|
Canadian Foundation For Innovation
The Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI; french: Fondation canadienne pour l'innovation, ''FCI'') is an independent not-for-profit organization that invests in research facilities and equipment in Canada's universities, colleges, research hospitals, and non-profit research institutions. Creation The CFI was created by the Government of Canada through the Budget Implementation Act 1997, Bill C-93, to "help build and sustain a research landscape in Canada that will attract and retain the world's top talent, train the next generation of researchers, support private-sector innovation and create high-quality jobs that strengthen Canada's position in today's knowledge economy". Funding The infrastructure funded by the CFI includes the equipment, laboratories, databases, specimens, scientific collections, computer hardware and software, communications linkages and buildings necessary to conduct research. The CFI has established a merit-review process that relies on experts from across C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maclean's
''Maclean's'', founded in 1905, is a Canadian news magazine reporting on Canadian issues such as politics, pop culture, and current events. Its founder, publisher John Bayne Maclean, established the magazine to provide a uniquely Canadian perspective on current affairs and to "entertain but also inspire its readers". Rogers Media, the magazine's publisher since 1994 (after the company acquired Maclean-Hunter Publishing), announced in September 2016 that ''Maclean's'' would become a monthly beginning January 2017, while continuing to produce a weekly issue on the Texture app. In 2019, the magazine was bought by its current publisher, St. Joseph Communications."Toronto Life owner St. Joseph Communications to buy Rogers mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
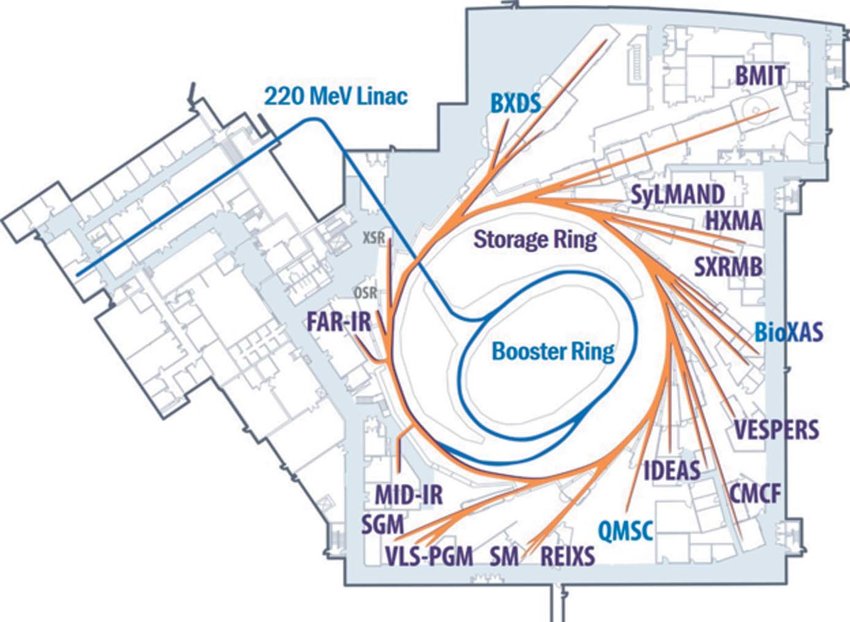
Canadian Light Source Synchrotron
The Canadian Light Source (CLS) (french: link=no, Centre canadien de rayonnement synchrotron – CCRS) is Canada's national synchrotron light source facility, located on the grounds of the University of Saskatchewan in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada. The CLS has a third-generation 2.9 GeV storage ring, and the building occupies a footprint the size of a Canadian football field. It opened in 2004 after a 30-year campaign by the Canadian scientific community to establish a synchrotron radiation facility in Canada. It has expanded both its complement of beamlines and its building in two phases since opening. As a national synchrotron facility with over 1000 individual users, it hosts scientists from all regions of Canada and around 20 other countries. Research at the CLS has ranged from viruses to superconductors to dinosaurs, and it has also been noted for its industrial science and its high school education programs. History The road to the CLS: 1972–1999 Canadian interes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNOLAB
SNOLAB is a Canadian underground science laboratory specializing in neutrino and dark matter physics. Located 2 km below the surface in Vale's Creighton nickel mine near Sudbury, Ontario, SNOLAB is an expansion of the existing facilities constructed for the original Sudbury Neutrino Observatory (SNO) solar neutrino experiment. SNOLAB is the world's deepest operational clean room facility. Although accessed through an active mine, the laboratory proper is maintained as a class-2000 cleanroom, with very low levels of dust and background radiation. SNOLAB's 2070 m (6800 feet) of overburden rock provides 6010 metre water equivalent (MWE) shielding from cosmic rays, providing a low-background environment for experiments requiring high sensitivities and extremely low counting The combination of great depth and cleanliness that SNOLAB affords allows extremely rare interactions and weak processes to be studied. In addition to neutrino and dark matter physics, SNOLAB is also host t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCGS Amundsen
