|
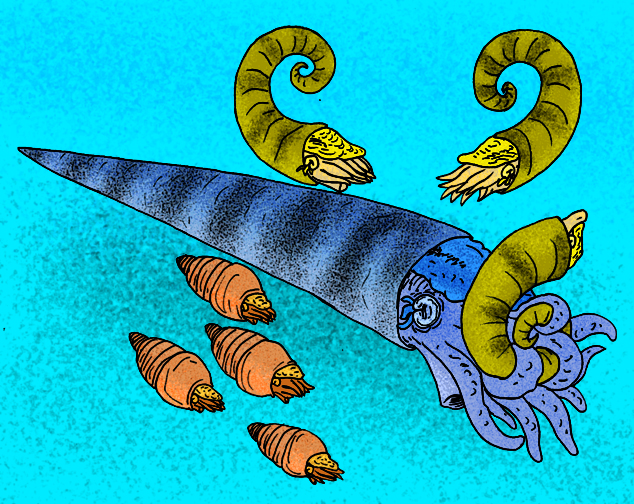
Cameroceras
''Cameroceras'' ("chambered horn") is a genus of extinct, giant orthoconic cephalopod that lived mainly during the Ordovician period. It first appears during the middle Ordovician, around 470 million years ago, and was a fairly common component of the fauna in some places during the period, inhabiting the shallow seas of Laurentia, Baltica and Siberia.Frey, R.C. 1995. U.S. Geological Survey, p.73 Its diversity and abundance became severely reduced following the Ordovician–Silurian extinction events, and the last remnants of the genus went extinct sometime during the Wenlock. In older literature ''Cameroceras'' was treated as the largest nautiloid with shell length about or even , however the large-sized species is no longer belong to genus ''Cameroceras'' but ''Endoceras giganteum'', and the -long specimen is highly doubtful. Description ''Cameroceras'' is a cephalopod, a taxon of molluscs that includes the octopuses, squids and cuttlefish. From comparison with living cephalo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cameroceras Trentonese
''Cameroceras'' ("chambered horn") is a genus of extinct, giant orthocone, orthoconic cephalopod that lived mainly during the Ordovician period. It first appears during the middle Ordovician, around 470 million years ago, and was a fairly common component of the fauna in some places during the period, inhabiting the shallow seas of Laurentia, Baltica and Siberia (continent), Siberia.Frey, R.C. 1995. U.S. Geological Survey, p.73 Its diversity and abundance became severely reduced following the Ordovician–Silurian extinction events, and the last remnants of the genus went extinct sometime during the Wenlock (Silurian), Wenlock. In older literature ''Cameroceras'' was treated as the largest nautiloid with shell length about or even , however the large-sized species is no longer belong to genus ''Cameroceras'' but ''Endoceras giganteum'', and the -long specimen is highly doubtful. Description ''Cameroceras'' is a cephalopod, a taxon of molluscs that includes the octopuses, squids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod Size
Cephalopods vary enormously in size. The smallest are only about long and weigh less than at maturity, while the largest—the giant and colossal squids—can exceed in length and weigh close to half a tonne (), making them the largest living invertebrates. Living species range in mass more than three-billion-fold, or across nine orders of magnitude, from the lightest hatchlings to the heaviest adults. Certain cephalopod species are also noted for having individual body parts of exceptional size. The giant and colossal squids, for example, have the largest known eyes among living animals. Nilsson ''et al.'', 2012:683 Cephalopods were at one time the largest of all organisms on Earth, and numerous species of comparable size to the largest present day squids are known from the fossil record, including enormous examples of ammonoids, belemnoids, nautiloids, orthoceratoids, teuthids, and vampyromorphids. In terms of mass, the largest of all known cephalopods were likely the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoceras
''Endoceras'' (Ancient Greek for "inner horn") is an extinct genus of large, straight shelled cephalopods from the Middle and Upper Ordovician that gives its name to the Nautiloid order Endocerida. The cross section in the mature portion is slightly wider than high, but is narrower laterally in the young. Sutures are straight and transverse. ''Endoceras'' has a large siphuncle, located close to the ventral margin, composed of concave segments, especially in the young but which may be tubular in the adult stage. Endocones are simple, subcircular in cross section, and penetrated by a narrow tube which may contain diaphragms reminiscent of the Ellesmerocerid ancestor. ''Endoceras'' was named by Hall in 1847. Distribution is widespread, especially in North America and Europe; and fossils have been found in Australia. ''Endoceras'' is similar to ''Cameroceras'', the two may be synonymous, but differs from the genus '' Nanno'' in that the siphuncle in ''Nanno'' fills the entire api ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician–Silurian Extinction Events
The Late Ordovician mass extinction (LOME), sometimes known as the end-Ordovician mass extinction or the Ordovician-Silurian extinction, is the first of the "big five" major Extinction event, mass extinction events in Earth's history, occurring roughly 443 Mya. It is often considered to be the second-largest known extinction event, in terms of the percentage of Genus, genera that became extinct. Extinction was global during this interval, eliminating 49–60% of marine genera and nearly 85% of marine species. Under most tabulations, only the Permian–Triassic extinction event, Permian-Triassic mass extinction exceeds the Late Ordovician mass extinction in biodiversity loss. The extinction event abruptly affected all major taxonomic groups and caused the disappearance of one third of all brachiopod and bryozoan families, as well as numerous groups of conodonts, trilobites, echinoderms, corals, Bivalvia, bivalves, and graptolites. Despite its taxonomic severity, the Late Ordovician m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chambered Nautilus
