|
Carpediemonadida
''Carpediemonas'' is genus of Metamonada, and belongs to the group Excavata. This organism is a unicellular flagellated eukaryote that was first discovered in substrate samples from the Great Barrier Reef. ''Carpediemonas'' can be found in anaerobic intertidal sediment, where it feeds on bacteria. A feature of this species is the presence of a feeding groove, a characteristic of the excavates. Like most other metamonads, ''Carpediemonas'' does not rely on an aerobic mitochondrion to produce energy. Instead, it contains hydrogenosome A hydrogenosome is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in some anaerobic ciliates, flagellates, and fungi. Hydrogenosomes are highly variable organelles that have presumably evolved from protomitochondria to produce molecular hydrogen and ATP i ...s that are used to produce ATP. This organism has two flagella: a posterior one used for feeding on the substrate, and an anterior one that moves in a slower sweeping motion. ''Carpediemonas'' is assi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpediemonas Bialata
''Carpediemonas'' is genus of Metamonada, and belongs to the group Excavata. This organism is a unicellular flagellated eukaryote that was first discovered in substrate samples from the Great Barrier Reef. ''Carpediemonas'' can be found in anaerobic intertidal sediment, where it feeds on bacteria. A feature of this species is the presence of a feeding groove, a characteristic of the excavates. Like most other metamonads, ''Carpediemonas'' does not rely on an aerobic mitochondrion to produce energy. Instead, it contains hydrogenosomes that are used to produce ATP. This organism has two flagella: a posterior one used for feeding on the substrate, and an anterior one that moves in a slower sweeping motion. ''Carpediemonas'' is assigned to the fornicates, where similar ''Carpediemonas''-like organisms are used in researching the evolution within excavates. Although ''Carpediemonas'' is a member of the metamonads, it is unusual in the sense that it is free-living and has three basal b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpediemonas Frisia
''Carpediemonas'' is genus of Metamonada, and belongs to the group Excavata. This organism is a unicellular flagellated eukaryote that was first discovered in substrate samples from the Great Barrier Reef. ''Carpediemonas'' can be found in anaerobic intertidal sediment, where it feeds on bacteria. A feature of this species is the presence of a feeding groove, a characteristic of the excavates. Like most other metamonads, ''Carpediemonas'' does not rely on an aerobic mitochondrion to produce energy. Instead, it contains hydrogenosomes that are used to produce ATP. This organism has two flagella: a posterior one used for feeding on the substrate, and an anterior one that moves in a slower sweeping motion. ''Carpediemonas'' is assigned to the fornicates, where similar ''Carpediemonas''-like organisms are used in researching the evolution within excavates. Although ''Carpediemonas'' is a member of the metamonads, it is unusual in the sense that it is free-living and has three basal b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpediemonas Membranifera
''Carpediemonas'' is genus of Metamonada, and belongs to the group Excavata. This organism is a unicellular flagellated eukaryote that was first discovered in substrate samples from the Great Barrier Reef. ''Carpediemonas'' can be found in anaerobic intertidal sediment, where it feeds on bacteria. A feature of this species is the presence of a feeding groove, a characteristic of the excavates. Like most other metamonads, ''Carpediemonas'' does not rely on an aerobic mitochondrion to produce energy. Instead, it contains hydrogenosomes that are used to produce ATP. This organism has two flagella: a posterior one used for feeding on the substrate, and an anterior one that moves in a slower sweeping motion. ''Carpediemonas'' is assigned to the fornicates, where similar ''Carpediemonas''-like organisms are used in researching the evolution within excavates. Although ''Carpediemonas'' is a member of the metamonads, it is unusual in the sense that it is free-living and has three basal b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
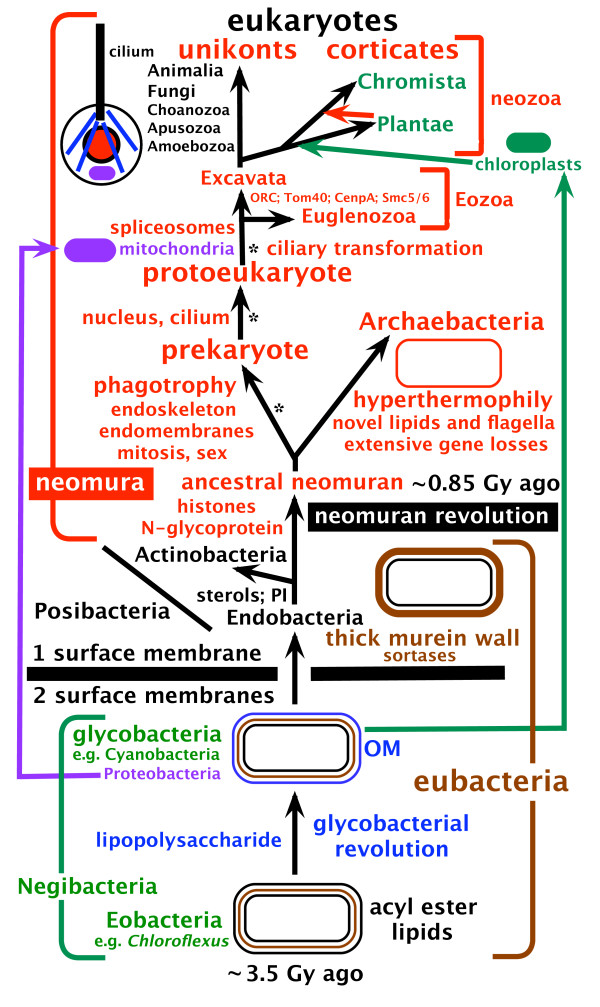
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excavata
Excavata is a major supergroup of unicellular organisms belonging to the domain Eukaryota. It was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and introduced by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002 as a formal taxon. It contains a variety of free-living and symbiotic forms, and also includes some important parasites of humans, including ''Giardia'' and ''Trichomonas''. Excavates were formerly considered to be included in the now obsolete Protista kingdom. They are classified based on their flagellar structures, and they are considered to be the most basal flagellate lineage. Phylogenomic analyses split the members of Excavata into three different and not all closely related groups: Discobids, Metamonads and Malawimonads. Except for Euglenozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic. Characteristics Most excavates are unicellular, heterotrophic flagellates. Only the Euglenozoa are photosynthetic. In some (particularly anaerobic intestinal parasites), the mitochondria have been greatly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fornicata
Trichozoa is a group of excavates. "Fornicata" is a similar grouping, but it excludes Parabasalia.Tree at "Eopharyngia" is an even more narrow grouping, including and but not Carpediemonas
''Carpediemonas'' is genus of Metamonada, ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Cavalier-Smith
Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, FRS, FRSC, NERC Professorial Fellow (21 October 1942 – 19 March 2021), was a professor of evolutionary biology in the Department of Zoology, at the University of Oxford. His research has led to discovery of a number of unicellular organisms (protists) and advocated for a variety of major taxonomic groups, such as the Chromista, Chromalveolata, Opisthokonta, Rhizaria, and Excavata. He was known for his systems of classification of all organisms. Life and career Cavalier-Smith was born on 21 October 1942 in London. His parents were Mary Maude (née Bratt) and Alan Hailes Spencer Cavalier Smith. He was educated at Norwich School, Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge (MA) and King's College London (PhD). He was under the supervision of Sir John Randall for his PhD thesis between 1964 and 1967; his thesis was entitled "''Organelle Development in'' Chlamydomonas reinhardii". From 1967 to 1969, Cavalier-Smith was a guest investigato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archiv Für Protistenkunde
''Protist'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal focusing on protists. It was founded as ''Archiv für Protistenkunde'' by editor Fritz Shaudinn in 1902, and originally published by Gustav Fischer and later Jena. The journal is now published by Elsevier, and is currently edited by Michael Melkonian (Botanical Institute, University of Cologne). The journal changed its name to ''Protist'' in 1998. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the following bibliographic databases: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 2.702. References Further reading * * External links *{{Official, https://www.elsevier.com/journals/protist Publications established in 1902 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagella
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' for example uses its multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium, where it may cause a gastric ulcer to develop. In some bacteria the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its lash-like swimming motion. The flagellum in archaea is called the archaellum to note its difference from the bacterial flagellum. Eukaryoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, Australia, separated from the coast by a channel 100 miles wide in places and over 200 feet deep. The Great Barrier Reef can be seen from outer space and is the world's biggest single structure made by living organisms. This reef structure is composed of and built by billions of tiny organisms, known as coral polyps. It supports a wide diversity of life and was selected as a World Heritage Site in 1981. CNN labelled it one of the seven natural wonders of the world in 1997. Australian World Heritage places included it in its list in 2007. The Queensland National Trust named it a state icon of Queensland in 2006. A large part of the reef is protected by the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park, which helps to limit the impact of human use, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrion
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'' was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures. One eukaryote, ''Monocercomonoides'', is known to have completely lost its mitochondria, and one multicellular organism, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |