|
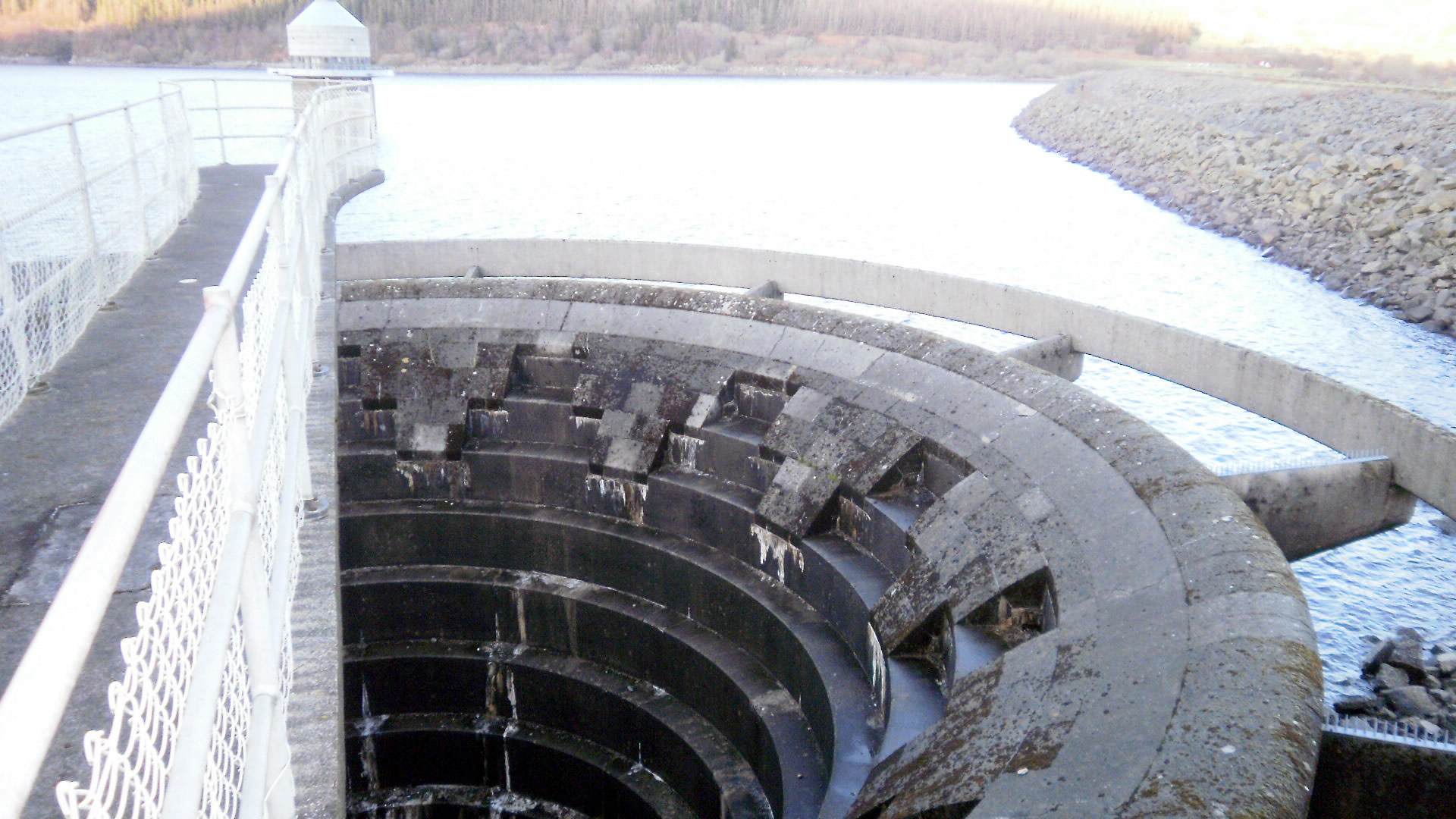
Caruachi Dam
The Caruachi Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Caroní River in Bolivar state, Venezuela. It supports a hydroelectric power facility with a capacity. It is about downstream from the Guri Dam belonging to the Central Hidroeléctrica Simón Bolívar, and about from where the Caroni and Orinoco rivers meet at Ciudad Guayana.Official site of EDELCA and the Caruachi Project , published 2007, accessed 2007-11-23 The dam The first of the -generators supplied for the project began commercial ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caroní River
The Caroní River is the second most important river of Venezuela, the second in flow, and one of the longest, from the Kukenan tepui through to its confluence with the Orinoco River. The name "Caroní" is applied starting from the confluence of the Kukenan with the Yuruaní River at from the source of the Kukenan and from its discharge in the Orinoco. The confluence takes place in Bolivar State. Hydraulic regime The Caroní is one of the rivers with the highest discharge rates in the world, with respect to the area of its basin. The average discharge is , with variations caused by the wet/dry seasons. The average maximum discharge is , and the average minimum is . Among the historic extremes are . The Caroní supplies 15.5 percent of the discharge of the Orinoco river. One of the characteristics of the Caroní's water is the dark color, caused by the high amount of humic acids due to the incomplete decomposition of the phenol content of the vegetation. The Caroní t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Infrastructure Completed In 2006
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams Completed In 2006
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees (also known as dikes) are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. The earliest known dam is the Jawa Dam in Jordan, dating to 3,000 BC. The word ''dam'' can be traced back to Middle English, and before that, from Middle Dutch, as seen in the names of many old cities, such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam. History Ancient dams Early dam building took place in Mesopotamia and the Middle East. Dams were used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Conventional Hydroelectric Power Stations
This article lists hydroelectric power stations that generate power using the conventional dammed method. This list includes power stations that are larger than in maximum net capacity, and are operational or under construction. Those power stations that are smaller than , or those that are only at a planning/proposal stage may be found in regional lists, listed at the end of the page. The largest hydroelectric power station is the Three Gorges Dam in China, rated at in total installed capacity. After passing on 7 December 2007 the mark of the Itaipu Dam, the facility was ranked as the largest power-generating facility ever built. The dam is high, long and in width. Power is generated by 32 turbines rated at , and two turbines rated , which are used to power the facility itself. Construction of this dam commenced in 1994, and was completed in 2012, nearly two decades after it started. The next six largest dams after the Three Gorges Dam are the Itaipu Dam, Xiluodu Dam, Bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spillway
