capturing antigen to support B cell, promoting debris removal from germinal centers, and protecting against autoimmunity. Disease processes that FDC may contribute include primary FDC-tumor, chronic inflammatory conditions, HIV-1 infection development, and neuroinvasive scrapie. Location and molecular markers Follicular DCs are a non-migratory population found in primary and secondary follicles of the B cell areas of lymph nodes, spleen, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). They form a stable network due to intercellular connections between FDCs processes and intimate interaction with f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaposi's Sarcoma
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is a type of cancer that can form masses in the skin, in lymph nodes, in the mouth, or in other organs. The skin lesions are usually painless, purple and may be flat or raised. Lesions can occur singly, multiply in a limited area, or may be widespread. Depending on the sub-type of disease and level of immune suppression, KS may worsen either gradually or quickly. Except for Classical KS where there is generally no immune suppression, KS is caused by a combination of immune suppression (such as due to HIV/AIDS) and infection by Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8 – also called KS-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)). Four sub-types are described: classic, endemic, immunosuppression therapy-related (also called iatrogenic), and epidemic (also called AIDS-related). Classic KS tends to affect older men in regions where KSHV is highly prevalent (Mediterranean, Eastern Europe, Middle East), is usually slow-growing, and most often affects only the legs. Endemic KS is most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune Lymphoproliferative Syndrome
Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS) is a form of lymphoproliferative disorder (LPDs). It affects lymphocyte apoptosis. It is a rare genetic disorder of abnormal lymphocyte survival caused by defective Fas mediated apoptosis. Normally, after infectious insult, the immune system down-regulates by increasing Fas expression on activated B and T lymphocytes and Fas-ligand on activated T lymphocytes. Fas and Fas-ligand interact to trigger the caspase cascade, leading to cell apoptosis. Patients with ALPS have a defect in this apoptotic pathway, leading to chronic non-malignant lymphoproliferation, autoimmune disease, and secondary cancers. Signs and symptoms All people with ALPS have signs of lymphoproliferation, which makes it the most common clinical manifestation of the disease. The increased proliferation of lymphoid cells can cause the size of lymphoid organs such as the lymph nodes and spleen to increase ( lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly, present in respectively over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, drenching sweats, unintended weight loss, itching, and constantly feeling tired. The enlarged lymph nodes are usually painless. The sweats are most common at night. Many subtypes of lymphomas are known. The two main categories of lymphomas are the non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) (90% of cases) and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) (10%). The World Health Organization (WHO) includes two other categories as types of lymphoma – multiple myeloma and immunoproliferative diseases. Lymphomas and leukemias are a part of the broader group of tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Risk factors for Hodgkin lymphoma include infection with Epstein–Barr virus and a history of the disease in the family. Risk factors for common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Lymphoproliferative disorders (LPDs) refer to a specific class of diagnoses, comprising a group of several conditions, in which lymphocytes are produced in excessive quantities. These disorders primarily present in patients who have a compromised immune system. Due to this factor, there are instances of these conditions being equated with " immunoproliferative disorders"; although, in terms of nomenclature, lymphoproliferative disorders are a subclass of immunoproliferative disorders—along with hypergammaglobulinemia and paraproteinemias. Lymphoproliferative disorders (examples) * Follicular lymphoma * chronic lymphocytic leukemia * acute lymphoblastic leukemia * hairy cell leukemia * Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) * B-cell lymphomas * T-cell lymphomas * multiple myeloma * Waldenström's macroglobulinemia * Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome * Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) * Lymphocyte-variant hypereosinophilia * Pityriasis Lichenoides (PL, PLC, PLVA) * post-transpla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves and blood. This may result in a low red blood cell count, inflammation around the lungs, and inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the joint capsule. It also affects the underlying bone and cartilage. The diagnosis is made mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is most commonly on the face. Often there are periods of illness, called flares, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms. The cause of SLE is not clear. It is thought to involve a mixture of genetics combined with environmental factors. Among identical twins, if one is affected there is a 24% chance the other one will also develop the disease. Female sex hormones, sunlight, smoking, vitamin D deficiency, and certain infections are also believed to increase a person's risk. The mechanism involves an immune response by autoantibodies against a person's own tissues. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune Disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly any body part can be involved. Common symptoms can be diverse and transient, ranging from mild to severe, and generally include low grade fever and feeling tired. The cause is unknown. Some autoimmune diseases such as lupus run in families, and certain cases may be triggered by infections or other environmental factors. Some common diseases that are generally considered autoimmune include celiac disease, diabetes mellitus type 1, graves' disease, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis, alopecia areata, addison’s disease, pernicious anemia, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. The diagnosis can be difficult to determine. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the condition. Nonsteroidal ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of active TB is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epstein–Barr Virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), formally called ''Human gammaherpesvirus 4'', is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus. It is best known as the cause of infectious mononucleosis ("mono" or "glandular fever"). It is also associated with various non-malignant, premalignant, and malignant Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative diseases such as Burkitt lymphoma, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, and Hodgkin's lymphoma; non-lymphoid malignancies such as gastric cancer and nasopharyngeal carcinoma; and conditions associated with human immunodeficiency virus such as hairy leukoplakia and central nervous system lymphomas. The virus is also associated with the childhood disorders of Alice in Wonderland syndrome and acute cerebellar ataxia and, by some evidence, higher risks of developing certain autoimmune diseases, especially dermatomyositis, systemic lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |