|
Captain R. T. Claridge
Captain Richard Tappin Claridge, FSA (c. 1797/1799 – 5 August 1857), was a prominent asphalt contractor and captain in the Middlesex UK Militia, who became best known for his prominent promotion of hydropathy, now known as hydrotherapy, in the 1840s. It was also known as the ''Cold Water system'' or ''Cold Water cure''. Claridge is widely credited with introducing the methods of Vincent Priessnitz to England, thus initiating the populist movement of the time. Indeed, much of what is popularly known about Priessnitz in the English-speaking world comes from two seminal publications. Firstly, Claridge's ''Hydropathy; or The Cold Water Cure, as practised by Vincent Priessnitz...'' (1842 & 1843). Secondly, Richard Metcalfe's ''Life of Vincent Priessnitz'' (1898), with Metcalfe himself drawing upon Claridge, although Metcalfe also later wrote a historical overview and added more about Claridge and his role in the promotion of hydropathy. Biographical synopsis Richard Tappin Clarid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow Of The Society Of Antiquaries
A fellow is a concept whose exact meaning depends on context. In learned or professional societies, it refers to a privileged member who is specially elected in recognition of their work and achievements. Within the context of higher educational institutions, a fellow can be a member of a highly ranked group of teachers at a particular college or university or a member of the governing body in some universities (such as the Fellows of Harvard College); it can also be a specially selected postgraduate student who has been appointed to a post (called a fellowship) granting a stipend, research facilities and other privileges for a fixed period (usually one year or more) in order to undertake some advanced study or research, often in return for teaching services. In the context of research and development-intensive large companies or corporations, the title "fellow" is sometimes given to a small number of senior scientists and engineers. In the context of medical education in No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The National Archives
National archives are central archives maintained by countries. This article contains a list of national archives. Among its more important tasks are to ensure the accessibility and preservation of the information produced by governments, both analogically and digitally, for the government itself, researchers and generations to come. Some national archives collections are large, holding millions of items spanning several centuries, while others created recently have modest collections. In the last decade, digitization projects have made possible to browse records and contents online, although no archive have their entire collections published on the web. A B C D * Danish National Archives * Archivo General de la Nación de República Dominicana E * National Archives of Ecuador * Egyptian National Library and Archives * National Archives of Estonia * Eswatini National Archives * National Archives and Library of Ethiopia F * Jane Cameron National Archives (Falkla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the West Midlands metropolitan county, and approximately 4.3 million in the wider metropolitan area. It is the largest UK metropolitan area outside of London. Birmingham is known as the second city of the United Kingdom. Located in the West Midlands region of England, approximately from London, Birmingham is considered to be the social, cultural, financial and commercial centre of the Midlands. Distinctively, Birmingham only has small rivers flowing through it, mainly the River Tame and its tributaries River Rea and River Cole – one of the closest main rivers is the Severn, approximately west of the city centre. Historically a market town in Warwickshire in the medieval period, Birmingham grew during the 18th century during the Midla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beckenham
Beckenham () is a town in Greater London, England, within the London Borough of Bromley, in Greater London. Until 1965 it was part of the historic county of Kent. It is located south-east of Charing Cross, situated north of Elmers End and Eden Park, east of Penge, south of Lower Sydenham and Bellingham, and west of Bromley and Shortlands. Its population at the 2011 census counted 46,844 inhabitants. Beckenham was, until the coming of the railway in 1857, a small village, with most of its land being rural and private parkland. John Barwell Cator and his family began the leasing and selling of land for the building of villas which led to a rapid increase in population, between 1850 and 1900, from 2,000 to 26,000. Housing and population growth has continued at a lesser pace since 1900. The town, directly west of Bromley, has areas of commerce and industry, principally around the curved network of streets featuring its high street and is served in transport by three main railw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarmacadam
Tarmacadam is a road surfacing material made by combining crushed stone, tar, and sand, patented by Welsh inventor Edgar Purnell Hooley in 1902. It is a more durable and dust-free enhancement of simple compacted stone macadam surfaces invented by Scottish engineer John Loudon McAdam in the early 1800s. The terms "tarmacadam" and tarmac are also used for a variety of other materials, including tar- grouted macadam, bituminous surface treatments and modern asphalt concrete. Origins Macadam roads pioneered by British engineer John Loudon McAdam in the 1820s are prone to rutting and generating dust. Methods to stabilise macadam surfaces with tar date back to at least 1834 when John Henry Cassell, operating from ''Cassell's Patent Lava Stone Works'' in Millwall, England, patented "lava stone". This method involved spreading tar on the subgrade, placing a typical macadam layer, and finally sealing the macadam with a mixture of tar and sand. Tar-grouted macadam was in use well before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macadam
Macadam is a type of road construction, pioneered by Scottish engineer John Loudon McAdam around 1820, in which crushed stone is placed in shallow, convex layers and compacted thoroughly. A binding layer of stone dust (crushed stone from the original material) may form; it may also, after rolling, be covered with a cement or bituminous binder to keep dust and stones together. The method simplified what had been considered state-of-the-art at that point. Predecessors Pierre-Marie-Jérôme Trésaguet Pierre-Marie-Jérôme Trésaguet is sometimes considered the first person to bring post-Roman science to road building. A Frenchman from an engineering family, he worked paving roads in Paris from 1757 to 1764. As chief engineer of road construction of Limoges, he had opportunity to develop a better and cheaper method of road construction. In 1775, Tresaguet became engineer-general and presented his answer for road improvement in France, which soon became standard practice there. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bituminous Limestone
Bituminous limestone is limestone impregnated and sometimes deeply colored with bituminous matter derived from the decomposition of animal and plant remains entombed within the mass or in its vicinity. Uses The amount of bituminous matter or asphalt in the pores of the rock is sometimes sufficient to permit the material being used for asphalt pavements after simply powdering and heating it. Still better results are obtained by mixing it with bituminous sandstone. Sources In the United States, bituminous limestone has been found in Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah. Much bituminous limestone was also mined in Germany, Switzerland ). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ..., and France, from where large quantities of it were exported to the United States. Notes References *{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubitt Town
Cubitt Town is a district on the eastern side of the Isle of Dogs in London, England. This part of the former Metropolitan Borough of Poplar was redeveloped as part of the Port of London in the 1840s and 1850s by William Cubitt, Lord Mayor of London (1860–1862), after whom it is named. It is on the east of the Isle, facing the Royal Borough of Greenwich across the River Thames. To the west is Millwall, to the east and south is Greenwich, to the northwest Canary Wharf, and to the north — across the Blue Bridge — is Blackwall. The district is situated within the Blackwall & Cubitt Town Ward of Tower Hamlets London Borough Council. History It is named after William Cubitt, Lord Mayor of London (1860–1862), who was responsible for the development of the housing and amenities of the area in the 1840s and 1850s, mainly to house the growing population of workers in the local docks, shipbuilding yards and factories. As it grew, Cubitt also created many local businesses employi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one of the greatest figures of the Industrial Revolution, hochanged the face of the English landscape with his groundbreaking designs and ingenious constructions." Brunel built dockyards, the Great Western Railway (GWR), a series of steamships including the first propeller-driven transatlantic steamship, and numerous important bridges and tunnels. His designs revolutionised public transport and modern engineering. Though Brunel's projects were not always successful, they often contained innovative solutions to long-standing engineering problems. During his career, Brunel achieved many engineering firsts, including assisting in the building of the first tunnel under a navigable river (the River Thames) and the development of the , the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marc Isambard Brunel
Sir Marc Isambard Brunel (, ; 25 April 1769 – 12 December 1849) was a French-British engineer who is most famous for the work he did in Britain. He constructed the Thames Tunnel and was the father of Isambard Kingdom Brunel. Born in France, Brunel fled to the United States during the French Revolution. In 1796, he was appointed Chief Engineer of New York City. He moved to London in 1799, where he married Sophia Kingdom. In addition to the construction of the Thames Tunnel, his work as a mechanical engineer included the design of machinery to automate the production of pulley blocks for the Royal Navy. Brunel preferred the given name Isambard, but is generally known to history as Marc to avoid confusion with his more famous son. Early life in France Brunel was the second son of Jean Charles Brunel and Marie-Victoire Lefebvre. Jean Charles was a prosperous farmer in Hacqueville, Normandy, and Marc was born on the family farm. It was customary for the first son to inher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middlesex
Middlesex (; abbreviation: Middx) is a Historic counties of England, historic county in South East England, southeast England. Its area is almost entirely within the wider urbanised area of London and mostly within the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Greater London, with small sections in neighbouring ceremonial counties. Three rivers provide most of the county's boundaries; the River Thames, Thames in the south, the River Lea, Lea to the east and the River Colne, Hertfordshire, Colne to the west. A line of hills forms the northern boundary with Hertfordshire. Middlesex county's name derives from its origin as the Middle Saxons, Middle Saxon Province of the Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon Kingdom of Essex, with the county of Middlesex subsequently formed from part of that territory in either the ninth or tenth century, and remaining an administrative unit until 1965. The county is the List of counties of England by area in 1831, second smallest, after Ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
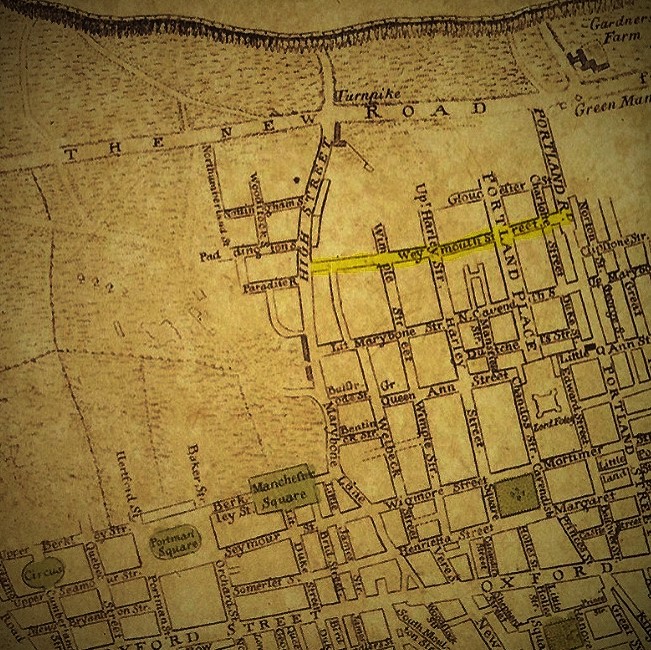
Weymouth Street
Weymouth Street lies in the Marylebone district of the City of Westminster and connects Marylebone High Street with Great Portland Street. The area was developed in the late 18th century by Henrietta Cavendish Holles and her husband Edward Harley, 2nd Earl of Oxford. This part of Marylebone originally belonged to the Manor of Tyburn which existed at the time of the Domesday Book (1086). History The area of Marylebone in which Weymouth Street is located originally belonged to the Manor of Tyburn which existed at the time of the Domesday Book (1086). Weymouth Street was first laid out and built up in the late 1770s and early 1780s in line with the development of Harley Street, Portland Place and Great Portland Street. Approximately a century later, the street was partially rebuilt and modernised mainly with neoclassical architecture. At the beginning of the 1900s, following lease expiries, large mansion blocks were developed near the main intersections of the street. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |