|
Carver A. Mead
Carver Andress Mead (born May 1, 1934) is an American scientist and engineer. He currently holds the position of Gordon and Betty Moore Professor Emeritus of Engineering and Applied Science at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), having taught there for over 40 years. He taught Deborah Chung, the first female engineering graduate of Caltech. He advised the first female electrical engineering student at Caltech, Louise Kirkbride. His contributions as a teacher include the classic textbook ''Introduction to VLSI Systems'' (1980), which he coauthored with Lynn Conway. A pioneer of modern microelectronics, he has made contributions to the development and design of semiconductors, digital chips, and silicon compilers, technologies which form the foundations of modern very-large-scale integration chip design. In the 1980s, he focused on electronic modelling of human neurology and biology, creating " neuromorphic electronic systems." Mead has been involved in the found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakersfield, California
Bakersfield is a city in Kern County, California, United States. It is the county seat and largest city of Kern County. The city covers about near the southern end of the San Joaquin Valley and the Central Valley region. Bakersfield's population as of the 2020 census was 403,455, making it the 48th-most populous city in the United States of America and the 9th-most populous city in California. The Bakersfield–Delano Metropolitan Statistical Area, which includes all of Kern County, had a 2020 census population of 909,235, making it the 62nd-largest metropolitan area in the United States. The more built-up portion of the metro area that includes Bakersfield and areas immediately around the city, such as East Bakersfield, Oildale, and Rosedale, has a population of 523,994. Bakersfield is a significant hub for both agriculture and energy production. Kern County is the most productive oil-producing county in California and the fourth-most productive agricultural county (by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kernville, California
Kernville is a census-designated place (CDP) in the southern Sierra Nevada, in Kern County, California, United States. Kernville is located northeast of Bakersfield, at an elevation of . The population was 1,395 at the 2010 census, down from 1,736 at the 2000 census. History The Kern River was named after artist and topographer Edward Kern, who accompanied John C. Fremont on his 1845 expedition. They camped at what was a fork of two rivers, now the middle of Lake Isabella. An 1858 gold rush led to the formation of a town briefly called Rogersville, then Williamsburg, which was in 1863 renamed Whiskey Flat after a bar opened. In 1864, the town was renamed Kernville. After decades of planning, the Isabella Dam project began in 1948. As a result, Kernville was relocated upstream to its present location at the tip of the northeast fork of the man-made lake, along with certain historic buildings. Downtown visibly retains Kernville's gold rush and Old West roots, attracting tourist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schottky Barrier
A Schottky barrier, named after Walter H. Schottky, is a potential energy barrier for electrons formed at a metal–semiconductor junction. Schottky barriers have rectifying characteristics, suitable for use as a diode. One of the primary characteristics of a Schottky barrier is the Schottky barrier height, denoted by ΦB (see figure). The value of ΦB depends on the combination of metal and semiconductor. Not all metal–semiconductor junctions form a rectifying Schottky barrier; a metal–semiconductor junction that conducts current in both directions without rectification, perhaps due to its Schottky barrier being too low, is called an ohmic contact. Physics of formation When a metal is put in direct contact with a semiconductor, a so called Schottky barrier can be formed, leading to a rectifying behavior of the electrical contact. This happens both when the semiconductor is n-type and its work function is smaller than the work function of the metal, and when the semic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
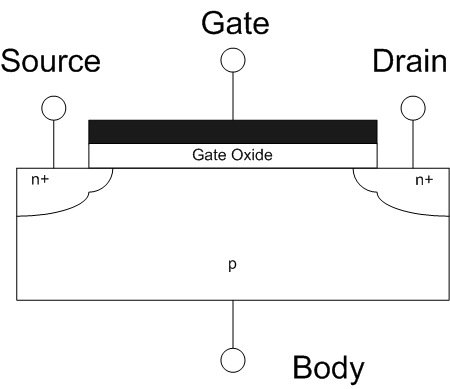
Field-effect Transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Arsenide
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a Zincblende (crystal structure), zinc blende crystal structure. Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monolithic microwave integrated circuits, infrared light-emitting diodes, laser diodes, solar cells and optical windows. GaAs is often used as a substrate material for the epitaxial growth of other III-V semiconductors, including indium gallium arsenide, aluminum gallium arsenide and others. Preparation and chemistry In the compound, gallium has a +3 oxidation state. Gallium arsenide single crystals can be prepared by three industrial processes: * The vertical gradient freeze (VGF) process. * Crystal growth using a horizontal zone furnace in the Bridgman-Stockbarger technique, in which gallium and arsenic vapors react, and free molecules deposit on a seed crystal at the cooler end of the furnace. * Liquid encapsulated Czochralski process, Czoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterojunction
A heterojunction is an interface between two layers or regions of dissimilar semiconductors. These semiconducting materials have unequal band gaps as opposed to a homojunction. It is often advantageous to engineer the electronic energy bands in many solid-state device applications, including semiconductor lasers, solar cells and transistors. The combination of multiple heterojunctions together in a device is called a heterostructure, although the two terms are commonly used interchangeably. The requirement that each material be a semiconductor with unequal band gaps is somewhat loose, especially on small length scales, where electronic properties depend on spatial properties. A more modern definition of heterojunction is the interface between any two solid-state materials, including crystalline and amorphous structures of metallic, insulating, fast ion conductor and semiconducting materials. Manufacture and applications Heterojunction manufacturing generally requires the use of mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band-gap Engineering
Band-gap engineering is the process of controlling or altering the band gap of a material. This is typically done to semiconductors by controlling the composition of alloys, constructing layered materials with alternating compositions, or by inducing strain either epitaxially or topologically. A band gap is the range in a solid where no electron state can exist. The band gap of insulators is much larger than in semiconductors. Conductors or metals have a much smaller or nonexistent band gap than semiconductors since the valence and conduction bands overlap. Controlling the band gap allows for the creation of desirable electrical properties. Molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE) Molecular-beam epitaxy is a technique used to construct thin epitaxial films of materials ranging from oxides to semiconductors to metals. Different beams of atoms and molecules in an ultra-high vacuum environment are shot onto a nearly atomically clean crystal, creating a layering effect. This is a type of thin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
III-V Compound Semiconductor
Semiconductor materials are nominally small band gap insulators. The defining property of a semiconductor material is that it can be compromised by doping it with impurities that alter its electronic properties in a controllable way. Because of their application in the computer and photovoltaic industry—in devices such as transistors, lasers, and solar cells—the search for new semiconductor materials and the improvement of existing materials is an important field of study in materials science. Most commonly used semiconductor materials are crystalline inorganic solids. These materials are classified according to the periodic table groups of their constituent atoms. Different semiconductor materials differ in their properties. Thus, in comparison with silicon, compound semiconductors have both advantages and disadvantages. For example, gallium arsenide (GaAs) has six times higher electron mobility than silicon, which allows faster operation; wider band gap, which allows op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Electron
Hot or the acronym HOT may refer to: Food and drink *Pungency, in food, a spicy or hot quality *Hot, a wine tasting descriptor Places *Hot district, a district of Chiang Mai province, Thailand **Hot subdistrict, a sub-district of Hot District, Thailand ** Tha Kham, Chiang Mai, also known as Hot, a town in Hot District, Chiang Mai province, Thailand *Hot, Albania, a village in the Malësi e Madhe municipality, Shkodër County, Albania Music * H.O.T. pronounced "H. O. T.", (High-Five of Teenagers), a South Korean boy band *Hawaii Opera Theatre, an opera company in Honolulu, Hawaii *Hot (American vocal group), best known for 1977 hit "Angel in Your Arms" 1976–1980 *Hot 97, branding for hip-hop radio station WQHT in New York City Albums * ''Hot'' (Freda Payne album), 1979 * ''Hot'' (Half Japanese album), 1995 * ''Hot'' (Inna album) or the title song (see below), 2009 * ''Hot'' (James Brown album) or the title song (see below), 1976 * ''Hot'' (Mel B album), 2000 * ''Hot'' (Paul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Tunneling
Quantum tunnelling, also known as tunneling ( US) is a quantum mechanical phenomenon whereby a wavefunction can propagate through a potential barrier. The transmission through the barrier can be finite and depends exponentially on the barrier height and barrier width. The wavefunction may disappear on one side and reappear on the other side. The wavefunction and its first derivative are continuous. In steady-state, the probability flux in the forward direction is spatially uniform. No particle or wave is lost. Tunneling occurs with barriers of thickness around 1–3 nm and smaller. Some authors also identify the mere penetration of the wavefunction into the barrier, without transmission on the other side as a tunneling effect. Quantum tunneling is not predicted by the laws of classical mechanics where surmounting a potential barrier requires sufficient kinetic energy. Quantum tunneling plays an essential role in physical phenomena such as nuclear fusion and alpha radioact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use. Electrical engineering is now divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering, systems engineering, power engineering, telecommunications, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, photovoltaic cells, electronics, and optics and photonics. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics, electromagnetics and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology, electrochemistry, renewable energies, mechatronics/control, and electrical m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communications. The term "amateur" is used to specify "a duly authorised person interested in radioelectric practice with a purely personal aim and without pecuniary interest;" (either direct monetary or other similar reward) and to differentiate it from commercial broadcasting, public safety (such as police and fire), or professional two-way radio services (such as maritime, aviation, taxis, etc.). The amateur radio service (''amateur service'' and '' amateur-satellite service'') is established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) through the Radio Regulations. National governments regulate technical and operational characteristics of transmissions and issue individual station licenses with a unique identifying call sign, which mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |