|
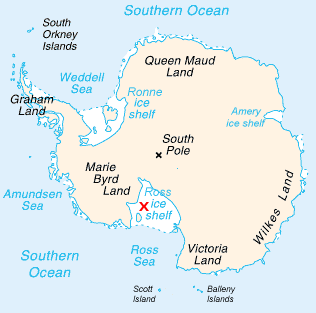
Cape Selborne
Cape Selborne () is a high snow-covered cape at the south side of Barne Inlet, the terminus of Byrd Glacier at the west side of the Ross Ice Shelf. Discovered by the ''Discovery'' expedition (1901–1904) and named for William Waldegrave Palmer Selborne, Second Earl of Selborne, who entered the Cabinet as First Lord of the Admiralty in 1900. Cape Selborne marks the boundary between the Shackleton Coast to the south and the Hillary Coast The Hillary Coast is a portion of the coast of Antarctica along the western margin of the Ross Ice Shelf between Minna Bluff and Cape Selborne. It was named by the New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1961 for Sir Edmund Hillary, the le ... to the north. Headlands of the Ross Dependency Shackleton Coast Hillary Coast {{ShackletonCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barne Inlet
Barne Inlet () is a reentrant (an inlet formed by two spurs of land) on the west side of the Ross Ice Shelf, on the coast of Antarctica. It lies between Cape Kerr and Cape Selborne. It is about wide, and is occupied by the lower part of Byrd Glacier. It was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–1904) and named for Lieutenant Michael Barne, Royal Navy, a member of the expedition, who with Sub-Lieutenant George Mulock Captain George Francis Arthur Mulock, DSO, RN, FRGS (7 February 1882 – 26 December 1963) was an Anglo-Irish Royal Navy officer, cartographer and polar explorer who participated in an expedition to the Antarctic regions: the Discovery Expedi ... mapped the coastline this far south in 1903. References Inlets of Antarctica Hillary Coast {{RossDependency-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byrd Glacier
The Byrd Glacier is a major glacier in Antarctica, about long and wide, draining an extensive area of the polar plateau and flowing eastward between the Britannia Range and Churchill Mountains to discharge into the Ross Ice Shelf at Barne Inlet. Its valley below the glacier used to be recognised as one of the lowest points not to be covered by water on Earth (assuming ice doesn't count as water), reaching below sea level. It was named by the NZ-APC after Rear Admiral Byrd, US Navy Antarctic explorer. On the south side of Byrd Glacier is Blake Massif. See also * Glaciology * Ice stream * List of Antarctic ice streams * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * List of places in Antarctica below sea level ** Denman Glacier Denman Glacier is a glacier wide, descending north some , which debouches into the Shackleton Ice Shelf east of David Island, Queen Mary Land. It was discovered in November 1912 by the Western Base party of the Australasian Antarctic Expedition ... Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Waldegrave Palmer Selborne
William is a masculine given name of Norman French origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Liam, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germanic name is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Selborne
Earl of Selborne, in the County of Southampton, is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. It was created in 1882 for the lawyer and Liberal Party (UK), Liberal politician Roundell Palmer, 1st Earl of Selborne, Roundell Palmer, 1st Baron Selborne, along with the subsidiary title of Viscount Wolmer, of Blackmoor in the County of Southampton. He had already been made Baron Selborne, of Selborne in the County of Southampton, in 1872, also in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. Both his son, the second Earl, and grandson, the third Earl, were prominent Liberal Unionist politicians. The latter was in 1941 called to the House of Lords through a writ of acceleration in his father's barony of Selborne. The third Earl's grandson, the fourth Earl, served as one of the ninety elected hereditary peers that remain in the House of Lords after the passing of the House of Lords Act 1999, and sat as a Conservative Party (UK), Conservative. As of 2021, the titles are held by the latter's son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Lord Of The Admiralty
The First Lord of the Admiralty, or formally the Office of the First Lord of the Admiralty, was the political head of the English and later British Royal Navy. He was the government's senior adviser on all naval affairs, responsible for the direction and control of the Admiralty, and also of general administration of the Naval Service of the Kingdom of England, Great Britain in the 18th century, and then the United Kingdom, including the Royal Navy, the Royal Marines, and other services. It was one of the earliest known permanent government posts. Apart from being the political head of the Naval Service the post holder was simultaneously the pre-eminent member of the Board of Admiralty. The office of First Lord of the Admiralty existed from 1628 until it was abolished when the Admiralty, Air Ministry, Ministry of Defence, and War Office were all merged to form the new Ministry of Defence in 1964. Its modern-day equivalent is the Secretary of State for Defence. History In 1628 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shackleton Coast
Shackleton Coast is that portion of the coast along the west side of the Ross Ice Shelf between Cape Selborne and Airdrop Peak at the east side of Beardmore Glacier in Antarctica. Named by New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee (NZ-APC) in 1961 after Sir Ernest Shackleton. He accompanied Scott on the southern journey during the ''Discovery'' expedition (1901–04) and subsequently led three Antarctic expeditions. On the British Antarctic Expedition (1907–09), Shackleton discovered the area beyond Shackleton Inlet to the Beardmore Glacier, and was the first to find a practicable route to the South Pole. Lack of food stopped him 97 miles (180 km) from his goal. Further reading * Ute Christina Herzfeld, Atlas of Antarctica: Topographic Maps from Geostatistical Analysis of Satellite Radar Altimeter Data', P 243 * Gunter Faure, Teresa M. Mensing, The Transantarctic Mountains: Rocks, Ice, Meteorites and Water', PP 162, 427, 709 External links Shackleton Coaston USGS w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillary Coast
The Hillary Coast is a portion of the coast of Antarctica along the western margin of the Ross Ice Shelf between Minna Bluff and Cape Selborne. It was named by the New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1961 for Sir Edmund Hillary, the leader of the New Zealand Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition, 1956–58. Various New Zealand parties carried out detailed surveys of portions of this coast and pioneered routes up Skelton Glacier Skelton Glacier is a large glacier flowing from the polar plateau into the Ross Ice Shelf at Skelton Inlet on the Hillary Coast, south of Victoria Land, Antarctica. Discovery and naming Named after the Skelton Inlet by the New Zealand party ... and Darwin Glacier to the polar plateau. References Coasts of the Ross Dependency Edmund Hillary {{RossDependency-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headlands Of The Ross Dependency
A headland, also known as a head, is a coastal landform, a point of land usually high and often with a sheer drop, that extends into a body of water. It is a type of promontory. A headland of considerable size often is called a cape.Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, pp. 80, 246. . Headlands are characterised by high, breaking waves, rocky shores, intense erosion, and steep sea cliff. Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is flanked by land on three sides, whereas a headland is flanked by water on three sides. Headlands and bays form on discordant coastlines, where bands of rock of alternating resistance run perpendicular to the coast. Bays form when weak (less resistant) rocks (such as sands and clays) are eroded, leaving bands of stronger (more resistant) rocks (such as chalk, limestone, and granite) forming a headland, or peninsula. Through the deposition of sediment within the bay and the erosion of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |