|
Cape Breton Development Corporation
The Cape Breton Development Corporation, or DEVCO, was a Government of Canada Crown corporation. It ceased operation on December 31, 2009, after being amalgamated with Enterprise Cape Breton Corporation (ECBC). DEVCO was organized primarily into two divisions: a community economic development organization, and the coal division. From March 30, 1968, until November 23, 2001, DEVCO's coal division operated Canada's largest underground coal mines, located in eastern Cape Breton County, Nova Scotia. Following decommissioning of its mines, DEVCO sold all non-mining surface assets to the private sector on December 18, 2001, including the Devco Railway and is now remediating its mine sites. Creation of DEVCO In 1965, the Dominion Steel and Coal Corporation, or DOSCO (then a subsidiary of the Hawker Siddeley Group) announced that its mines had only 15 years of production left and concluded that the expense of opening new underground mines in the Sydney Coal Field would be too expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DEVCO Logo
The Cape Breton Development Corporation, or DEVCO, was a Government of Canada Crown corporation. It ceased operation on December 31, 2009, after being amalgamated with Enterprise Cape Breton Corporation (ECBC). DEVCO was organized primarily into two divisions: a community economic development organization, and the coal division. From March 30, 1968, until November 23, 2001, DEVCO's coal division operated Canada's largest underground coal mines, located in eastern Cape Breton County, Nova Scotia, Cape Breton County, Nova Scotia. Following decommissioning of its mines, DEVCO sold all non-mining surface assets to the private sector on December 18, 2001, including the Devco Railway and is now remediating its mine sites. Creation of DEVCO In 1965, the Dominion Steel and Coal Corporation, or DOSCO (then a subsidiary of the Hawker Siddeley Group) announced that its mines had only 15 years of production left and concluded that the expense of opening new underground mines in the Sydne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydney Steel Corporation
Sydney Steel Corporation (SYSCO) was a Crown corporation in the province of Nova Scotia, Canada. It owned and operated a steel mill in Sydney. Early history of steelmaking in Sydney An integrated steel mill was established on the southeast side of Sydney Harbour in the Whitney Pier neighbourhood of Sydney, Nova Scotia in 1901 by American investors. This entity was named Dominion Iron and Steel Company Limited (DISCO). Coal from the Dominion Coal Company Limited (DOMCO) was used to create coke to fuel the blast furnaces for smelting iron ore which arrived from Bell Island in Newfoundland. In 1920, DISCO, the Nova Scotia Steel and Coal Company (SCOTIA) in Sydney Mines, and the Wabana ore mine on Bell Island were acquired by the British Empire Steel Corporation (BESCO). In 1930, BESCO reorganized as Dominion Steel and Coal Corporation (DOSCO). Hawker Siddeley Canada purchased DOSCO in 1957. Donald Commission Hawker Siddeley sought to eliminate money losing operations and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donkin, Nova Scotia
Donkin is a Canadian rural village with a population of 532 as of Canada 2021 Census, 2021. Located on the picturesque coastline of Nova Scotia's Cape Breton Island, it is a part of the Cape Breton Regional Municipality. The smaller communities of Port Caledonia and Schooner Pond are directly adjacent to the village proper, connected by a single strip of road called the Donkin Highway. Geography As part of the Cape Breton Regional Municipality, Donkin is located 11 km east of the town of Glace Bay and 32 km east from the city of Sydney, Nova Scotia, Sydney. The nearest village is Port Morien which is 10 km away. Donkin sits on the northeasternmost tip of Cape Breton, along the Marconi Trail which stretches from Glace Bay to Louisbourg, Nova Scotia, Louisbourg. Its coastline offers scenery and several sandy beaches as well as vantage points for bird watching. It is not uncommon to spot whales, seals and other marine life from the shore as well as passing cargo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingan Generating Station
The Lingan Generating Station is a 620 MW Canadian coal-fired electrical generating station located in the community of Lingan in Nova Scotia's Cape Breton Regional Municipality. Lingan is operated by Nova Scotia Power Inc. and is their largest generating station. Lingan Generating Station rests on the shores of the Cabot Strait, open to Indian Bay, approximately south-west of the headland named North Head and north of the headland named Little Head. Its civic address is 2599 Hinchey Avenue, Lingan, NS. A thermal generating station, Lingan was opened by then-provincial Crown corporation Nova Scotia Power Corporation on November 1, 1979 at the height of the 1970s oil crisis. It was designed to burn bituminous coal mined by the Cape Breton Development Corporation (DEVCO) at the nearby Lingan Colliery and the adjacent Phalen Colliery as a means of reducing Nova Scotia's reliance of foreign oil for electrical generation. History In the years following World War II, Nova Scotia, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova Scotia Power Incorporated
Nova Scotia Power Inc. is a vertically integrated electric utility in Nova Scotia, Canada. It is privately owned by Emera and regulated by the provincial government via the Nova Scotia Utility and Review Board (NSUARB). Nova Scotia Power Inc provides electricity to 520,000 residential, commercial and industrial customers in Nova Scotia. History 20th century The Nova Scotia Power Commission was formed in 1919 by the provincial government, following the lead of several other Canadian provinces in establishing Crown corporation electrical utilities. The commission constructed and opened its first hydro plant at Tantallon the following year. Throughout the 1920s-1960s, the commission grew as private and municipal owned hydro plants and electrical utilities went bankrupt or sold their assets. In 1960, Nova Scotia was connected to the New Brunswick Electric Power Commission in the first electrical inter-connection between provinces in Canada. The Nova Scotia Power Commission underwent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boularderie Island
Boularderie Island (pronounced "bull-awn-dree") is an island separating the Cabot Strait from Bras d'Or Lake on the eastern coast of Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, Canada. It takes its name from Louis-Simon le Poupet de la Boularderie, who was granted the area as a concession from the King of France. Geography At 40 km (25 mi) long and between 3 km (2 mi) to 10 km (6 mi) wide, Boularderie Island is Nova Scotia's second largest island after Cape Breton Island. Two outlets of Bras d'Or Lake run on each side of the island to the Atlantic Ocean: * the Great Bras d'Or channel runs along the island's northwestern shore, and * St. Andrews Channel and the Little Bras d'Or channel run along the island's southeastern shore. The extreme northeastern end of the island at Point Aconi fronts the Cabot Strait, whereas the extreme southwestern end at Kempt Head fronts the northern basin of Bras d'Or Lake. The majority of the island is heavily forested, howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Waterford, Nova Scotia
New Waterford (Irish language: ''Port Lairge Ùr'') is an urban community in the Cape Breton Regional Municipality of Nova Scotia, Canada. Geography Formerly known as Barrachois (from barachois, meaning small port, lagoon or pond), its present name is likely derived from the Irish seaport Waterford, from which many early settlers came. Coal mining in the vicinity began as early as 1854 at Lingan and later at Low Point in 1865. New Waterford is located northeast of Sydney, Nova Scotia. It is located near the ocean and is bordered on one side by cliffs. New Waterford has a rather flat terrain and has several fresh water lakes located nearby. Economy New Waterford is a fishing port and former coal-mining community that has been in economic decline in recent years. There are ongoing efforts to revitalize the area's economy including a slow but steady increase in jobs in the technology sector. Many residents had been reliant on the coal and steel industries, which are now closed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a unit of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territories (NWT) to the north, and the U.S. state of Montana to the south. It is one of the only two landlocked provinces in Canada (Saskatchewan being the other). The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly continental climate but experiences quick temperature changes due to air aridity. Seasonal temperature swings are less pronounced in western Alberta due to occasional Chinook winds. Alberta is the fourth largest province by area at , and the fourth most populous, being home to 4,262,635 people. Alberta's capital is Edmonton, while Calgary is its largest city. The two are Alberta's largest census metropolitan areas. More tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Trudeau
Joseph Philippe Pierre Yves Elliott Trudeau ( , ; October 18, 1919 – September 28, 2000), also referred to by his initials PET, was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 15th prime minister of Canada The prime minister of Canada (french: premier ministre du Canada, link=no) is the head of government of Canada. Under the Westminster system, the prime minister governs with the Confidence and supply, confidence of a majority the elected Hou ... from 1968 to 1979 and from 1980 to 1984. He also briefly served as the Leader of the Opposition (Canada), leader of the Opposition from 1979 to 1980. He served as leader of the Liberal Party of Canada from 1968 to 1984. Trudeau was born and raised in Montreal, Quebec; he rose to prominence as a lawyer, intellectual, and activist in Quebec politics. Although he aligned himself with the social democratic New Democratic Party, he felt that they could not achieve power, and instead joined the Liberal Party. He was e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
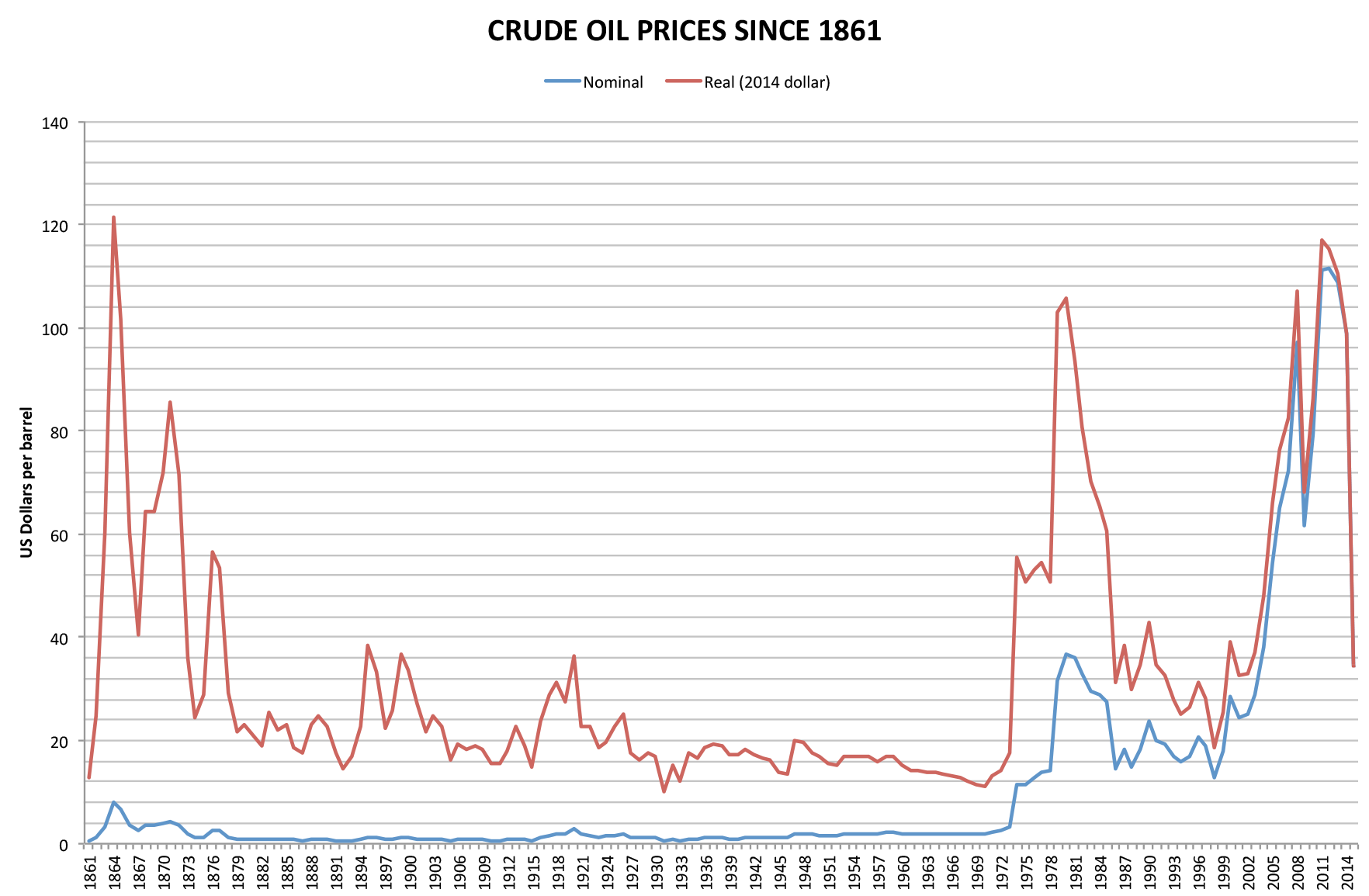
1973 Oil Crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War. The initial nations targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the United States, though the embargo also later extended to Portugal, Rhodesia and South Africa. By the end of the embargo in March 1974, the price of oil had risen nearly 300%, from US to nearly globally; US prices were significantly higher. The embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long-term effects on global politics and the global economy. It was later called the "first oil shock", followed by the 1979 oil crisis, termed the "second oil shock". Background Arab-Israeli conflict Ever since the recreation of the State of Israel in 1948 there has been Arab–Israeli conflict in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yom Kippur War
The Yom Kippur War, also known as the Ramadan War, the October War, the 1973 Arab–Israeli War, or the Fourth Arab–Israeli War, was an armed conflict fought from October 6 to 25, 1973 between Israel and a coalition of Arab states led by Egypt and Syria. The majority of combat between the two sides took place in the Sinai Peninsula and the Golan Heights—both of which were occupied by Israel in 1967—with some fighting in African Egypt and northern Israel. Egypt's initial objective in the war was to seize a foothold on the eastern bank of the Suez Canal and subsequently leverage these gains to negotiate the return of the rest of the Israeli-occupied Sinai Peninsula. The war began on October 6, 1973, when the Arab coalition jointly launched a surprise attack against Israel on the Jewish holy day of Yom Kippur, which had occurred during the 10th of the Islamic holy month of Ramadan in that year. Following the outbreak of hostilities, both the United States and the Soviet U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |