|
Carbotubulus
''Carbotubulus'' is a genus of extinct worm belonging to the group Lobopodia and known from the Carboniferous Carbondale Formation of the Mazon Creek area in Illinois, US. A monotypic genus, it contains one species ''Carbotubulus waloszeki''. It was discovered and described by Joachim T. Haug, Georg Mayer, Carolin Haug, and Derek E.G. Briggs in 2012. With an age of about 300 million years, it is the first long-legged lobopodian discovered after the period of Cambrian explosion. Discovery and naming ''Carbotubulus'', represented by a single fossil, was discovered by Joachim T. Haug (University of Greifswald, Germany), Georg Mayer (Leipzig University), Carolin Haug (Yale University, US), and Derek E.G. Briggs (Yale University) from the Carbondale Formation ( Francis Creek Shale Member) of the Mazon Creek area in Illinois, US. It was recovered from the location named Pit 11 along with a fossil of an extinct velvet worm '' Helenodora inopinata'' (also mentioned as ''Ilyodes inopina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallucigeniidae
Hallucigeniidae is a family of extinct worms belonging to the group Lobopodia that originated during the Cambrian explosion. It is based on the species ''Hallucigenia sparsa'', the fossil of which was discovered by Charles Doolittle Walcott in 1911 from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia. The name ''Hallucigenia'' was created by Simon Conway Morris in 1977, from which the family was erected after discoveries of other hallucigeniid worms from other parts of the world. Classification of these lobopods and their relatives are still controversial, and the family consists of at least four genera. History of discovery The first fossil of hallucigeniid worm was discovered by an American palaeontologist Charles Doolittle Walcott from the Walcott Quarry that contains the Cambrian Burgess Shale. In 1911, Walcott gave the name ''Canadia sparsa'' as he believed that it was related to the polychaete worm (Annelida) '' Canadia spinosa'', which he described simultaneously. British palaeont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
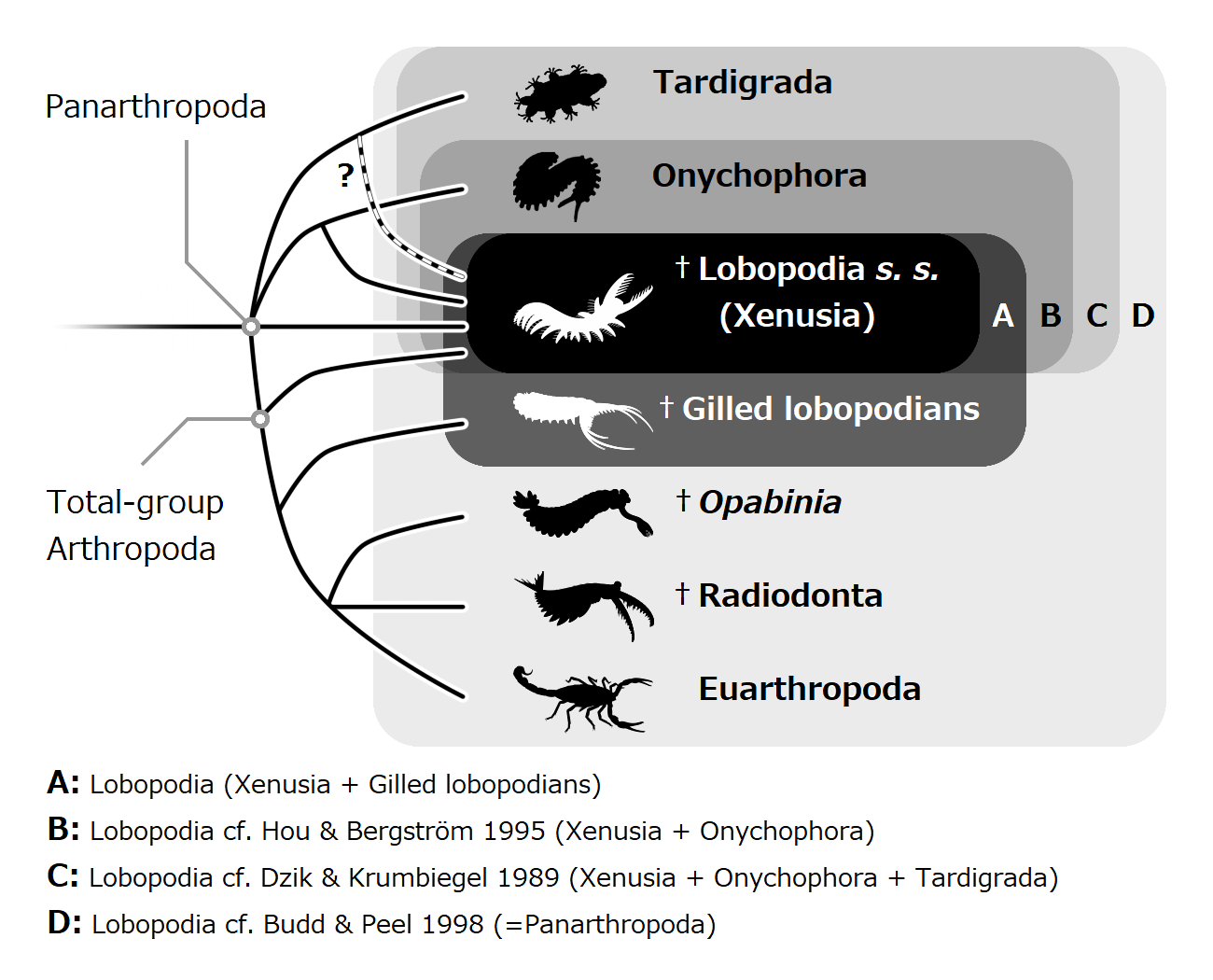
Lobopods
The lobopodians, members of the informal group Lobopodia (from the Greek, meaning "blunt feet"), or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998), are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, worm-like fossil panarthropods such as ''Aysheaia'' and ''Hallucigenia''. The oldest near-complete fossil lobopodians date to the Lower Cambrian; some are also known from Ordovician, Silurian and Carboniferous Lagerstätten. Some bear toughened claws, plates or spines, which are commonly preserved as carbonaceous or mineralized microfossils in Cambrian strata. The grouping is considered to be paraphyletic, as the three living panarthropod groups (Arthropoda, Tardigrada and Onychophora) are thought to have evolved from lobopodian ancestors. Definitions The Lobopodian concept varies from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thanahita Distos
''Thanahita'' is a genus of extinct lobopodian and known from the middle Silurian Herefordshire Lagerstätte at the England–Wales border in UK. It is monotypic and contains one species, ''Thanahita distos.'' Discovered in 2018, it is estimated to have lived around 430 million years ago and is the only known extinct lobopodian in Europe, and the first Silurian lobopodian known worldwide. Discovery ''Thanahita'' was discovered in 2018 during a palaeontological expedition funded by the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) and the Leverhulme Trust. The team of researchers comprised Derek J. Siveter (University of Oxford), Derek E. G. Briggs (Yale University), David J. Siveter (University of Leicester), Mark D. Sutton (Imperial College London) and David Legg (University of Manchester). The fossil was discovered from the Herefordshire Lagerstätte, which has been known to be a rich source of fossils of diverse animals. The only fossil of ''Thanahita'' (designated OUMNH C.29 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobopodia
The lobopodians, members of the informal group Lobopodia (from the Greek language, Greek, meaning "blunt feet"), or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998), are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, worm-like fossil panarthropods such as ''Aysheaia'' and ''Hallucigenia''. The oldest near-complete fossil lobopodians date to the Lower Cambrian; some are also known from Ordovician, Silurian and Carboniferous Lagerstätten. Some bear toughened claws, plates or spines, which are commonly preserved as small carbonaceous fossil, carbonaceous or Small Shelly Fossils, mineralized microfossils in Cambrian strata. The grouping is considered to be paraphyletic, as the three living panarthropod groups (Arthropoda, Tardigrada and Onychophora) are thought to have evolved from lobopodian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Taxon
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallucigenia
''Hallucigenia'' is a genus of Cambrian animal resembling worms, known from articulated fossils in Burgess Shale-type deposits in Canada and China, and from isolated spines around the world. The generic name reflects the type species' unusual appearance and eccentric history of study; when it was erected as a genus, ''H. sparsa'' was reconstructed as an enigmatic animal upside down and back to front. ''Hallucigenia'' was later recognized as a lobopodian, a grade of Paleozoic panarthropods from which the velvet worms, water bears, and arthropods arose. Description ''Hallucigenia'' is a long tubular animal with up to ten pairs of slender legs (lobopods). The first 2 or 3 leg pairs are slender and featureless, while the remaining 7 or 8 pairs each terminate with 1 or 2 claws. Above the trunk region are 7 pairs of rigid conical sclerites (spines) corresponding to the 3rd–9th leg pairs. The trunk is either featureless (''H. sparsa'') or divided by heteronomous annulations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 2012
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England–Wales Border
The England–Wales border ( cy, Y ffin rhwng Cymru a Lloegr; shortened: Ffin Cymru a Lloegr), sometimes referred to as the Wales–England border or the Anglo-Welsh border, runs for from the Dee estuary, in the north, to the Severn estuary in the south, separating England and Wales. It has followed broadly the same line since the 8th century, and in part that of Offa's Dyke; the modern boundary was fixed in 1536, when the former marcher lordships which occupied the border area were abolished and new county boundaries were created. The administrative boundary of Wales was confirmed in the Local Government Act 1972. Whether Monmouthshire was part of Wales, or an English county treated for most purposes as though it were Welsh, was also settled by the 1972 Act, which included it in Wales. Geography The modern boundary between Wales and England runs from the salt marshes of the Dee estuary adjoining the Wirral Peninsula, across reclaimed land to the River Dee at Saltney ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herefordshire Lagerstätte
Coalbrookdale Formation, earlier known as Wenlock Shale or Wenlock Shale Formation and also referred to as Herefordshire Lagerstätte in palaeontology, is a fossil-rich deposit ('' Konservat-Lagerstätte'') in Powys and Herefordshire at the England–Wales border in UK. It belongs to the Wenlock Series of the Silurian Period within the Homerian Age (about 430 million years ago). It is known for its well-preserved fossils of various invertebrate animals many of which are in their three-dimensional structures. Some of the fossils are regarded as earliest evidences and evolutionary origin of some of the major groups of modern animals. Roderick Murchison first described the geological setting of Coalbrookdale Formation by which he gave the name Silurian in 1935, referring to the Silures, a Celtic tribe of Wales. It is assigned to the Wenlock Group in 1978 based on the age of crustacean fossils found around the region. Robert J. King of the University of Leicester discovered the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbondale Formation
The Carbondale Formation is a geologic formation in Indiana. It preserves fossils dating back to the Carboniferous period. See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Indiana This article contains a list of fossil-bearing stratigraphic units in the state of Indiana, Indiana, U.S. Sites See also * Paleontology in Indiana References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Indiana Fossiliferous ... References * Carboniferous Indiana Carboniferous Illinois Carboniferous southern paleotropical deposits {{Indiana-geologic-formation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods (myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) became fully terrestrialized. A significant evolutionary milestone during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiodictyon Catenulum
''Cardiodictyon'' is a genus of lobopodian known from 518 millions years old Chengjiang Lagerstätte. 525 millions years old partial fossil is also reported. It has ~25 pairs of legs, each associated with a pair of dorsal plates. Each leg terminates in a pair of claws. It may or may not have a head shield, though it certainly has an expanded head. In 2022, a 518 million years old specimen of ''C. catenulum'' was researched and shown an unsegmented head and a brain composed of three separate cephalic A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals may ... parts. However, although "three parts" in this study means prosocerebrum, protocerebrum and deutocerebrum, it is different from earlier studies that referred protocerebrum, deutocerebrum and tritocerebrum as tripartite brain of ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |