|
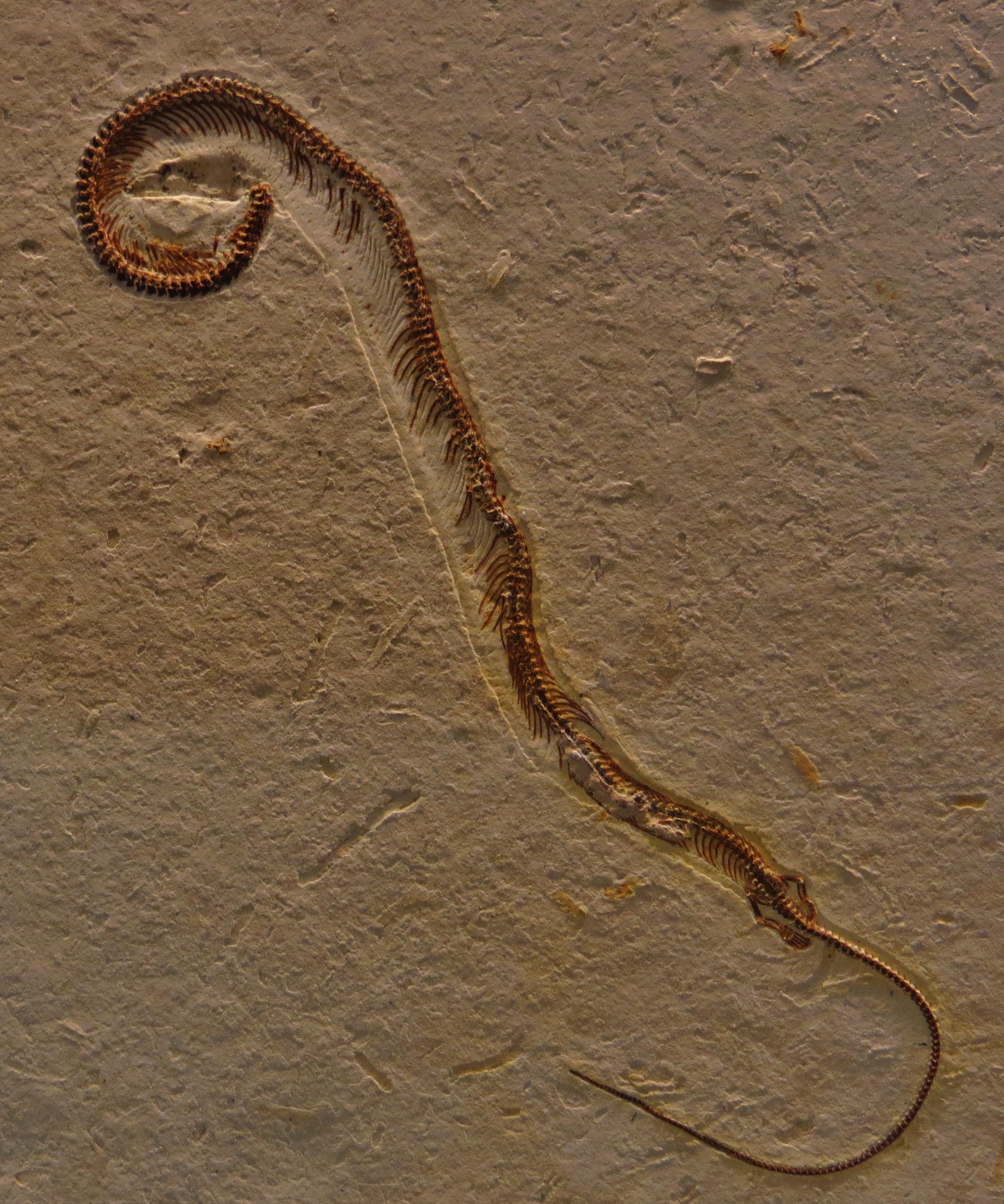
Cargninia
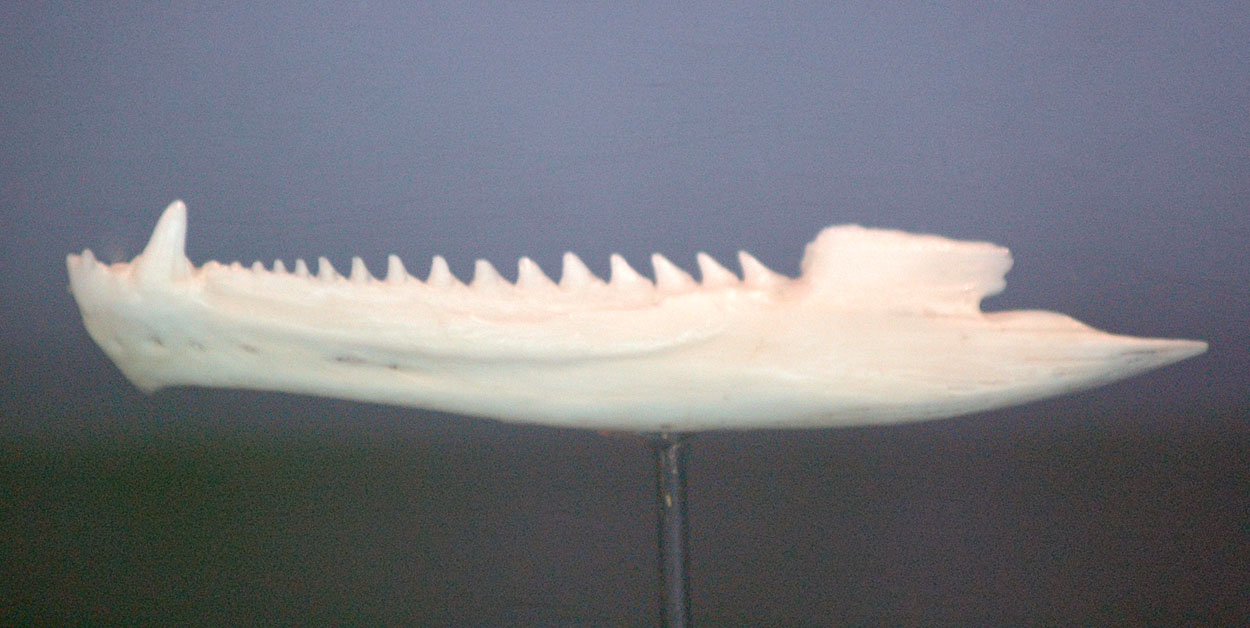
''Cargninia'' is an extinct genus of basal lepidosauromorph from the Late Triassic of Brazil. The type and only known species is ''Cargninia enigmatica''. It is known from the holotype UFRGS PV 1027 T, a partial left dentary (lower jaw bone) found in what is now Faxinal do Soturno, Rio Grande do Sul, southern Brazil, in the geopark Paleorrota. This locality is from the middle section of the Norian-age Caturrita Formation. ''Cargninia'' was named by José Fernando Bonaparte, César Leandro Schultz, Marina Bento Soares and Agustín G. Martinelli in 2010. The generic name honors Daniel Cargnin, a Brazilian priest and fossil collector, and the specific name means “enigmatic”, in reference to its uncertain phylogenetic placement. The preserved dentary has small, peg-like teeth, with the underlying jaw bone about four times deeper than the height of each tooth crown. The jaw was originally collected with eleven preserved teeth and two or three more spaces fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
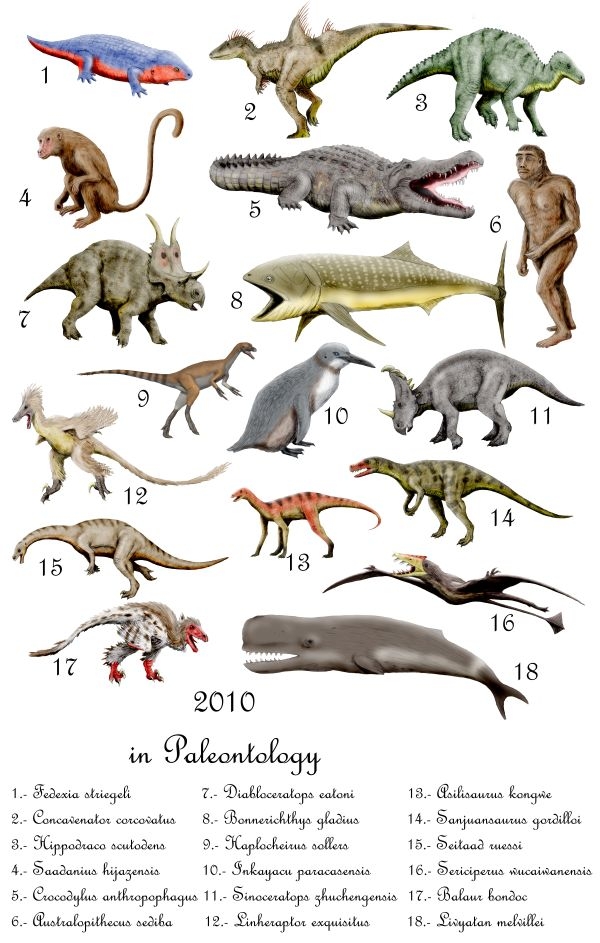
2010 In Paleontology
Plants Angiosperms Molluscs Newly named bivalves Arthropods Fishes Amphibians Newly named amphibians Basal reptiles Newly named basal reptiles Ichthyopterygians Newly named ichthyopterygians Lepidosauromorphs Newly named plesiosaurs Newly named basal lepidosaurs Newly named lizards Newly named snakes Turtles Newly named turtles Archosauromorphs Newly named basal archosauromorphs Archosaurs Synapsids Newly named non-mammalian synapsids Mammals Other animals Footnotes Complete author list As science becomes more collaborative, papers with large numbers of authors are becoming more common. To prevent the deformation of the tables, these footnotes list the contributors to papers that erect new genera and have many authors. References {{Reflist, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caturrita Formation
The Caturrita Formation is a geological formation, rock formation found in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Its sediments were deposited in the Paraná Basin. The formation is from the Upper Triassic and forms part of the Santa Maria Supersequence in the upper section of the Rosário do Sul Group. Etymology The formation received this name, because Caturrita is a neighbourhood (barrio) of Santa Maria, Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Maria. In Portuguese ''caturrita'' also refers to the monk parakeet. Stratigraphy The sediments of the Caturrita Formation belong to the second unit of the Santa Maria Supersequence and overlie the Alemoa Member of the Santa Maria Formation. The clayey sediments of the Alemoa Member gradually give way to the more sandy, rarely conglomeratic, Caturrita Formation, which finishes with an unconformity. After this erosional event follow the Rhaetian sediments of the Mata Sandstone, the third unit of the Santa Maria Supersequence. The Caturrita Formation was once re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidosauromorpha
Lepidosauromorpha (in PhyloCode known as ''Pan-Lepidosauria'') is a group of reptiles comprising all diapsids closer to lizards than to archosaurs (which include crocodiles and birds). The only living sub-group is the Lepidosauria, which contains two subdivisions, Squamata, which contains lizards and snakes, and Rhynchocephalia, the only extant species of which is the tuatara. Lepidosauromorphs are distinguishable from archosauromorphs (reptiles closer to archosaurs) by their primitive sprawling gait (allowing for the same sinusoidal trunk and tail movement seen in fish), the sliding "joint" between the coracoids and the sternum (for a longer stride), and their pleurodont dentition. In contrast, Archosauromorphs possess a parasagittal gait, a reduction in their dermal girdle, a reduction and/or loss of the sternum, and a more thecodont dentition. Living lepidosauromorphs have retained an ectothermic (" cold blooded") metabolism, unlike the ancestral condition in archosauromorphs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrodont
Acrodonty (from Greek ''akros'' 'highest' + ''dont'' 'tooth') is an anatomical placement of the teeth at the summit of the alveolar ridge of the jaw, without sockets, characteristic of bony fish. Functionally, acrodont tooth implantation may be related to strong bite force. Acrodonty in the Animal Kingdom Squamata: Within squamate reptiles, acrodont tooth implantation is best known in Acrodonta and some species of amphisbaenians, though some snakes are also referred to as being acrodont. Acrodonta is unique in that the name of the clade is based upon this trait. Most other squamate reptiles have pleurodont dentition, though some snakes are occasionally described as having acrodont dentition. Rhynchocephalia: Acrodont tooth implantation is common within Rhynchocephalia, including ''Sphenodon''. Amphibia: Acrodont tooth implantation also present in some frogs and the temnospondyl ''Microposaurus ''Microposaurus'' (meaning "small eyed lizard"; from Greek , "small" + , "face" o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Name Of A Biological Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should clearly demonstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Cargnin (paleontologist)
Daniel Cargnin (1930–2002) was a Brazilian priest and amateur paleontologist born in Nova Palma, in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, in 1930. He died in 2002, and at his request was buried in the town of Mata, Rio Grande do Sul, Mata. An autodidact and amateur paleontologist, from 1964 until 1969 he lived in the city of Santa Maria (Rio Grande do Sul), Santa Maria, where he made great contributions to paleontology, working in the geopark Paleorrota, contributing to the collection of the Museum Vincente Pallotti. In 1969, along with Abraham Cargnin, he created the Museum of Paleontology of UFRGS and the PUCRS. In 1976 he moved to the city of Mata, Rio Grande do Sul, Mata where he contributed greatly to the preservation of fossils found in the region. In his honor was created APEDAC (''Associação Padre Daniel Cargnin'') (''Association Father Daniel Cargnin''), which aims to divulge the geopark Paleorrota to a wider audience. The city of Mata received a museum named i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleurodont
Pleurodont is a form of tooth implantation common in reptiles of the order Squamata, as well as in at least one temnospondyl. The labial (cheek) side of pleurodont teeth are fused (ankylosed) to the inner surface of the jaw bones which host them. The lingual (tongue) side of pleurodont teeth are not attached to bone, and instead are typically held in place by connective ligaments. This contrasts with thecodont Thecodontia (meaning 'socket-teeth'), now considered an obsolete taxonomic grouping, was formerly used to describe a diverse "order" of early archosaurian reptiles that first appeared in the latest Permian period and flourished until the end of th ... implantation, in which the teeth are set in sockets and surrounded by bone on all sides. References External links Tooth Implantation at palaeos.comOral Cavity of Reptiles - Anatomy and Physiology Dentition types Reptile anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor. It is thus a way of defining a clade, a group consisting of a species and all its extant or extinct descendants. For example, Neornithes (birds) can be defined as a crown group, which includes the most recent common ancestor of all modern birds, and all of its extant or extinct descendants. The concept was developed by Willi Hennig, the formulator of phylogenetic systematics, as a way of classifying living organisms relative to their extinct relatives in his "Die Stammesgeschichte der Insekten", and the "crown" and "stem" group terminology was coined by R. P. S. Jefferies in 1979. Though formulated in the 1970s, the term was not commonly used until its reintroduction in 2000 by Graham Budd and Sören Jensen. Contents of the crown gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidosauria
The Lepidosauria (, from Greek meaning ''scaled lizards'') is a subclass or superorder of reptiles, containing the orders Squamata and Rhynchocephalia. Squamata includes snakes, lizards, and amphisbaenians. Squamata contains over 9,000 species, making it by far the most species-rich and diverse order of reptiles in the present day. Rhynchocephalia was a formerly widespread and diverse group of reptiles in the Mesozoic Era. However, it is represented by only one living species: the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus),'' a superficially lizard-like reptile native to New Zealand. Lepidosauria is a monophyletic group (i.e. a clade), containing all descendants of the last common ancestor of squamates and rhynchocephalians. Lepidosaurs can be distinguished from other reptiles via several traits, such as large keratinous scales which may overlap one another. Purely in the context of modern taxa, Lepidosauria can be considered the sister taxon to Archosauria, which includes Aves (birds) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marina Bento Soares
A marina (from Spanish , Portuguese and Italian : ''marina'', "coast" or "shore") is a dock or basin with moorings and supplies for yachts and small boats. A marina differs from a port in that a marina does not handle large passenger ships or cargo from freighters. The word ''marina'' may also refer to an inland wharf on a river or canal that is used exclusively by non-industrial pleasure craft such as canal narrowboats. Emplacement Marinas may be located along the banks of rivers connecting to lakes or seas and may be inland. They are also located on coastal harbors (natural or man made) or coastal lagoons, either as stand alone facilities or within a port complex. History In the 19th century, the few existing pleasure craft shared the same facilities as trading and fishing vessels. The marina appeared in the 20th century with the popularization of yachting. Facilities and services A marina may have refuelling, washing and repair facilities, marine and boat chandle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |