|
Cassegrain , a Catholic priest and teacher and probably the inventor of the Cassegrain Reflector
{{disambig ...
Cassegrain may refer to * Cassegrain reflector, a design used in telescopes * Cassegrain antenna, a type of parabolic antenna * Cassegrain (crater), on the Moon * a Belgian canned vegetables producer now part of Bonduelle S.A. People : * Guillaume Cassegrain, a French sculptor * Giovanni Cassegrain, a French sculptor * Jean Cassegrain, a French businessman, founder of Longchamp in 1948 * Laurent Cassegrain Laurent Cassegrain (; – 1 September 1693) was a Catholic priest who is notable as the probable inventor of the Cassegrain reflector, a folded two-mirror reflecting telescope design. Biography Laurent Cassegrain was born in the region of Chartr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassegrain Reflector
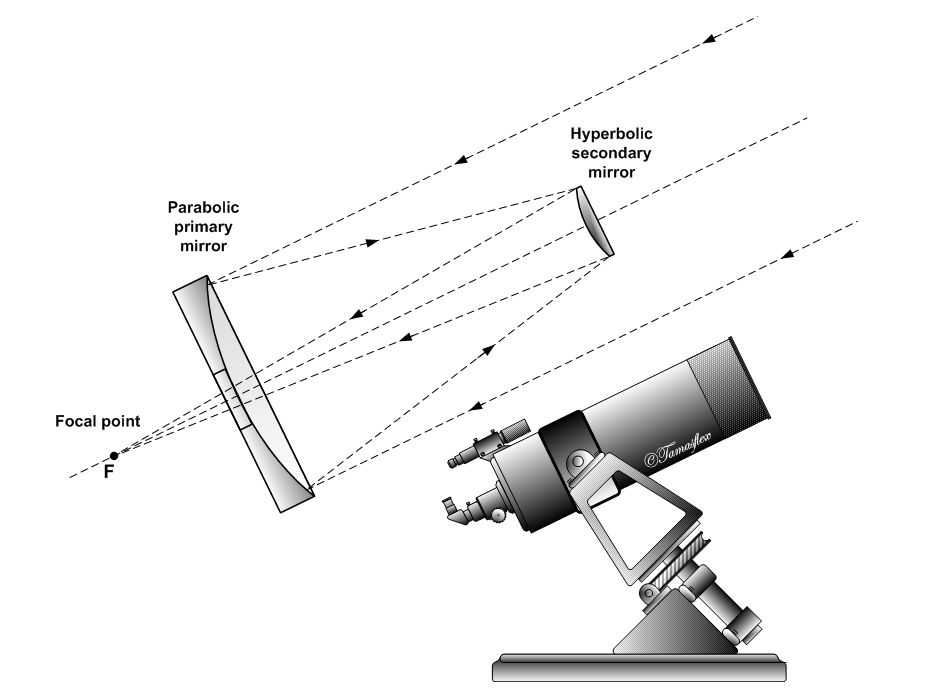
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the primary mirror (or both). The classic Cassegr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Cassegrain
Longchamp is a French leather goods company, founded in Paris in 1948 by Jean Cassegrain. The company pioneered luxury leather-covered pipes before expanding into small leather goods. Longchamp debuted women's handbags in 1971, becoming one of France's leading leather goods makers. Today, the company designs and manufactures leather and canvas handbags, luggage, shoes, travel items, fashion accessories, and women's ready-to-wear. The house is privately owned and managed by the Cassegrain founding family and does business in 80 countries through around 1,500 retail outlets. History Early history In 1948, Jean Cassegrain took over his father's traditional tobacco business "Au Sultan" in Paris. After the Second World War, Jean Cassegrain catered to Allied troops with his tobacco and smoking accessories. Pipe sales were the most profitable part of his business. Little by little, soldiers became the store's best customers. When they left Paris at the end of the conflict, Jean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guillaume Cassegrain
Laurent Cassegrain (; – 1 September 1693) was a Catholic priest who is notable as the probable inventor of the Cassegrain reflector, a folded two-mirror reflecting telescope design. Biography Laurent Cassegrain was born in the region of Chartres around 1629 and was the son of Mathurin Cassegrain and Jehanne Marquet. It is unknown what his education was but he was a priest and professor by 1654. He may have been interested in acoustics, optics and mechanics. At the time of his death he was working as a teacher giving science classes at the Collège de Chartres, a French lycée, i.e., a high-school like institution. He died at Chaudon (Eure-et-Loir) on 1 September 1693. Connection with the Cassegrain reflector The Cassegrain reflector is a reflecting telescope design that solved the problem of viewing an image without obstructing the primary mirror by using a convex secondary mirror on the optical axis to bounce the light back through a hole in the primary mirror thus permittin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Cassegrain
Laurent Cassegrain (; – 1 September 1693) was a Catholic priest who is notable as the probable inventor of the Cassegrain reflector, a folded two-mirror reflecting telescope design. Biography Laurent Cassegrain was born in the region of Chartres around 1629 and was the son of Mathurin Cassegrain and Jehanne Marquet. It is unknown what his education was but he was a priest and professor by 1654. He may have been interested in acoustics, optics and mechanics. At the time of his death he was working as a teacher giving science classes at the Collège de Chartres, a French lycée, i.e., a high-school like institution. He died at Chaudon (Eure-et-Loir) on 1 September 1693. Connection with the Cassegrain reflector The Cassegrain reflector is a reflecting telescope design that solved the problem of viewing an image without obstructing the primary mirror by using a convex secondary mirror on the optical axis to bounce the light back through a hole in the primary mirror thus permittin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassegrain Antenna