A spillway is a structure used to provide the controlled release of water downstream from a dam or levee, typically into the riverbed of the dammed river itself. In the United Kingdom, they may be known as overflow channels. Spillways ensure that water does not damage parts of the structure not designed to convey water. Spillways can include floodgates and fuse plugs to regulate water flow and reservoir level. Such features enable a spillway to regulate downstream flow—by releasing water in a controlled manner before the reservoir is full, operators can prevent an unacceptably large release later. Other uses of the term "spillway" include bypasses of dams and outlets of channels used during high water, and outlet channels carved through natural dams such as moraines. Water normally flows over a spillway only during flood periods, when the reservoir has reached its capacity and water continues entering faster than it can be released. In contrast, an intake tower is a structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GE Renewable Energy
GE Renewable Energy is an American wind turbine manufacturer division of General Electric headquartered in Boulogne-Billancourt, Greater Paris, France focusing on production of energy from renewable sources. Its portfolio of products includes wind ( onshore and offshore), hydroelectric and solar ( concentrated and photovoltaic) power generating solutions. It is the world’s largest wind turbine manufacturer. History GE Renewable Energy was created in 2015, combining the wind power assets GE purchased from Alstom with those previously owned by GE and operated under the Power & Water division. Upon the division's creation, the headquarters of GE Renewable Energy moved from Schenectady, New York to Paris, France, part of conditions for the Alstom purchase. Sub-Divisions Wind GE Wind Energy was formed out of the assets of Enron Wind purchased in 2002, and subsequently expanded with the purchase of ScanWind in 2009. GE Wind Energy expanded into offshore wind energy with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
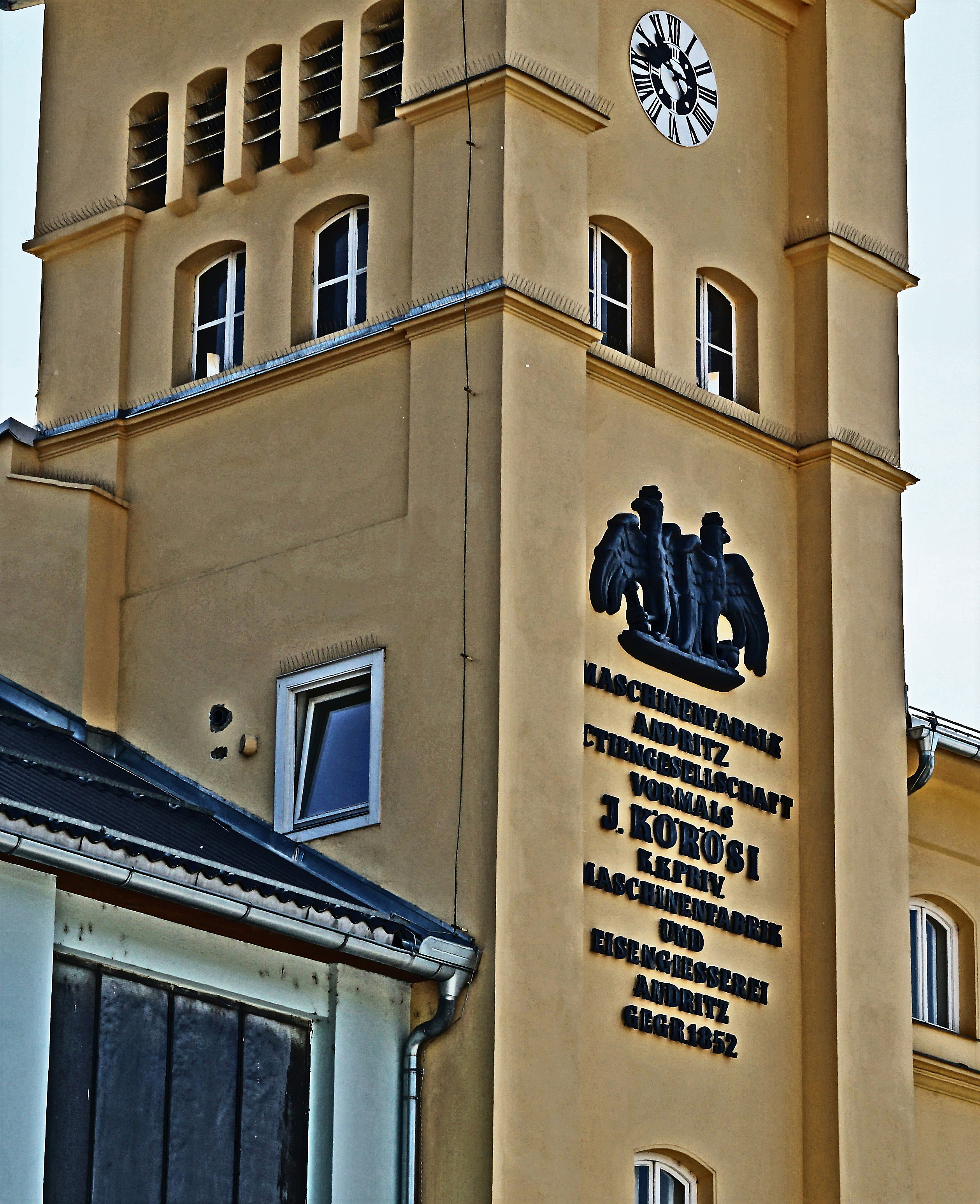
Andritz Hydro
Andritz AG is an international technology group, offering plants, equipment, systems and services for various industries. The group's headquarters are in Graz, Austria. The group gets its name from the district of Andritz in which it is located and is listed on the Vienna Stock Exchange. Andritz employs more than 27,000 employees at over 280 production and service facilities. In 2020, the company reported a revenue of EUR 6.7 billion, and a net income of EUR 203.7 million. Business areas Andritz consists of 4 main business areas: *Hydro *Pulp and Paper *Metals *Separation and the business fields Feed & Biofuel Pumps Automation Andritz Metals The business area Andritz Metals (former "Rolling Mills and Strip Processing") is the third largest business unit. Andritz Metals designs, develops and erects complete lines for the production and further processing of cold-rolled carbon steel, stainless steel and non-ferrous metal strips, including furnaces, presses and acid regeneration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uninterruptible Power Supply
An uninterruptible power supply or uninterruptible power source (UPS) is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source or mains power fails. A UPS differs from an auxiliary or emergency power system or standby generator in that it will provide near-instantaneous protection from input power interruptions, by supplying energy stored in batteries, supercapacitors, or flywheels. The on-battery run-time of most uninterruptible power sources is relatively short (only a few minutes) but sufficient to start a standby power source or properly shut down the protected equipment. It is a type of continual power system. A UPS is typically used to protect hardware such as computers, data centers, telecommunication equipment or other electrical equipment where an unexpected power disruption could cause injuries, fatalities, serious business disruption or data loss. UPS units range in size from ones designed to protect a single computer without a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alstom Power
Alstom SA is a French multinational rolling stock manufacturer operating worldwide in rail transport markets, active in the fields of passenger transportation, signalling, and locomotives, with products including the AGV, TGV, Eurostar, Avelia and New Pendolino high-speed trains, in addition to suburban, regional and metro trains, and Citadis trams. Alsthom (originally Als-Thom) was formed by a merger between Compagnie Française Thomson-Houston and the electric engineering division of Société Alsacienne de Constructions Mécaniques in 1928. Significant later acquisitions included the Constructions Electriques de France (1932), shipbuilder Chantiers de l'Atlantique (1976), and parts of ACEC (Belgium, late-1980s). A merger with parts of the General Electric Company (UK) formed GEC Alsthom in 1989. Throughout the 1990s, the company expanded its holdings in the rail sector, via the acquisition of German rolling stock manufacturer Linke-Hofmann-Busch and Italian rail signalli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmission must be taken into account. This applies especially to radio-frequency engineering because the short wavelengths mean that wave phenomena arise over very short distances (this can be as short as millimetres depending on frequency). However, the theory of transmission lines was historically developed to explain phenomena on very long telegraph lines, especially submarine telegraph cables. Transmission lines are used for purposes such as connecting radio transmitters and receivers with their antennas (they are then called feed lines or feeders), distributing cable television signals, trunklines routing calls between telephone switching centres, computer network connections and high speed computer data buses. RF engineers commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Substation
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions. Between the generating station and consumer, electric power may flow through several substations at different voltage levels. A substation may include transformers to change voltage levels between high transmission voltages and lower distribution voltages, or at the interconnection of two different transmission voltages. They are a common component of the infrastructure, for instance there are 55,000 substations in the United States. Substations may be owned and operated by an electrical utility, or may be owned by a large industrial or commercial customer. Generally substations are unattended, relying on SCADA for remote supervision and control. The word ''substation'' comes from the days before the distribution system became a grid. As central generation stations became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |