|
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of diseases that affect the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. An irregular heart beat and fainting may occur. Those affected are at an increased risk of sudden cardiac death. Types of cardiomyopathy include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (broken heart syndrome). In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy the heart muscle enlarges and thickens. In dilated cardiomyopathy the ventricles enlarge and weaken. In restrictive cardiomyopathy the ventricle stiffens. In many cases, the cause cannot be determined. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is usually inherited, whereas dilated cardiomyopathy is inherited in about one third of cases. Dilated cardiomyopathy may also result from alcohol, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM, or HOCM when obstructive) is a condition in which the heart becomes thickened without an obvious cause. The parts of the heart most commonly affected are the interventricular septum and the ventricles. This results in the heart being less able to pump blood effectively and also may cause electrical conduction problems. People who have HCM may have a range of symptoms. People may be asymptomatic, or may have fatigue, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Symptoms may be worse when the person is dehydrated. Complications may include heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, and sudden cardiac death. HCM is most commonly inherited from a person's parents in an autosomal dominant pattern. It is often due to mutations in certain genes involved with making heart muscle proteins. Other inherited causes of left ventricular hypertrophy may include Fabry disease, Friedreich's ataxia, and certain me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM, or HOCM when obstructive) is a condition in which the heart becomes thickened without an obvious cause. The parts of the heart most commonly affected are the interventricular septum and the ventricles. This results in the heart being less able to pump blood effectively and also may cause electrical conduction problems. People who have HCM may have a range of symptoms. People may be asymptomatic, or may have fatigue, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Symptoms may be worse when the person is dehydrated. Complications may include heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, and sudden cardiac death. HCM is most commonly inherited from a person's parents in an autosomal dominant pattern. It is often due to mutations in certain genes involved with making heart muscle proteins. Other inherited causes of left ventricular hypertrophy may include Fabry disease, Friedreich's ataxia, and certain me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
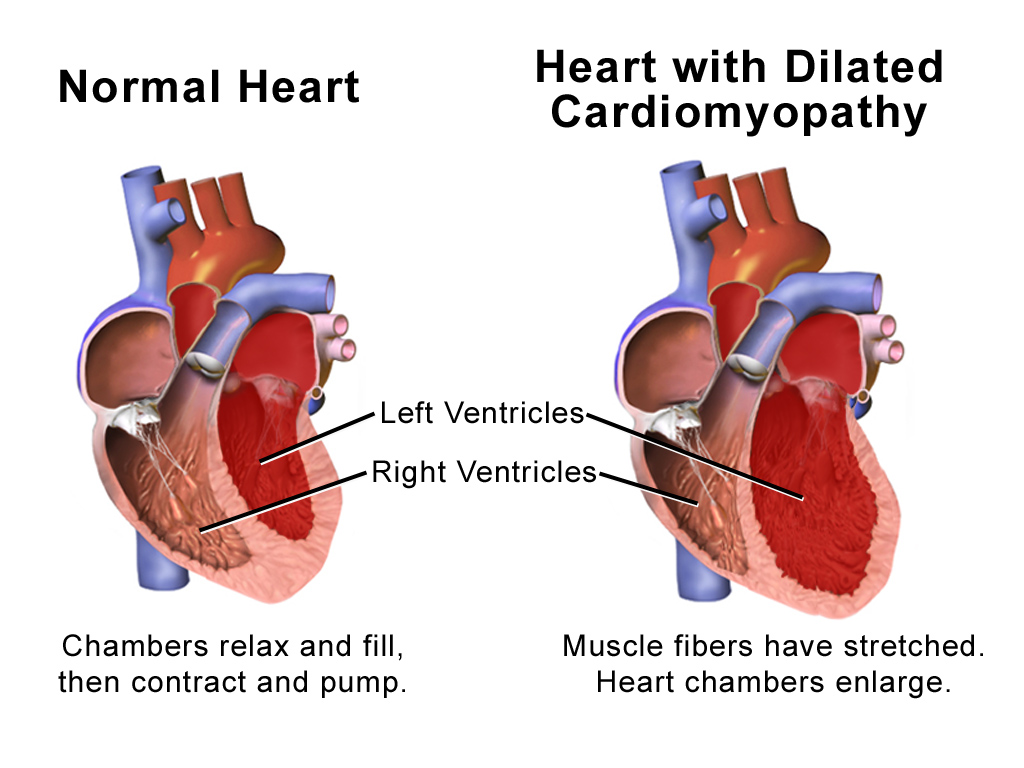
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Complications can include heart failure, heart valve disease, or an irregular heartbeat. Causes include genetics, alcohol, cocaine, certain toxins, complications of pregnancy, and certain infections. Coronary artery disease and high blood pressure may play a role, but are not the primary cause. In many cases the cause remains unclear. It is a type of cardiomyopathy, a group of diseases that primarily affects the heart muscle. The diagnosis may be supported by an electrocardiogram, chest X-ray, or echocardiogram. In those with heart failure, treatment may include medications in the ACE inhibitor, beta blocker, and diuretic families. A low salt diet may also be helpful. In those with certain types of irregular heartbeat, blood thinners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Complications can include heart failure, heart valve disease, or an irregular heartbeat. Causes include genetics, alcohol, cocaine, certain toxins, complications of pregnancy, and certain infections. Coronary artery disease and high blood pressure may play a role, but are not the primary cause. In many cases the cause remains unclear. It is a type of cardiomyopathy, a group of diseases that primarily affects the heart muscle. The diagnosis may be supported by an electrocardiogram, chest X-ray, or echocardiogram. In those with heart failure, treatment may include medications in the ACE inhibitor, beta blocker, and diuretic families. A low salt diet may also be helpful. In those with certain types of irregular heartbeat, blood thinners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM), arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD), or arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), most commonly is an inherited heart disease. ACM is caused by genetic defects of the parts of heart muscle (also called ''myocardium'' or ''cardiac muscle'') known as desmosomes, areas on the surface of heart muscle cells which link the cells together. The desmosomes are composed of several proteins, and many of those proteins can have harmful mutations. ARVC can also develop in intense endurance athletes in the absence of desmosomal abnormalities. Exercise-induced ARVC cause possibly is a result of excessive right ventricular wall stress during high intensity exercise. The disease is a type of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy that primarily involves the right ventricle, though cases of exclusive left ventricular disease have been reported. It is characterized by hypokinetic areas involving the free wall of the ventricle, with fibrofatt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM), arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD), or arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), most commonly is an inherited heart disease. ACM is caused by genetic defects of the parts of heart muscle (also called ''myocardium'' or ''cardiac muscle'') known as desmosomes, areas on the surface of heart muscle cells which link the cells together. The desmosomes are composed of several proteins, and many of those proteins can have harmful mutations. ARVC can also develop in intense endurance athletes in the absence of desmosomal abnormalities. Exercise-induced ARVC cause possibly is a result of excessive right ventricular wall stress during high intensity exercise. The disease is a type of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy that primarily involves the right ventricle, though cases of exclusive left ventricular disease have been reported. It is characterized by hypokinetic areas involving the free wall of the ventricle, with fibrofatt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
Restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) is a form of cardiomyopathy in which the walls of the heart are rigid (but not thickened). Thus the heart is restricted from stretching and filling with blood properly. It is the least common of the three original subtypes of cardiomyopathy: hypertrophic, dilated, and restrictive. It should not be confused with constrictive pericarditis, a disease which presents similarly but is very different in treatment and prognosis. Signs and symptoms Untreated hearts with RCM often develop the following characteristics: * M or W configuration in an invasive hemodynamic pressure tracing of the RA * Square root sign of part of the invasive hemodynamic pressure tracing Of The LV * Biatrial enlargement * Thickened LV walls (with normal chamber size) * Thickened RV free wall (with normal chamber size) * Elevated right atrial pressure (>12mmHg), * Moderate pulmonary hypertension, * Normal systolic function, * Poor diastolic function, typically Grade III - IV Dias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
Restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) is a form of cardiomyopathy in which the walls of the heart are rigid (but not thickened). Thus the heart is restricted from stretching and filling with blood properly. It is the least common of the three original subtypes of cardiomyopathy: hypertrophic, dilated, and restrictive. It should not be confused with constrictive pericarditis, a disease which presents similarly but is very different in treatment and prognosis. Signs and symptoms Untreated hearts with RCM often develop the following characteristics: * M or W configuration in an invasive hemodynamic pressure tracing of the RA * Square root sign of part of the invasive hemodynamic pressure tracing Of The LV * Biatrial enlargement * Thickened LV walls (with normal chamber size) * Thickened RV free wall (with normal chamber size) * Elevated right atrial pressure (>12mmHg), * Moderate pulmonary hypertension, * Normal systolic function, * Poor diastolic function, typically Grade III - IV Dias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy or Takotsubo syndrome (TTS), also known as stress cardiomyopathy, is a type of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy in which there is a sudden temporary weakening of the muscular portion of the heart. It usually appears after a significant stressor, either physical or emotional; when caused by the latter, the condition is sometimes called broken heart syndrome. Examples of physical stressors that can cause TTS are sepsis, shock, and pheochromocytoma, and emotional stressors include bereavement, divorce, or the loss of a job. Reviews suggest that of patients diagnosed with the condition, about 70–80% recently experienced a major stressor, including 41–50% with a physical stressor and 26–30% with an emotional stressor. TTS can also appear in patients who have not experienced major stressors. The pathophysiology is not well understood, but a sudden massive surge of catecholamines such as adrenaline and norepinephrine from extreme stress or a tumor secreting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Muscle
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell's m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by alterin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by alterin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)