CCGS ''Amundsen''CCGS stands for Canadian Coast Guard Ship is a and Arctic research vessel operated by the Canadian Coast Guard. The vessel entered service in 1979 as ''Franklin'' and was renamed ''Sir John Franklin'' in 1980 and served as such until 1996. Declared surplus, the vessel was used as an accommodation ship in Labrador in 1996 and placed in reserve in 2000. In 2003, the ship was reactivated and underwent conversion to an Arctic research vessel. The ship recommissioned as ''Amundsen''. Design and description The ''Pierre Radisson'' class were designed for Coast Guard operations in the Arctic Ocean.Maginley and Collin, p. 154 ''Amundsen'' has a standard displacement of and is fully loaded. The vessel has a gross tonnage of 5,911 and a net tonnage of 1,678. The ship is long overall with a beam of and a draught of .Saunders, p. 95 The vessel is propelled by two fixed-pitch propellers and one bow thruster powered by a diesel-electric system comprising six Alco M251 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
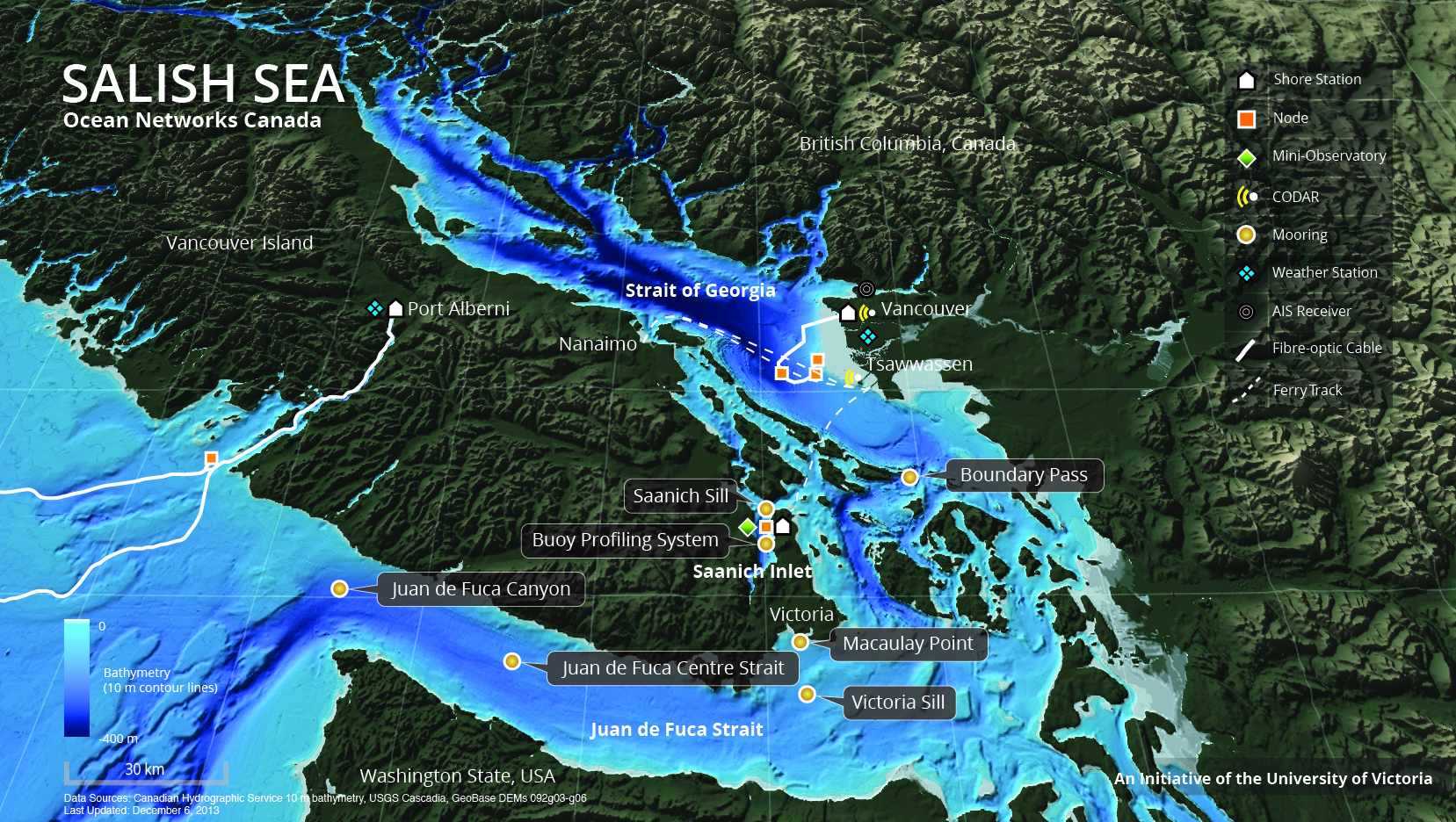
Ocean Networks Canada
Ocean Networks Canada is a University of Victoria initiative that operates the NEPTUNE and VENUS cabled ocean observatories in the northeast Pacific Ocean and the Salish Sea. Additionally, Ocean Networks Canada operates smaller community-based observatories offshore from Cambridge Bay, Nunavut., Campbell River, Kitamaat Village and Digby Island. These observatories collect data on physical, chemical, biological, and geological aspects of the ocean over long time periods. As with other ocean observatories such as ESONET, Ocean Observatories Initiative, MACHO and DONET, scientific instruments connected to Ocean Networks Canada are operated remotely and provide continuous streams of freely available data to researchers and the public. Over 200 gigabytes of data are collected every day. The VENUS Observatory is situated at three main sites in the Salish Sea, including Saanich Inlet (depth 100 m), the eastern and central Strait of Georgia (depths 170–300 m), and the Fraser River delt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Tracking Network
The Ocean Tracking Network is a research effort using implanted acoustic transmitters to study fish migration Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or body of water to another. Many types of fish migrate on a regular basis, on time scales ranging from daily to annually or longer, and over distances ranging from a few metres to thousa ... patterns. It is based at Dalhousie University in Nova Scotia. The technology used by the Ocean Tracking Network comes from the Pacific Ocean Shelf Tracking Project (POST) and the Tagging of Pacific Pelagics (TOPP) project. References * External links * Fisheries databases {{biology-org-stub Acoustics Sound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census Of Marine Life
The Census of Marine Life was a 10-year, US $650 million scientific initiative, involving a global network of researchers in more than 80 nations, engaged to assess and explain the diversity, distribution, and abundance of life in the oceans. The world's first comprehensive Census of Marine Life — past, present, and future — was released in 2010 in London. Initially supported by funding from the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, the project was successful in generating many times that initial investment in additional support and substantially increased the baselines of knowledge in often underexplored ocean realms, as well as engaging over 2,700 different researchers for the first time in a global collaborative community united in a common goal, and has been described as "one of the largest scientific collaborations ever conducted". Project history According to Jesse Ausubel, Senior Research Associate of the Program for the Human Environment of Rockefeller University and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barcode Of Life
The Consortium for the Barcode of Life (CBOL) was an international initiative dedicated to supporting the development of DNA barcoding as a global standard for species identification. CBOL's Secretariat Office is hosted by the National Museum of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, in Washington, DC. Barcoding was proposed in 2003 by Prof. Paul Hebert of the University of Guelph in Ontario as a way of distinguishing and identifying species with a short standardized gene sequence. Hebert proposed the 658 bases of the Folmer region of the mitochondrial gene cytochrome-C oxidase-1 as the standard barcode region. Hebert is the Director of the Biodiversity Institute of Ontario, the Canadian Centre for DNA Barcoding, and the International Barcode of Life Project (iBOL), all headquartered at the University of Guelph. The Barcode of Life Data Systems (BOLD) is also located at the University of Guelph. CBOL was created in May 2004 with support of the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Departments And Agencies Of Canada
Federal or foederal (archaic) may refer to: Politics General *Federal monarchy, a federation of monarchies *Federation, or ''Federal state'' (federal system), a type of government characterized by both a central (federal) government and states or regional governments that are partially self-governing; a union of states *Federal republic, a federation which is a republic *Federalism, a political philosophy *Federalist, a political belief or member of a political grouping *Federalization, implementation of federalism Particular governments *Federal government of the United States **United States federal law **United States federal courts *Government of Argentina *Government of Australia *Government of Pakistan *Federal government of Brazil *Government of Canada *Government of India *Federal government of Mexico * Federal government of Nigeria *Government of Russia *Government of South Africa *Government of Philippines Other *''The Federalist Papers'', critical early arguments in fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funding Bodies Of Canada
Funding is the act of providing resources to finance a need, program, or project. While this is usually in the form of money, it can also take the form of effort or time from an organization or company. Generally, this word is used when a firm uses its internal reserves to satisfy its necessity for cash, while the term financing is used when the firm acquires capital from external sources. Sources of funding include credit, venture capital, donations, grants, savings, subsidies, and taxes. Fundings such as donations, subsidies, and grants that have no direct requirement for return of investment are described as "soft funding" or "crowdfunding". Funding that facilitates the exchange of equity ownership in a company for capital investment via an online funding portal per the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act (alternately, the "JOBS Act of 2012") (U.S.) is known as equity crowdfunding. Funds can be allocated for either short-term or long-term purposes. Economics In economics fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology Companies Of Canada
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, industry, communication, transportation, and daily life. Technologies include physical objects like utensils or machines and intangible tools such as software. Many technological advancements have led to societal changes. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used in the prehistoric era, followed by fire use, which contributed to the growth of the human brain and the development of language in the Ice Age. The invention of the wheel in the Bronze Age enabled wider travel and the creation of more complex machines. Recent technological developments, including the printing press, the telephone, and the Internet have lowered communication barriers and ushered in the knowledge economy. While technology contributes to economic de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Management
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |