|
Cape Canaveral Launch Complex 12
Launch Complex 12 (LC-12) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida was a launch pad used by Atlas rockets and missiles between 1958 and 1967. It was the second-most southern of the pads known as Missile Row, between LC-11 to the south and LC-13 to the north. Along with Complexes 11, 13 and 14, 12 featured a more robust design than many contemporary pads, due to the greater power of the Atlas compared to other rockets of the time. It was larger, and featured a concrete launch pedestal that was tall and a reinforced blockhouse. The rockets were delivered to the launch pad by means of a ramp on the southwest side of the launch pedestal. Atlas A, C and D missiles were tested from the site. It was also used for orbital launches of Atlas-Able and later Atlas-Agena rockets, and two Project FIRE suborbital tests for Project Apollo, using Atlas D rockets. LC-12's first launch was Atlas 10A on January 10, 1958. During the second half of the year, a larger umbilical service to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida. Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the station is the primary launch site for the Space Force's Eastern RangeCAST 1999, p. 1-12. with three launch pads currently active (Space Launch Complexes 37B, 40, and 41). The facility is south-southeast of NASA's Kennedy Space Center on adjacent Merritt Island, with the two linked by bridges and causeways. The Cape Canaveral Space Force Station Skid Strip provides a runway close to the launch complexes for military airlift aircraft delivering heavy and outsized payloads to the Cape. A number of American space exploration pioneers were launched from CCSFS, including the first U.S. Earth satellite (1958), first U.S. astronaut (1961), first U.S. astronaut in orbit (1962), first two-man U.S. spacecraft (1965), first U.S. unmanned lunar land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project FIRE
A project is any undertaking, carried out individually or collaboratively and possibly involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a particular goal. An alternative view sees a project managerially as a sequence of events: a "set of interrelated tasks to be executed over a fixed period and within certain cost and other limitations". A project may be a temporary (rather than a permanent) social system ( work system), possibly staffed by teams (within or across organizations) to accomplish particular tasks under time constraints. A project may form a part of wider programme management or function as an ''ad hoc'' system. Note that open-source software "projects" or artists' musical "projects" (for example) may lack defined team-membership, precise planning and/or time-limited durations. Overview The word ''project'' comes from the Latin word ''projectum'' from the Latin verb ''proicere'', "before an action," which in turn comes from ''pro-'', which d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launch Tower
A service structure is a steel framework or tower that is built on a rocket launch pad to facilitate assembly and servicing. An umbilical tower also usually includes an elevator which allows maintenance and crew access. Immediately before ignition of the rocket's motors, all connections between the tower and the craft are severed, and the bridges over which these connections pass often quickly swing away to prevent damage to the structure or vehicle. Kennedy Space Center During the Space Shuttle program, the structures at the Launch Complex 39 pads contained a two-piece access tower system, the Fixed Service Structure (FSS) and the Rotating Service Structure (RSS). The FSS permitted access to the Shuttle via a retractable arm and a "beanie cap" to capture vented liquid oxygen, LOX from the external tank. The RSS contained the Payload Changeout Room, which offered "clean" access to the orbiter's payload bay, protection from the elements, and protection in winds up to . The FSS on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere (less than 1% that of Earth's), and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos (moon), Phobos and Deimos (moon), Deimos. Some of the most notable surface features on Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and List of tallest mountains in the Solar System, highest known mountain in the Solar System and Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The North Polar Basin (Mars), Borealis basin in the Northern Hemisphere covers approximately 40% of the planet and may be a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariner 4
Mariner 4 (together with Mariner 3 known as Mariner-Mars 1964) was the Mariner program, fourth in a series of spacecraft intended for planetary exploration in a flyby mode. It was designed to conduct closeup scientific observations of Mars and to transmit these observations to Earth. Launched on November 28, 1964, Mariner 4 performed the first successful planetary flyby, flyby of the planet Mars, returning the first close-up pictures of the Martian surface. It captured the first images of another planet ever returned from outer space, deep space; their depiction of a cratered, dead planet largely changed the scientific community's view of life on Mars. Other mission objectives were to perform field and particle measurements in outer space#Interplanetary space, interplanetary space in the vicinity of Mars and to provide experience in and knowledge of the engineering capabilities for interplanetary flights of long duration. Initially expected to remain in space for eight months ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
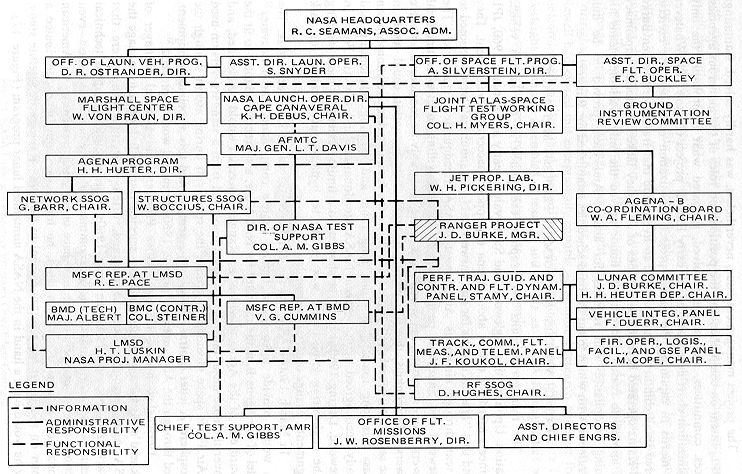
Ranger Program
The Ranger program was a series of unmanned space missions by the United States in the 1960s whose objective was to obtain the first close-up images of the surface of the Moon. The Ranger spacecraft were designed to take images of the lunar surface, transmitting those images to Earth until the spacecraft were destroyed upon impact. A series of mishaps, however, led to the failure of the first six flights. At one point, the program was called "shoot and hope". Congress launched an investigation into "problems of management" at NASA Headquarters and Jet Propulsion Laboratory. After two reorganizations of the agencies, Ranger 7 successfully returned images in July 1964, followed by two more successful missions. Ranger was originally designed, beginning in 1959, in three distinct phases, called "blocks". Each block had different mission objectives and progressively more advanced system design. The JPL mission designers planned multiple launches in each block, to maximize the engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranger 7
Ranger 7 was the first space probe of the United States to successfully transmit close images of the lunar surface back to Earth. It was also the first completely successful flight of the Ranger program. Launched on July 28, 1964, Ranger 7 was designed to achieve a lunar-impact trajectory and to transmit high-resolution photographs of the lunar surface during the final minutes of flight up to impact. The spacecraft carried six television vidicon cameras – two wide-angle (channel F, cameras A and B) and four narrow-angle (channel P) – to accomplish these objectives. The cameras were arranged in two separate chains, or channels, each self-contained with separate power supplies, timers, and transmitters so as to afford the greatest reliability and probability of obtaining high-quality video pictures. Ranger 7 transmitted over 4,300 photographs during the final 17 minutes of its flight. After 68.6 hours of flight, the spacecraft landed between Mare Nubium and Oceanus Procellarum. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariner 2
Mariner 2 (Mariner-Venus 1962), an American space probe to Venus, was the first robotic space probe to conduct a successful planetary encounter. The first successful spacecraft in the NASA Mariner program, it was a simplified version of the Block I spacecraft of the Ranger program and an exact copy of Mariner 1. The missions of the Mariner 1 and 2 spacecraft are sometimes known as the Mariner R missions. Original plans called for the probes to be launched on the Atlas-Centaur, but serious developmental problems with that vehicle forced a switch to the much smaller Agena B second stage. As such, the design of the Mariner R vehicles was greatly simplified. Far less instrumentation was carried than on the Soviet Venera probes of this period—for example, forgoing a TV camera—as the Atlas-Agena B had only half as much lift capacity as the Soviet 8K78 booster. The Mariner 2 spacecraft was launched from Cape Canaveral on August 27, 1962, and passed as close as to Venus on Decemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Landing
A hard landing occurs when an aircraft or spacecraft hits the ground with a greater vertical speed and force than in a normal landing. Landing is the final phase in flight, in which the aircraft returns to the ground. The average vertical speed in a landing is around ; any greater vertical speed should be classed by crew as ''hard''. Crew judgment is most reliable to determine hard landing, as determination based on recorded acceleration value is difficult and not advisable, partially because there is no recording of true vertical acceleration. Hard landings can be caused by weather conditions, mechanical problems, overweight aircraft, pilot decision and/or pilot error. The term ''hard landing'' usually implies that the pilot still has total or partial control over the aircraft, as opposed to an uncontrolled descent into terrain (a crash). Hard landings can vary in their consequences, from mild passenger discomfort to vehicle damage, structural failure, injuries, and/or loss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranger 4
Ranger 4 was a spacecraft of the Ranger program, launched in 1962. It was designed to transmit pictures of the lunar surface to Earth stations during a period of 10 minutes of flight prior to crashing upon the Moon, to rough-land a seismometer capsule on the Moon, to collect gamma-ray data in flight, to study radar reflectivity of the lunar surface, and to continue testing of the Ranger program for development of lunar and interplanetary spacecraft. An onboard computer failure caused failure of the deployment of the solar panels and navigation systems; as a result the spacecraft crashed on the far side of the Moon without returning any scientific data. It was the first spacecraft of the United States to reach another celestial body. Spacecraft design Ranger 4 was a Block II Ranger spacecraft virtually identical to Ranger 3. The basic vehicle was , high and consisted of a lunar capsule covered with a balsawood impact-limiter, in diameter, a mono-propellant mid-course motor, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)