In telecommunications and radar, a Cassegrain antenna is a parabolic antenna in which the feed antenna is mounted at or behind the surface of the concave main parabolic reflector dish and is aimed at a smaller convex secondary reflector suspended in front of the primary reflector. The beam of radio waves from the feed illuminates the secondary reflector, which reflects it back to the main reflector dish, which reflects it forward again to form the desired beam. The Cassegrain design is widely used in parabolic antennas, particularly in large antennas such as those in satellite ground stations, radio telescopes, and communication satellites. Geometry The primary reflector is a paraboloid, while the shape of the convex secondary reflector is a hyperboloid. The geometrical condition for radiating a collimated, plane wave beam is that the feed antenna is located at the far focus of the hyperboloid, while the focus of the primary reflector coincides with the near focus of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassegrain (crater)
Cassegrain is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, beyond the southeastern limb. It lies to the southeast of the larger crater Lebedev, and to the northeast of the comparably-sized Priestley. It is named after the inventor of the Cassegrain reflector, who was later identified as most likely Laurent Cassegrain. The interior of this crater has a relatively dark-hued floor, a feature it has in common with other craters to the west and northwest that form part of the Mare Australe Mare Australe (Latin ''austrāle'' the "Southern Sea") is a lunar mare located in the southeastern hemisphere of the Moon. It is 997 kilometers in diameter, overlapping the near and far sides of the Moon. Smooth, dark volcanic basalt lines the .... The floor is level and mostly featureless, except for some deposits in the northwest corner. The rim is more heavily worn in the northwest corner than elsewhere, and the remaining inner wall displays a slumped shelf below the ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonduelle S
Bonduelle is a French company producing processed vegetables. History * The company was founded in 1853, when Louis Bonduelle-Dalle (23 October 1802 - 13 November 1880) and Louis Lesaffre-Roussel (1802–1869) established a grain and juniper berry distillery in Marquette-lez-Lille. On June 17, 1862, they expanded to a farm in Renescure, which they turned into a grain alcohol distillery. * 1901 the company and its seven production sites were divided into three family owned companies: Bonduelle, Lesaffre and Lemaître. * 1926 the business began canning peas. Demand in the 1930s enabled the company to expand, but the firm's operations were suspended in 1940 through the end of World War II. * The mid 1960s, the company began to improve its exports, and in 1968, began freezing vegetables. Several European subsidiaries were launched: in Germany in 1969, in Italy in 1972 and in England in 1973. By 1973, exports accounted for half of the company's turnover. * 1980, Bonduelle acquired B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna (radio)
In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver (radio), receiver. In Transmission (telecommunications), transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves (radio waves). In Receiver (radio), reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be Amplifier, amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment. An antenna is an array of conductor (material), conductors (Driven element, elements), electrically connected to the receiver or transmitter. Antennas can be designed to transmit and receive radio waves in all horizontal directions equally (omnidirectional antennas), o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_store_front.jpg)