The chambered nautilus (''Nautilus pompilius''), also called the pearly nautilus, is the best-known species of nautilus. The shell, when cut away, reveals a lining of lustrous nacre and displays a nearly perfect equiangular spiral, although it is not a golden spiral. The shell exhibits countershading, being light on the bottom and dark on top. This is to help avoid predators, because when seen from above, it blends in with the darkness of the sea, and when seen from below, it blends in with the light coming from above. The range of the chambered nautilus encompasses much of the south Pacific; It has been found near reefs and on the seafloor off of the coasts of Australia, Japan, and Micronesia. The eyes of the chambered nautilus, like those of all ''Nautilus'' species, are more primitive than those of most other cephalopods; the eye has no lens and thus is comparable to a pinhole camera. The species has about 90 cirri (referred to as "tentacles", see ) that do not have suckers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic Life Of Ontario
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838 by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (), "life", meaning "ancient life" ). It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from , and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): # Cambrian # Ordovician # Silurian # Devonian # Carboniferous # Permian The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic was a time of dramatic geological, climatic, and evolutionary change. The Cambrian witnessed the most rapid and widespread diversification of life in Earth's history, known as the Cambrian explosion, in which most modern phyla first appeared. Arthropods, molluscs, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and synapsids all evolved during the Paleozoic. Life began in the ocean but even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1842
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician Cephalopods Of North America
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier Cambri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Nautiloid Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treatise On Invertebrate Paleontology
The ''Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology'' (or ''TIP'') published by the Geological Society of America and the University of Kansas Press, is a definitive multi-authored work of some 50 volumes, written by more than 300 paleontologists, and covering every phylum, class, order, family, and genus of fossil and extant (still living) invertebrate animals. The prehistoric invertebrates are described as to their taxonomy, morphology, paleoecology, stratigraphic and paleogeographic range. However, taxa with no fossil record whatsoever have just a very brief listing. Publication of the decades-long ''Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology'' is a work-in-progress; and therefore it is not yet complete: For example, there is no volume yet published regarding the post-Paleozoic era caenogastropods (a molluscan group including the whelk and Common periwinkle, periwinkle). Furthermore, every so often, previously published volumes of the ''Treatise'' are revised. Evolution of the proje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trenton Limestone
The Trenton Formation is a geologic formation in Canada and Michigan, Ohio, and Indiana in the United States. It preserves fossils dating back to the Ordovician period. See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Michigan * Trenton Gas Field The Trenton Gas Field is located in east central Indiana and the most western portion of west central Ohio. The field was discovered in 1876, but the size and magnitude of the field was not known until the 1880s. The field was the largest natural g ... * Indiana gas boom * Petroleum industry in Ohio References * Ordovician System of North America Ordovician Michigan Ordovician geology of New York (state) Ordovician geology of Virginia Ordovician southern paleotemperate deposits Middle Ordovician Series {{Michigan-geologic-formation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meniscoceras
''Meniscoceras'' is a straight and slender Chazyan endocerid described by Rousseau Flower in 1941 The genus was originally included in the Proterocameroceratidae (Flower, 1955) but later (Flower, 1976) placed with its predecessor, ''Najaceras'', in the Najaceratidae. The siphuncle in ''Mensicoceras'' is large with short septal necks and thin connecting rings. Endocones are vertically asymmetric. The central cavity is dorsally concave where a broad dorsal process is formed in which is said to contain a pair of dorso-lateral blades, and flat ventrally. ''Mensicoceras'' from the Chazy and the earlier ''Najaceras'' from the Whiterock age are similar in having a longitudual process formed along the inner dorsal side of the siphuncle around which the endocones form, but differ in details such as with the central opening. On that basis the two have been separated into their own family, the Najaceratidae (Flower 1971,1976). The ''Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology The ''Treati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |