|
Cardiovascular Examination
The cardiovascular examination is a portion of the physical examination that involves evaluation of the cardiovascular system. The exact contents of the examination will vary depending on the presenting complaint but a complete examination will involve the heart (cardiac examination), lungs ( pulmonary examination), belly (abdominal examination) and the blood vessels (peripheral vascular examination). The cardiac examination is based on the different methods of evaluation, comprising the following sections: measurement of vital signs; inspection and palpation, percussion and auscultation, pulmonary examination, abdominal examination and peripheral vascular examination. The evaluation of a real patient will require switching between the different methods and even different organs to save time and keep the patient comfortable: for example, listening to the heart and the lungs of a young child before they get bored. The only materials needed are a sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record. Types Routine The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, physician assistant, a certified nurse pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
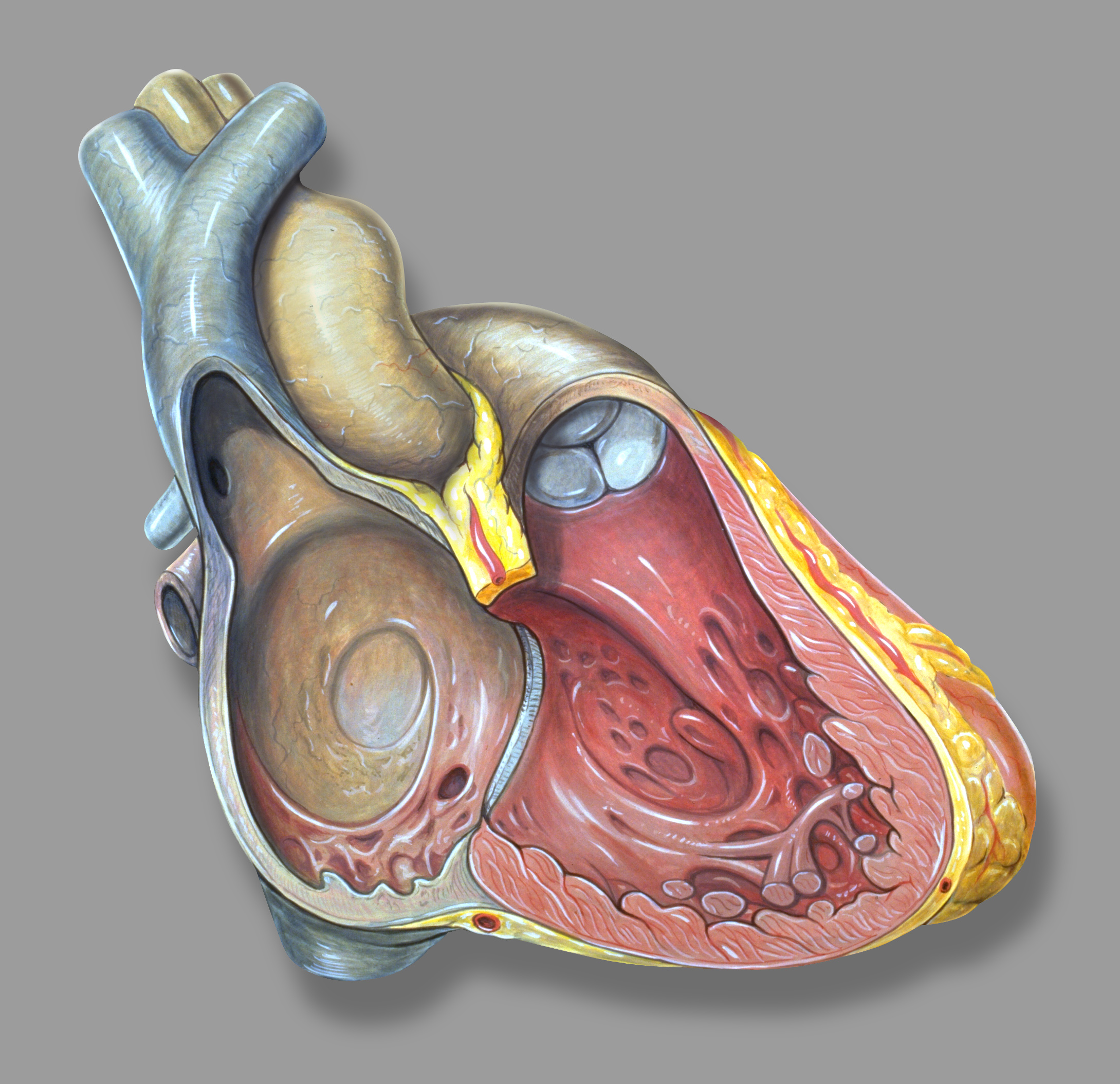
Atrium (heart)
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do. Structure Humans have a four-chambered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulatory System
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek ''kardia'' meaning ''heart'', and from Latin ''vascula'' meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with the ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The Closed circulatory system, circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Some in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
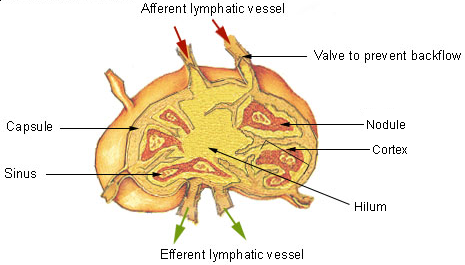
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the Latin word ''lympha'' refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha") back towards the heart, for re-circulation. Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres. The other main function is that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's Tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area may feel heavy, and joint stiffness. Other symptoms depend on the underlying cause. Causes may include Chronic venous insufficiency, venous insufficiency, heart failure, kidney problems, hypoalbuminemia, low protein levels, liver problems, deep vein thrombosis, infections, angioedema, certain medications, and lymphedema. It may also occur after prolonged sitting or standing and during menstruation or pregnancy. The condition is more concerning if it starts suddenly, or pain or shortness of breath is present. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. If the underlying mechanism involves Hypernatremia, sodium retention, decreased salt intake and a diuretic may be used. Elevating the legs and support stockings may be useful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popliteal Artery
The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior tibial artery, anterior and Posterior tibial artery, posterior tibial arteries. The deepest (most anterior) structure in the fossa, the popliteal artery runs close to the joint capsule of the knee as it spans the Intercondylar fossa of femur, intercondylar fossa. Five genicular branches of the popliteal artery supply the capsule and ligaments of the knee joint. The genicular arteries are the superior lateral, superior medial, middle, inferior lateral, and inferior medial genicular arteries. They participate in the formation of the periarticular genicular anastomosis, a network of vessels surrounding the knee that provides collateral circulation capable of maintaining blood supply to the leg during full knee flexion, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruit
Bruit, also called vascular murmur, is the abnormal sound generated by turbulent flow of blood in an artery due to either an area of partial obstruction or a localized high rate of blood flow through an unobstructed artery. The bruit may be heard (" auscultated") by securely placing the head of a stethoscope to the skin over the turbulent flow, and listening. Most bruits occur only in systole, so the bruit is intermittent and its frequency dependent on the heart rate. Anything increasing the blood flow velocity such as fever, anemia, hyperthyroidism, or physical exertion, can increase the amplitude of the bruit. Etymology It is naturalized from the French word for "noise", although another notes that and are also common, and others give only for the cardiac sense. Associated terms Describing location of a partial obstruction * Peripheral vascular disease; femoral artery stenosis * Renal artery stenosis * Stroke, carotid artery stenosis * Aortic aneurysm * Tinnitus – a sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation. Structure Sections In anatomical sources, the aorta is usually divided into sections. One way of classifying a part of the aorta is by anatomical compartment, where the thoracic aorta (or thoracic portion of the aorta) runs from the heart to the diaphragm. The aorta then continues downward as the abdominal aorta (or abdominal portion of the aorta) from the diaphragm to the aortic bifurcation. Another system divides the aorta with respect to its course and the direction of blood flow. In this system, the aorta starts as the ascending aorta, travels superiorly from the heart, and then makes a hairpin turn known as the aortic arch. Following the aortic arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Cavity
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contains many organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle under the lungs, and its floor is the pelvic inlet, opening into the pelvis. Structure Organs Organs of the abdominal cavity include the stomach, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, small intestine, kidneys, large intestine, and adrenal glands. Peritoneum The abdominal cavity is lined with a protective membrane termed the peritoneum. The inside wall is covered by the parietal peritoneum. The kidneys are located behind the peritoneum, in the retroperitoneum, outside the abdominal cavity. The viscera are also covered by visceral peritoneum. Between the visceral and parietal peritoneum is the peritoneal cavity, which is a potential space. It contains a serous fluid called peritoneal fluid tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Location Of Heart Sounds For Auscultation
In geography, location or place are used to denote a region (point, line, or area) on Earth's surface or elsewhere. The term ''location'' generally implies a higher degree of certainty than ''place'', the latter often indicating an entity with an ambiguous boundary, relying more on human or social attributes of place identity and sense of place than on geometry. Types Locality A locality, settlement, or populated place is likely to have a well-defined name but a boundary that is not well defined varies by context. London, for instance, has a legal boundary, but this is unlikely to completely match with general usage. An area within a town, such as Covent Garden in London, also almost always has some ambiguity as to its extent. In geography, location is considered to be more precise than "place". Relative location A relative location, or situation, is described as a displacement from another site. An example is "3 miles northwest of Seattle". Absolute location An absolute locatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) is a condition defined by an abnormal enlargement of the cardiac muscle surrounding the right ventricle. The right ventricle is one of the four chambers of the heart. It is located towards the lower-end of the heart and it receives blood from the right atrium and pumps blood into the lungs. Since RVH is an enlargement of muscle it arises when the muscle is required to work harder. Therefore, the main causes of RVH are pathologies of systems related to the right ventricle such as the pulmonary artery, the tricuspid valve or the airways. RVH can be benign and have little impact on day-to-day life or it can lead to conditions such as heart failure, which has a poor prognosis. Signs and symptoms Symptoms Although presentations vary, individuals with right ventricular hypertrophy can experience symptoms that are associated with pulmonary hypertension, heart failure and/or a reduced cardiac output. These include: * Difficulty breathing on exertio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Lateral Decubitus Position
Lyingalso called recumbency, prostration, or decubitus in medicine ()is a type of human position in which the body is more or less horizontal and supported along its length by the surface underneath. Lying is the most common position while being immobilized (e.g. in bedrest), while sleeping, or while being struck by injury or disease. Positions When lying, the body may assume a great variety of shapes and positions. The following are the basic recognized ones. * Supine: lying on the back on the ground with the face up. * Prone: lying on the chest with the face down ("lying down" or "going prone"). See also "Prostration". * Lying on either side, with the body straight or bent/curled forward or backward. ** The fetal position is lying or sitting curled, with limbs close to the torso and the head close to the knees. ** The recovery position (coma position), one of a series of variations on a lateral recumbent or three-quarters prone position of the body, into which an uncon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |