|
Caseodus
''Caseodus'' is an extinct genus of eugeneodontid holocephalian from the Carboniferous of the United States (Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, South Dakota) and the Early Triassic of Canada (British Columbia). It was of medium size, measuring in length. Eugeneodontida are an extinct order of Chondrichthyes. They are characterized by the presence of tooth whorls. They include iconic genera, such as ''Helicoprion'' ("buzz-saw shark"), ''Ornithoprion'', '' Edestus'' or '' Fadenia''. ''Caseodus'' is one of the few eugeneodontid genera that survived the end-Permian mass extinction event. It is one of the last surviving genera of this clade A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, .... ''Caseodus'' is named after the late paleoichthyologist Gerard Case. References * Caseodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugeneodontida
The Eugeneodontida is an extinct and poorly known order of cartilaginous fishes. They possessed "tooth-whorls" on the symphysis of either the lower or both jaws and pectoral fins supported by long radials. They probably lacked pelvic fins and anal fins. The palatoquadrate was either fused to the skull or reduced. Now determined to be within the Holocephali, their closest living relatives are ratfish. The eugeneodonts are named after paleontologist Eugene S. Richardson, Jr. The Eugeneodontida disappeared in the Early Triassic. Members of the Eugeneodontida are further classified into different families, the most well-preserved members that have been discovered are commonly placed within the families Helicoprionidae ("spiral saws"), and Edestidae ("those which devour"), the former containing the genera ''Helicoprion'', '' Sarcoprion'', and '' Parahelicoprion'', and the latter containing the genera '' Edestus'', ''Lestrodus'', and '' Metaxyacanthus''. All eugeneodonts are thought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
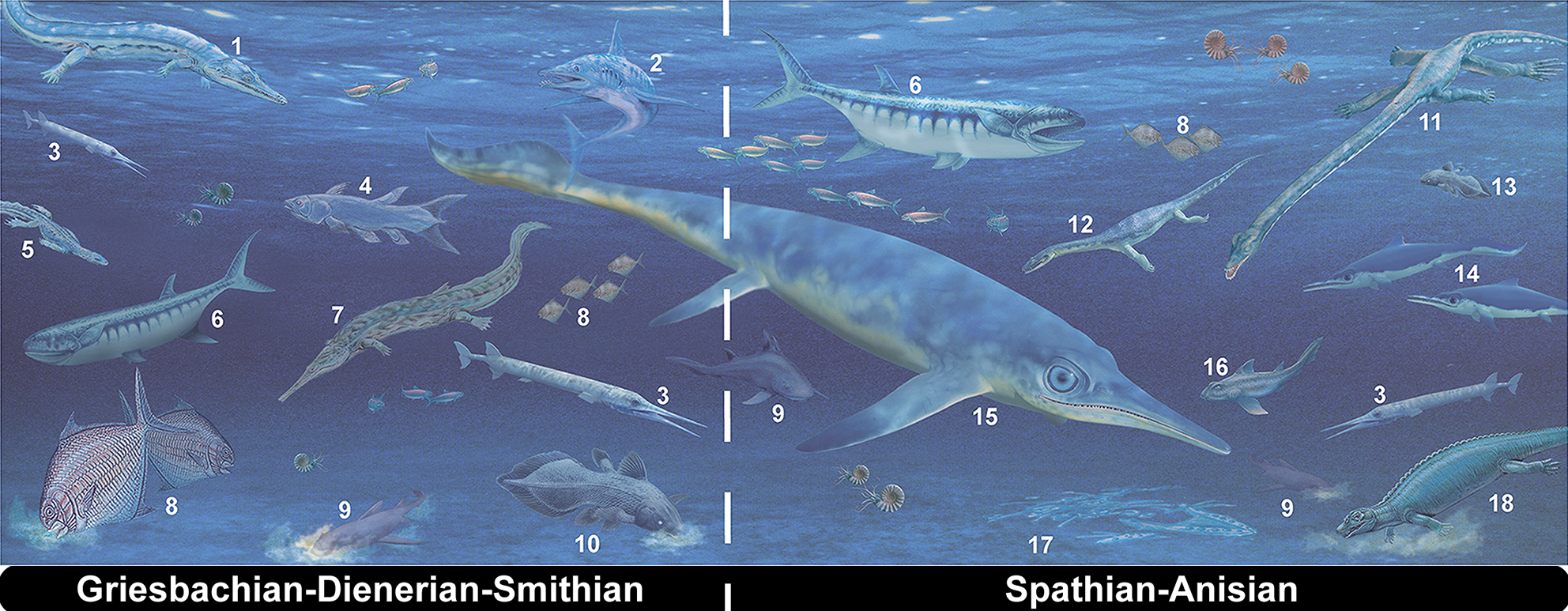
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Triassic span the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugeneodontid
The Eugeneodontida is an extinct and poorly known order of cartilaginous fishes. They possessed "tooth-whorls" on the symphysis of either the lower or both jaws and pectoral fins supported by long radials. They probably lacked pelvic fins and anal fins. The palatoquadrate was either fused to the skull or reduced. Now determined to be within the Holocephali, their closest living relatives are ratfish. The eugeneodonts are named after paleontologist Eugene S. Richardson, Jr. The Eugeneodontida disappeared in the Early Triassic. Members of the Eugeneodontida are further classified into different families, the most well-preserved members that have been discovered are commonly placed within the families Helicoprionidae ("spiral saws"), and Edestidae ("those which devour"), the former containing the genera ''Helicoprion'', '' Sarcoprion'', and ''Parahelicoprion'', and the latter containing the genera ''Edestus'', ''Lestrodus'', and '' Metaxyacanthus''. All eugeneodonts are thought to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fadenia
''Fadenia'' is an extinct genus of eugeneodontid holocephalian chondrichthyan from the Carboniferous Period of Missouri (United States), the Permian period of Greenland, and the Early Triassic epoch of Greenland and Sulphur Mountain Formation of British Columbia, Canada. Eugeneodontida are an extinct order of Chondrichthyes. They are characterized by the presence of tooth whorls. They include iconic genera, such as ''Helicoprion'' (buzz-saw shark), '' Ornithoprion'', '' Edestus'' or '' Caseodus''. ''Fadenia'' is one of the few eugeneodontid genera that survived the end-Permian mass extinction event. It is one of the last surviving genera of this clade. It could reach about in length. The first fossils of Fadenia were discovered and written about in the periodical Meddelelser om Grønland in 1932 by the Danish vertebrate palaeontologist Eigil Nielsen after studying the Upper Permian beds of Cape Stosch, in the fjord of Godthab Gulf in King Christian X Land, Greenland. He had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edestus
''Edestus'' is an extinct genus of edestoid cartilaginous fish known from the Late Carboniferous ( Pennsylvanian) of the United Kingdom, Russia, and the United States. Most remains consist of isolated curved blades or "whorls" that are studded with teeth, that in life were situated within the jaws. ''Edestus'' is a Greek name derived from the word ''edeste'' (to devour), in reference to the aberrant quality and size of the species' teeth. The largest species, ''E. heinrichi'', has been conservatively estimated to reach greater than 6.7 m (22 ft) in length, around the size of the largest known great white shark. Like its other relatives, such as ''Helicoprion'', and unlike modern sharks, the species of ''Edestus'' grew teeth in curved blades or "whorls". In ''Edestus''' case, only a single row of teeth occurred in the midline of each jaw, leading ''Edestus'' to sometimes be described as the "scissor tooth shark". The degree of curvature in the teeth brackets, along with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithoprion
''Ornithoprion'' is an extinct genus of eugeneodont holocephalan closely related to '' Caseodus.'' It lived in the Moscovian stage of the Carboniferous The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carbonifero ... from 315.2 to 307 million years ago. Various species had an elongated lower jaw. The discovery and description of ''Ornithoprion'' helped establish many aspects of eugeneodont skull anatomy, which previously could only be gleaned from tooth data. References Carboniferous fish of North America Carboniferous cartilaginous fish Prehistoric cartilaginous fish genera {{Paleo-cartilaginous-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicoprion
''Helicoprion'' is an extinct genus of shark-like eugeneodont fish. Almost all fossil specimens are of spirally arranged clusters of the individuals' teeth, called "tooth whorls", which in life were embedded in the lower jaw. As with most extinct cartilaginous fish, the skeleton is mostly unknown. Fossils of ''Helicoprion'' are known from a 20 million year timespan during the Permian period from the Artinskian stage of the Cisuralian (Early Permian) to the Roadian stage of the Guadalupian (Middle Permian). The closest living relatives of ''Helicoprion'' (and other eugeneodonts) are the chimaeras, though their relationship is very distant. The unusual tooth arrangement is thought to have been an adaption for feeding on soft bodied prey, and may have functioned as a deshelling mechanism for hard bodied cephalopods such as nautiloids and ammonoids. In 2013, systematic revision of ''Helicoprion'' via morphometric analysis of the tooth whorls found only ''H. davisii, H. bessonowi'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous Cartilaginous Fish
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' ("coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian lineages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Cartilaginous Fish Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |