|
Capital Punishment In Hong Kong
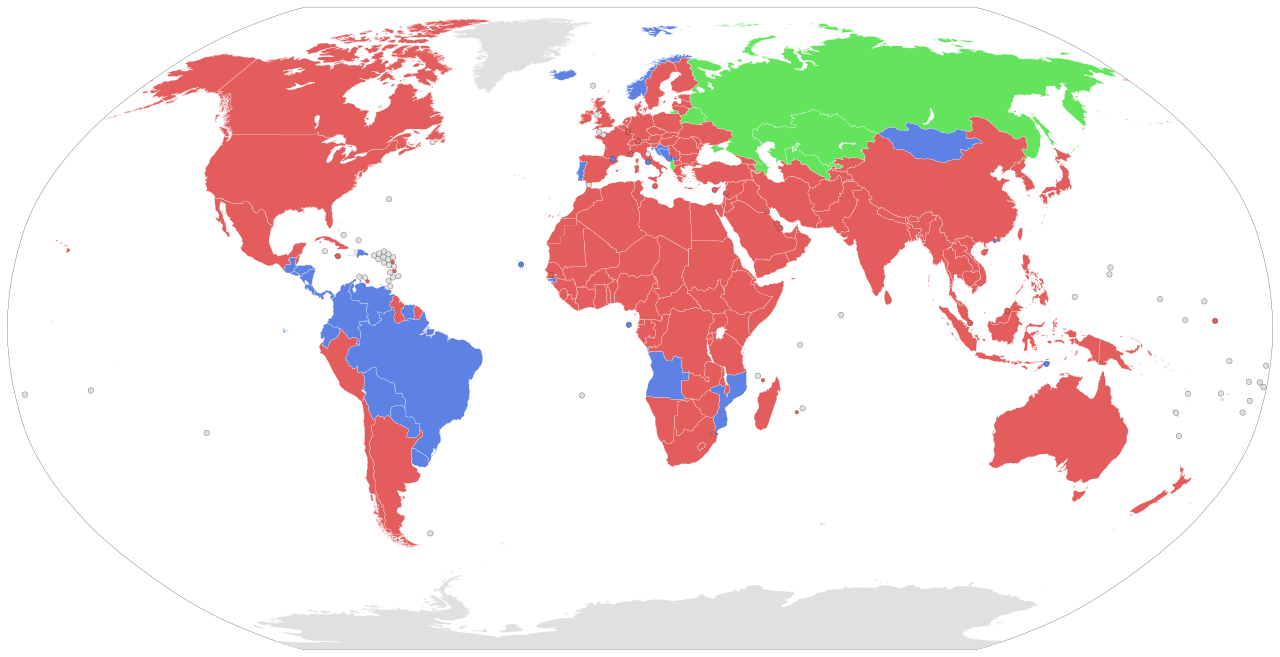
Capital punishment in Hong Kong was formally abolished on 23 April 1993 by virtue of the Crimes (Amendment) Ordinance 1993. Before then, capital punishment was the usual sentence given since the establishment of the Crown Colony of Hong Kong for offences such as murder, kidnapping ending in death, and piracy. The last execution in Hong Kong was carried out on 16 November 1966 when Wong Kai-Kei (), age 25, was hanged at Stanley Prison. Wong was a Chinese-Vietnamese who, on 3 July 1966, was burglarizing the Chung Keen Company building in Sham Shui Po when he was spotted by security guard Chan Fat-Sang (). Wong killed Chan and injured a woman in the subsequent fight, and was found guilty of murder and sentenced to execution by hanging. After his conviction, Wong attempted to appeal the sentence, claiming that he had confessed under duress, and also wrote to the Governor of Hong Kong David Trench seeking clemency. Reform Club chairman Brook Bernacchi published an open letter agains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that the person is responsible for violating norms that warrant said punishment. The sentence ordering that an offender is to be punished in such a manner is known as a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is known as an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is ''condemned'' and is commonly referred to as being "on death row". Crimes that are punishable by death are known as ''capital crimes'', ''capital offences'', or ''capital felonies'', and vary depending on the jurisdiction, but commonly include serious crimes against the person, such as murder, mass murder, aggravated cases of rape (often including child sexual abuse), terrorism, aircraft hijacking, war crimes, crimes against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Imprisonment
Life imprisonment is any sentence of imprisonment for a crime under which convicted people are to remain in prison for the rest of their natural lives or indefinitely until pardoned, paroled, or otherwise commuted to a fixed term. Crimes for which, in some countries, a person could receive this sentence include murder, torture, terrorism, child abuse resulting in death, rape, espionage, treason, drug trafficking, drug possession, human trafficking, severe fraud and financial crimes, aggravated criminal damage, arson, kidnapping, burglary, and robbery, piracy, aircraft hijacking, and genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes or any three felonies in case of three-strikes law. Life imprisonment (as a maximum term) can also be imposed, in certain countries, for traffic offences causing death. Life imprisonment is not used in all countries; Portugal was the first country to abolish life imprisonment, in 1884. Where life imprisonment is a possible sentence, ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment In United Kingdom
Capital punishment in the United Kingdom predates the formation of the UK, having been used within the British Isles from ancient times until the second half of the 20th century. The last executions in the United Kingdom were by hanging, and took place in 1964; :capital punishment for murder was suspended in 1965 and finally abolished in 1969 (1973 in Northern Ireland). Although unused, the death penalty remained a legally defined punishment for certain offences such as treason until it was completely abolished in 1998; the last execution for treason took place in 1946. In 2004 the 13th Protocol to the European Convention on Human Rights became binding on the United Kingdom; it prohibits the restoration of the death penalty as long as the UK is a party to the convention (regardless of the UK’s status in relation to the European Union). Background Capital punishment was historically used to punish inherently innocent things such as unemployment. In 16th-century England, no d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment In Taiwan
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Taiwan. The death penalty can be imposed for murder, treason, drug trafficking, piracy, terrorism, and especially serious cases of robbery, rape, and kidnapping, as well as for military offences, such as desertion during war time. In practice, however, all executions in Taiwan since the early 2000s have been for murder. Before 2000, Taiwan had a relatively high execution rate, when strict laws surrounding capital punishment were still in effect. However, controversial legal cases during the 1990s and the changing attitudes of officials towards abolition of the death penalty resulted in a significant drop in the number of executions, with only three in 2005 and none between 2006 and 2009. Executions resumed in 2010, and according to polls, more than 80% of Taiwanese people support the continued use of capital punishment. Capital offences Under military law The Criminal Law of the Armed Forces (陸海空軍刑法) rules that the followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment In China
Capital punishment in China is a legal penalty. It is commonly applied for murder and drug trafficking, although it is also a legal penalty for various other offenses. Executions are carried out by lethal injection or by shooting. In a survey conducted by the ''New York Times'' in 2014, it was found the death penalty retained widespread support in Chinese society. The use of capital punishment is active in most East Asian countries and territories, including Japan, North Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, Singapore, and Taiwan. According to Amnesty International, China executes more people than all other countries combined. The exact numbers of executions and death sentences are considered a state secret by China, and are not publicly available. According to the Dui Hua Foundation, a U.S.-based organization, the estimated number of executions has declined steadily in the twenty-first century, from 12,000 each year to 2,400. Although in 2022, World Coalition Agains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment In Macau
Capital punishment in Macau was formally abolished in 1976 and reiterated in the Penal Code of Macau in the 1995. Before that, capital punishment was last used in the 19th century. Under the principle of independence of legal system in Macau Basic Law, Macau continues its repudiation of capital punishment after the handover to The People's Republic of China in 1999 despite the fact that capital punishment is practised in The People's Republic of China. Macau was a Portuguese colony prior to returning to Chinese rule. Macau abided by the laws of their colonisers prior to their transfer. After the transfer of sovereignty, Macau developed their own laws. These laws were based largely upon the Portuguese laws. The final death sentence was handed some time during the 19th century. Although capital punishment is prohibited in Macau, the process of extradition to The People's Republic of China and other countries is still permitted. The Hong Kong protests of 2019 have caused questions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Rights In Hong Kong
Human rights protection is enshrined in the Basic Law and its Bill of Rights Ordinance (Cap.383). By virtue of the Bill of Rights Ordinance and Basic Law Article 39, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) is put into effect in Hong Kong. Any local legislation that is inconsistent with the Basic Law can be set aside by the courts. This does not apply to national legislation that applies to Hong Kong, such as the National Security Law, even if it is inconsistent with the Bills of Rights Ordinance, ICCPR, or the Basic Law. Hong Kong is generally perceived to enjoy a moderate level of civil liberties. Although the Hong Kong government claims that it respects the human rights of citizens, there are significant concerns surrounding human rights in practice, particularly in the political sphere and press. There are concerns over the freedoms to the people which is restricted by the Public Order Ordinance, as well as strong domestic and international cri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment In The People's Republic Of China
Capital punishment in China is a legal penalty. It is commonly applied for murder and drug trafficking, although it is also a legal penalty for various other offenses. Executions are carried out by lethal injection or by shooting. In a survey conducted by the ''New York Times'' in 2014, it was found the death penalty retained widespread support in Chinese society. The use of capital punishment is active in most East Asian countries and territories, including Japan, North Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, Singapore, and Taiwan. According to Amnesty International, China executes more people than all other countries combined. The exact numbers of executions and death sentences are considered a state secret by China, and are not publicly available. According to the Dui Hua Foundation, a U.S.-based organization, the estimated number of executions has declined steadily in the twenty-first century, from 12,000 each year to 2,400. Although in 2022, World Coalition Again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Republic Of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer Of The Sovereignty Of Hong Kong
Sovereignty of Hong Kong was transferred from the United Kingdom to the People's Republic of China (PRC) at midnight on 1 July 1997. This event ended 156 years of British rule in the former colony. Hong Kong was established as a special administrative region of China (SAR) for 50 years, maintaining its own economic and governing systems from those of mainland China during this time, although influence from the central government in Beijing increased after the passing of the Hong Kong national security law in 2020. Hong Kong had been a colony of the British Empire since 1841, except for four years of Japanese occupation from 1941 to 1945. After the First Opium War, its territory was expanded on two occasions; in 1860 with the addition of Kowloon Peninsula and Stonecutters Island, and again in 1898, when Britain obtained a 99-year lease for the New Territories. The date of the handover in 1997 marked the end of this lease. The 1984 Sino-British Joint Declaration had set the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hong Kong Basic Law
The Basic Law of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China is a national law of China that serves as the organic law for the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR). Comprising nine chapters, 160 articles and three annexes, the Basic Law was composed to implement Sino-British Joint Declaration#Annex I: Chinese basic policies for Hong Kong, Annex I of the 1984 Sino-British Joint Declaration. The Basic Law was enacted under the Constitution of the People's Republic of China, Constitution of China when it was adopted by the National People's Congress on 4 April 1990 and came into effect on 1 July 1997 when Hong Kong was Transfer of sovereignty over Hong Kong, transferred from the United Kingdom to China. It replaced Hong Kong's colonial constitution of the Hong Kong Letters Patent, Letters Patent and the Hong Kong Royal Instructions, Royal Instructions. Drafted on the basis of the Joint Declaration, the Basic Law lays out the basic p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One Country, Two Systems
"One country, two systems" is a constitutional principle of the People's Republic of China (PRC) describing the governance of the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau. The constitutional principle was formulated in the early 1980s during negotiations over Hong Kong between China and the United Kingdom. It provided that there would be only one China, but that these regions could retain their own economic and administrative systems, while the rest of Mainland China uses the socialism with Chinese characteristics system. Under the principle, each of the two regions could continue to have its own governmental system, legal, economic and financial affairs, including trade relations with foreign countries, all of which are independent from those of the Mainland. The PRC has also proposed to apply the principle in the unification it aims for with Taiwan. However, since 2020, as a result of the passage of the National Security Law by Hong Kong on 30 June of the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |