|
Carl Von Siebold
Prof Karl (Carl) Theodor Ernst von Siebold FRS(For) HFRSE (16 February 1804 – 7 April 1885) was a German physiologist and zoologist. He was responsible for the introduction of the taxa Arthropoda and Rhizopoda, and for defining the taxon Protozoa specifically for single-celled organisms. Biography He was born at Würzburg, Bavaria, the son of Elias von Siebild (sic), a professor of obstetrics, and his wife, Sophie von Schaffer. He was educated in Würzburg and the Gymnasium zum Grauen Kloster in Berlin. Von Siebold studied medicine and science chiefly at the University of Berlin (under K. A. Rudolphi) and also at Göttingen (under Johann Friedrich Blumenbach), submitting a thesis on the metamorphosis of the salamander. In 1831 he began to practice medicine in Heilsberg, East Prussia (now Lidzbark Warmiński), moving in 1834 to Königsberg, and then in the same year to be Director of the Midwifery School in Danzig. He became professor of zoology, comparative anatomy and veter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siebold 1804-1885
Siebold or von Siebold is a Germans, German surname: * Carl Caspar von Siebold (1736–1807), surgeon * Regina von Siebold (1771–1849), obstetrician * Adam Elias von Siebold (1775–1828), medical doctor * Charlotte von Siebold (1788–1859), gynaecologist * Philipp Franz von Siebold (1796–1866), German physician, significant for his study of Japanese flora and fauna; standard author abbreviation Siebold * Eduard Caspar Jacob von Siebold (1801–1861), medical doctor * Karl Theodor Ernst von Siebold (1804–1885), German physiologist and zoologist * Alexander von Siebold (1846–1911) was a German translator and interpreter active in Japan * Heinrich von Siebold (1852–1908), German diplomat and anthropologist * Percival Siebold (1917–1983), British scouting administrator * Peter Siebold (born 1971), American commercial astronaut See also * Seabold, a surname * Sebald (other) * Sebold (other) * Seibold, a surname * Sypolt, a surname {{surname German- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benennungen der bekanntesten Städte etc., Meere, Seen, Berge und Flüsse in allen Theilen der Erde nebst einem deutsch-lateinischen Register derselben''. T. Ein Supplement zu jedem lateinischen und geographischen Wörterbuche. Dresden: G. Schönfeld’s Buchhandlung (C. A. Werner), 1861, p. 71, 237.); Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. * , )Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benennungen der bekanntesten Städte etc., Meere, Seen, Berge und Flüsse in allen Theilen der Erde nebst einem deutsch-lateinischen Register derselben''. T. Ein Supplement zu jedem lateinischen und geographischen Wörterbuche. Dresden: G. Schönf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasciola Hepatica
''Fasciola hepatica'', also known as the common liver fluke or sheep liver fluke, is a parasitic trematode (fluke or flatworm, a type of helminth) of the class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes. It infects the livers of various mammals, including humans, and is transmitted by sheep and cattle to humans the world over. The disease caused by the fluke is called fasciolosis or fascioliasis, which is a type of helminthiasis and has been classified as a neglected tropical disease. Fasciolosis is currently classified as a plant/food-borne trematode infection, often acquired through eating the parasite's metacercariae encysted on plants. ''F. hepatica'', which is distributed worldwide, has been known as an important parasite of sheep and cattle for decades and causes significant economic losses in these livestock species, up to £23 million in the UK alone. Because of its relatively large size and economic importance, it has been the subject of many scientific investigations and may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinococcus Granulosus
''Echinococcus granulosus,'' also called the hydatid worm, hyper tape-worm or dog tapeworm, is a cyclophyllid cestode that dwells in the small intestine of canids as an adult, but which has important intermediate hosts such as livestock and humans, where it causes cystic echinococcosis, also known as hydatid disease. The adult tapeworm ranges in length from 3 mm to 6 mm and has three proglottids ("segments") when intact—an immature proglottid, mature proglottid and a gravid proglottid. The average number of eggs per gravid proglottid is 823. Like all cyclophyllideans, ''E. granulosus'' has four suckers on its scolex ("head"), and ''E. granulosus'' also has a rostellum with hooks. Several strains of ''E. granulosus'' have been identified, and all but two are noted to be infective in humans. The lifecycle of ''E. granulosus'' involves dogs and wild carnivores as a definitive host for the adult tapeworm. Definitive hosts are where parasites reach maturity and reprodu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
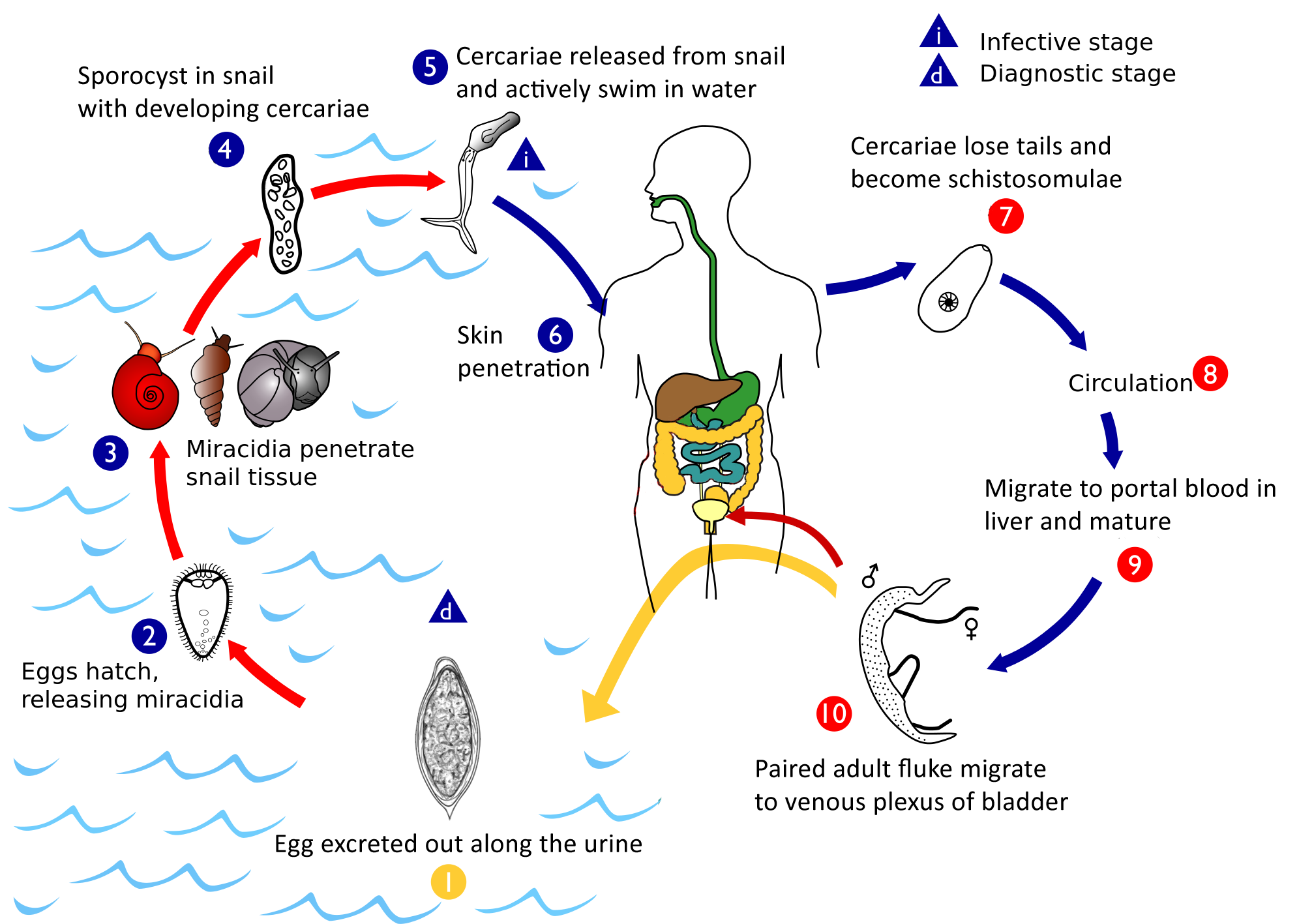
Schistosoma Haematobium
''Schistosoma haematobium'' (urinary blood fluke) is a species of digenetic trematode, belonging to a group (genus) of blood flukes (''Schistosoma''). It is found in Africa and the Middle East. It is the major agent of schistosomiasis, the most prevalent parasitic infection in humans. It is the only blood fluke that infects the urinary tract, causing urinary schistosomiasis, and is the leading cause of bladder cancer (only next to tobacco smoking). The diseases are caused by the eggs. Adults are found in the venous plexuses around the urinary bladder and the released eggs travels to the wall of the urine bladder causing haematuria and fibrosis of the bladder. The bladder becomes calcified, and there is increased pressure on ureters and kidneys otherwise known as hydronephrosis. Inflammation of the genitals due to ''S. haematobium'' may contribute to the propagation of HIV. ''S. haematobium'' was the first blood fluke discovered. Theodor Bilharz, a German surgeon working in Cair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Bilharz
Theodor Maximilian Bilharz (23 March 1825 – 9 May 1862) was a German physician who made pioneering discoveries in the field of parasitology. His contributions led to the foundation of tropical medicine. He is best remembered as the discoverer of the blood fluke '' Schistosoma haematobium'', the causative parasite of bloody urine ( haematuria) known since ancient times in Egypt. The parasite, as the cause of bladder cancer, is declared by the International Agency for Research on Cancer as Group 1 carcinogen. The infection is known by an eponymous term bilharzia or bilharziasis, as well as by schistosomiasis. Bilharz was born and educated in Sigmaringen, Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, Germany. After graduating in natural science and philosophy from the Albert-Ludwigs-Universität in 1845, he earned a medical degree from the University of Tübingen in 1849. In 1850, he followed his former teacher Wilhelm Griesinger to Egypt to work at the Qasr El Eyni Hospital in Cairo. He be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpeg/1200px-Brama_Zuraw_W_Gdansku_(153003103).jpeg)