|
Cape Expedition
The Cape Expedition was the deliberately misleading name given to a secret five-year wartime program of establishing coastwatching stations on New Zealand’s more distant uninhabited subantarctic islands. The decision to do so was made by the New Zealand Government's War Cabinet in December 1940, with the program terminating at the end of the Pacific War in 1945.Hall (1950). History It was suspected that the 6,000-ton German merchant vessel ''Erlangen'', which had sailed from Dunedin, supposedly for Australia, on 26 August 1939 – shortly before war had been declared in Europe – had, instead, supplemented her meagre coal reserves with timber from the Auckland Islands and headed for South America. The suspicion was later confirmed when the first coastwatchers in the program found areas of newly cut Southern Rata forest at Carnley Harbour on Auckland Island. Moreover, the loss of the ships SS ''Holmwood'' and MS ''Rangitane'' to German raiders in November 1940 gave ris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MS Rangitane (1929)
MS ''Rangitane'' was a passenger liner owned by the New Zealand Shipping Company. She was one of three sister ships (the other sisters were and ) delivered to the company in 1929 for the All-Red Route between Britain and New Zealand. ''Rangitane'' was built by John Brown & Company and launched on 27 May 1929. The three ships each measured about 16,700 gross register tons, registered length and beam. They could carry nearly 600 passengers in 1st, 2nd and 3rd classes, 200 crew members, and substantial cargo. They had Brown- Sulzer diesel engines with a total output of , turning twin propellers. In wartime, they carried only defensive armament. On her final voyage ''Rangitane'' was armed with a 4.7-inch gun and 40 rounds of ammunition. Sinking On her final voyage, which had been delayed by labour disputes, she carried 14,000 tons of cargo, including foodstuffs and silver bullion, valued at over £2 million at 1940 prices. She carried 111 passengers, including CORB nurses, Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildlife
Wildlife refers to domestication, undomesticated animal species (biology), species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wilderness, wild in an area without being species, introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game (hunting), game: those birds and mammals that were trophy hunting, hunted for sport. Wildlife can be found in all ecosystems. Deserts, plains, grasslands, woodlands, forests, and other areas, including the most developed urban areas, all have distinct forms of wildlife. While the term in popular culture usually refers to animals that are untouched by human factors, most scientists agree that much wildlife is human impact on the environment, affected by human behavior, human activities. Some wildlife threaten human safety, health, property, and quality of life. However, many wild animals, even the dangerous ones, have value to human beings. This value might be economic, educational, or emotional in nature. Humans have historically t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outboard Motor
An outboard motor is a propulsion system for boats, consisting of a self-contained unit that includes engine, gearbox and propeller or jet drive, designed to be affixed to the outside of the transom. They are the most common motorised method of propelling small watercraft. As well as providing propulsion, outboards provide steering control, as they are designed to pivot over their mountings and thus control the direction of thrust. The skeg also acts as a rudder when the engine is not running. Unlike inboard motors, outboard motors can be easily removed for storage or repairs. In order to eliminate the chances of hitting bottom with an outboard motor, the motor can be tilted up to an elevated position either electronically or manually. This helps when traveling through shallow waters where there may be debris that could potentially damage the motor as well as the propeller. If the electric motor required to move the pistons which raise or lower the engine is malfunctioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinghy
A dinghy is a type of small boat, often carried or towed by a larger vessel for use as a tender. Utility dinghies are usually rowboats or have an outboard motor. Some are rigged for sailing but they differ from sailing dinghies, which are designed first and foremost for sailing. A dinghy's main use is for transfers from larger boats, especially when the larger boat cannot dock at a suitably-sized port or marina. The term "dinghy towing" sometimes is used to refer to the practice of towing a car or other smaller vehicle behind a motorhome, by analogy to towing a dinghy behind a yacht. Etymology The term is a loanword from the Bengali ', Urdu ', and Hindi '. Types Dinghies usually range in length from about . Larger auxiliary vessels are generally called tenders, pinnaces or lifeboats. Folding and take-down multi-piece (nesting) dinghies are used where space is limited. Some newer dinghies have much greater buoyancy, giving them more carrying capacity than older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plywood
Plywood is a material manufactured from thin layers or "plies" of wood veneer that are glued together with adjacent layers having their wood grain rotated up to 90 degrees to one another. It is an engineered wood from the family of manufactured boards which include medium-density fibreboard (MDF), oriented strand board (OSB) and particle board (chipboard). All plywoods bind resin and wood fibre sheets (cellulose cells are long, strong and thin) to form a composite material. This alternation of the grain is called ''cross-graining'' and has several important benefits: it reduces the tendency of wood to split when nailed at the edges; it reduces expansion and shrinkage, providing improved dimensional stability; and it makes the strength of the panel consistent across all directions. There is usually an odd number of plies, so that the sheet is balanced—this reduces warping. Because plywood is bonded with grains running against one another and with an odd number of composite part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefabricated Home
Prefabricated homes, often referred to as prefab homes or simply prefabs, are specialist dwelling types of prefabricated building, which are manufactured off-site in advance, usually in standard sections that can be easily shipped and assembled. Some current prefab home designs include architectural details inspired by postmodernism or futurist architecture. "Prefabricated" may refer to buildings built in components (e.g. panels), modules (modular homes) or transportable sections (manufactured homes), and may also be used to refer to mobile homes, i.e., houses on wheels. Although similar, the methods and design of the three vary widely. There are two-level home plans, as well as custom home plans. There are considerable differences in the construction types. In the U.S., mobile and manufactured houses are constructed in accordance with HUD building codes, while modular houses are constructed in accordance with the IRC (International Residential Code). *Modular homes are created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Army
, image = New Zealand Army Logo.png , image_size = 175px , caption = , start_date = , country = , branch = , type = Army , role = Land warfare , website = https://www.nzdf.mil.nz/army/ , size = * 4,519 active personnel * 2,065 reserve , command_structure = , garrison = Wellington , garrison_label = , nickname = , patron = , motto = , colours = Red and black , colors_label = , march = , mascot = , equipment = List of equipment of the New Zealand Army , equipment_label = , battles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private (rank)
A private is a soldier, usually with the lowest rank in many armies. Soldiers with the rank of Private may be conscripts or they may be professional (career) soldiers. The term derives from the medieval term "private soldiers" (a term still used in the British Army), contrasting mercenary soldiers and denoting individuals who were either exclusively hired, conscripted, or mustered into service by a feudal nobleman commanding a battle group of an army. Asia Indonesia In Indonesia, this rank is referred to as '' Tamtama'' (specifically ''Prajurit'' which means soldier), which is the lowest rank in the Indonesian National Armed Forces and special Police Force. In the Indonesian Army, Indonesian Marine Corps, and Indonesian Air Force, "Private" has three levels, which are: Private (''Prajurit Dua''), Private First Class (''Prajurit Satu''), and Master Private (''Prajurit Kepala''). After this rank, the next promotion is to Corporal. File:prada pdh ad.png, Private (''Prajurit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
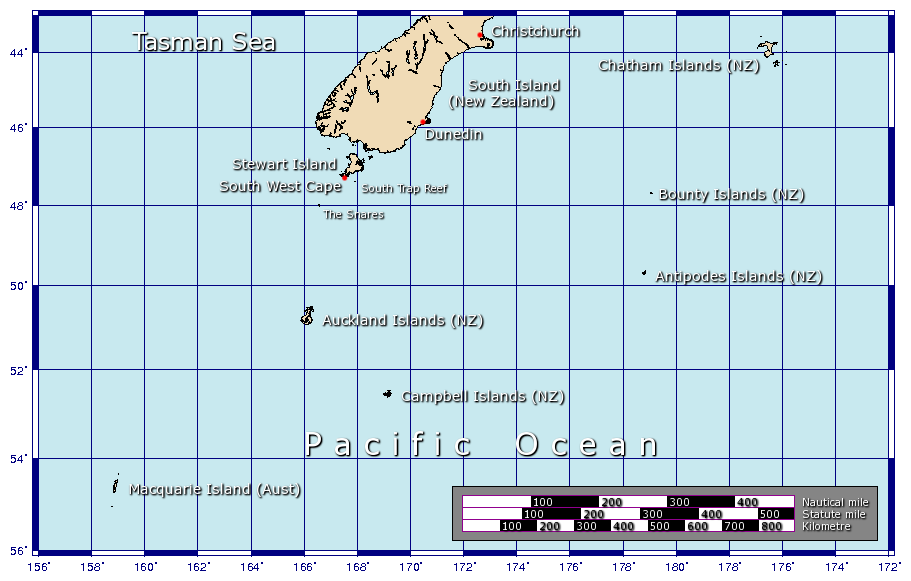
Campbell Island, New Zealand
Campbell Island / Motu Ihupuku is an uninhabited subantarctic island of New Zealand, and the main island of the Campbell Island group. It covers of the group's , and is surrounded by numerous stacks, rocks and islets like Dent Island, Folly Island (or Folly Islands), Isle de Jeanette-Marie, and Jacquemart Island, the latter being the southernmost extremity of New Zealand. The island is mountainous, rising to over in the south. A long fiord, Perseverance Harbour, nearly bisects it, opening out to sea on the east coast. The island is listed with the New Zealand Outlying Islands. The island is an immediate part of New Zealand, but not part of any region or district, but instead ''Area Outside Territorial Authority'', like all other outlying islands, other than the Solander Islands. It is the closest piece of land to the antipodal point of the United Kingdom, and Ireland, meaning that the furthest away city is Limerick, Ireland. Campbell Island is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseverance Harbour
Perseverance Harbour, also known as South harbour, is a large indentation in the coast of Campbell Island, one of New Zealand's subantarctic outlying islands. The harbour is a long lateral fissure which reaches the ocean in the island's southeast, and is overlooked by the island's highest point, Mount Honey. The Campbell Island Meteorological Station lies at the western end of the harbour. On 4 November 1810 the island's discoverer Captain Frederick Hasselborough (or "Hasselburgh" or "Hasselburg"; there are several spellings), who had returned from Sydney, was drowned in Perseverance Harbour, together with Elizabeth Farr, a young woman born at Norfolk Island Norfolk Island (, ; Norfuk: ''Norf'k Ailen'') is an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, directly east of Australia's Evans Head and about from Lord Howe Island. Together with ..., and a twelve- or thirteen-year-old Sydney boy George Allwright. Refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Ross
Port Ross is a natural harbour on Auckland Island in the Auckland Islands Group, a subantarctic chain that forms part of the New Zealand Outlying Islands. Guarding the mouth of Port Ross are Rose Island, Enderby Island, Ewing Island, and the tiny Ocean Island. The harbour is the most well-established congregation ground for southern right whales in New Zealand waters. In 1842, members of the Ngāti Mutunga Māori arrived in Port Ross from the Chatham Islands with Moriori slaves in an attempt to establish a settlement.Peat, Neville (2003) Subantarctic New Zealand: A Rare Heritage, Invercargill: Department of Conservation, , p. 75 In the late 1840s, an agricultural and whaling community set up in Erebus Cove, on the harbour, and named Hardwicke. Due to the inhospitable climate, the settlement was abandoned within three years. A cemetery remains, later used to bury victims of shipwrecks. Survivors of the 1866 wreck of the ''General Grant'' set up a camp in the harbour, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)





