|
Cascade Point
A Cascade point is a projectile point associated with the Cascade phase, an ancient culture of Native Americans that settled in the Pacific Northwest that existed from 9000 or 10000 BC until about 5500 BC. The Cascade (Bipointed) point is typically narrow, lanceolate leaf shaped, with either a pointed or rounded base. There are also two other variants, one with a shallow concave base and the other with a sharply contracting basal margin. Cascade points are generally regarded as poor temporal markers because they are found in early, middle, and even late Holocene contexts. It is unclear whether this broad timespan is a function of prolonged use of the point form, later groups recycling discarded artifacts, or a combination of both. The spatial and temporal distribution of foliate points in the northern Great Basin and present new data derived from work at a stratified rockshelter in Oregon's Warner Valley have been reviewed. Foliate projectile points have been uncovered there tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projectile Point
In North American archaeological terminology, a projectile point is an object that was hafted to a weapon that was capable of being thrown or projected, such as a javelin, dart, or arrow. They are thus different from weapons presumed to have been kept in the hand, such as knives, spears, axes, hammers, and maces. Stone tools, including projectile points, can survive for long periods, were often lost or discarded, and are relatively plentiful, especially at archaeological sites. They provide useful clues to the human past, including prehistoric trade. A distinctive form of point, identified though lithic analysis of the way it was made, is often a key diagnostic factor in identifying an archaeological industry or culture. Scientific techniques exist to track the specific kinds of rock or minerals that were used to make stone tools in various regions back to their original sources. As well as stone, projectile points were also made of worked wood, bone, antler, horn, or ivory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Cordilleran Culture
The old Cordilleran culture, also known as the Cascade phase, is an ancient culture of Native Americans that settled in the Pacific Northwestern region of North America that existed from 9000 or 10000 BC until about 5500 BC. The Cascade phase may be even older, depending on when human beings first arrived in America. They originated in Alaska, and migrated to occupy a wide area as far as Idaho and the plateaus of California, but they are generally not considered to be a maritime society. However, their spear points, or points resembling theirs, have been found as far south as Mexico and South America.Josephy, Alvin M (August 26, 1991). ''The Indian Heritage of America''. Houghton Mifflin Books. . p. 132 This was the typical artifact of these people — a simple, bi-facial, leaf-shaped projectile point which average about in length. These tools were used as spears or darts, or also knives, indicating the importance of hunting, although they also fished and gathered for subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples. Many Indigenous peoples of the Americas were traditionally hunter-gatherers and many, especially in the Amazon basin, still are, but many groups practiced aquaculture and agriculture. While some societies depended heavily on agriculture, others practiced a mix of farming, hunting, and gathering. In some regions, the Indigenous peoples created monumental architecture, large-scale organized cities, city-states, chiefdoms, states, kingdoms, republics, confederacies, and empires. Some had varying degrees of knowledge of engineering, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, writing, physics, medicine, planting and irrigation, geology, mining, metallurgy, sculpture, and gold smithing. Many parts of the Americas are still populated by Indigenous peoples; some countries have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common conception includes the U.S. states of Oregon, Washington (state), Washington, and Idaho, and the Canadian province of British Columbia. Some broader conceptions reach north into Alaska and Yukon, south into northern California, and east into western Montana. Other conceptions may be limited to the coastal areas west of the Cascade Mountains, Cascade and Coast Mountains, Coast mountains. The variety of definitions can be attributed to partially overlapping commonalities of the region's history, culture, geography, society, ecosystems, and other factors. The Northwest Coast is the coastal region of the Pacific Northwest, and the Northwest Plateau (also commonly known as "British Columbia Interi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanceolate
The following is a list of terms which are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple (a single leaf blade or lamina) or compound (with several leaflets). The edge of the leaf may be regular or irregular, may be smooth or bearing hair, bristles or spines. For more terms describing other aspects of leaves besides their overall morphology see the leaf article. The terms listed here all are supported by technical and professional usage, but they cannot be represented as mandatory or undebatable; readers must use their judgement. Authors often use terms arbitrarily, or coin them to taste, possibly in ignorance of established terms, and it is not always clear whether because of ignorance, or personal preference, or because usages change with time or context, or because of variation between specimens, even specimens from the same plant. For example, whether to call leaves on the same tree "acuminate", "lanceolate", or "linear" could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
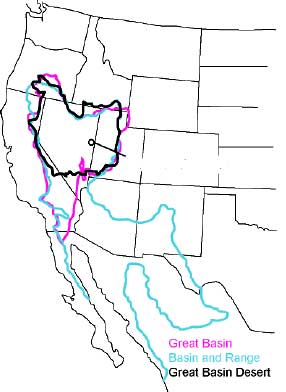
Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic basin, endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is noted for both its arid climate and the basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin in Death Valley to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than away at the summit of Mount Whitney. The region spans several physical geography, physiographic divisions, biomes, ecoregions, and deserts. Definition The term "Great Basin" is applied to hydrography, hydrographic, ecology, biological, floristic province, floristic, physiographic, topography, topographic, and Ethnography, ethnographic geographic areas. The name was originally coined by John C. Frémont, who, based on information gleaned from Joseph R. Walker as well as his own travels, recognized the hydrographic nature o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kennewick Man
Kennewick Man and Ancient One are the names generally given to the skeletal remains of a prehistoric Paleoamerican man found on a bank of the Columbia River in Kennewick, Washington, on July 28, 1996. It is one of the most complete ancient skeletons ever found. Radiocarbon tests on bone have shown it to date from 8,900 to 9,000 calibrated years before present,Preston, Douglas (September 2014)"The Kennewick Man Finally Freed to Share His Secrets" '' Smithsonian''. Retrieved November 8, 2014. but it was not until 2013 that ancient DNA analysis techniques had improved enough to shed light on the remains. The discovery led to controversy among scientists as well as Native American tribes for more than a decade. The Umatilla people and other tribes demanded that the remains be returned for reburial under the federal Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act (NAGPRA). The law was designed to return human remains and cultural objects which had long been unlawfully obtain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projectile Points
In North American archaeological terminology, a projectile point is an object that was hafted to a weapon that was capable of being thrown or projected, such as a javelin, dart, or arrow. They are thus different from weapons presumed to have been kept in the hand, such as knives, spears, axes, hammers, and maces. Stone tools, including projectile points, can survive for long periods, were often lost or discarded, and are relatively plentiful, especially at archaeological sites. They provide useful clues to the human past, including prehistoric trade. A distinctive form of point, identified though lithic analysis of the way it was made, is often a key diagnostic factor in identifying an archaeological industry or culture. Scientific techniques exist to track the specific kinds of rock or minerals that were used to make stone tools in various regions back to their original sources. As well as stone, projectile points were also made of worked wood, bone, antler, horn, or ivory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_2007.jpg)