|
Camels Head Halt Railway Station
Camels Head Halt railway station, named after a local public house in Plymouth, was opened as part of the city's suburban network by the London and South Western Railway in 1906, closing in 1942. It was located on the outskirts of the city in sight of the Great Western Railway main line that crossed the River Tamar by the Royal Albert Bridge. Infrastructure As stated the halt was named after a local pub and although it officially opened on 1 November 1906 it may have had services from Wednesday 26 September when the suburban service was actually launched. This difference could be the result of a complaint by the Plymouth, Devonport and South Western Junction Railway to the London and South Western Railway that while they had constructed the halt, the LSWR had not provided any service, with a subsequent report that services commenced before the official opening date. Camels Head Halt closed on the Sunday 4 May 1942. A 1964 photograph shows one platform, still with its nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west. Plymouth's early history extends to the Bronze Age when a first settlement emerged at Mount Batten. This settlement continued as a trading post for the Roman Empire, until it was surpassed by the more prosperous village of Sutton founded in the ninth century, now called Plymouth. In 1588, an English fleet based in Plymouth intercepted and defeated the Spanish Armada. In 1620, the Pilgrim Fathers departed Plymouth for the New World and established Plymouth Colony, the second English settlement in what is now the United States of America. During the English Civil War, the town was held by the Roundhead, Parliamentarians and was besieged between 1642 and 1646. Throughout the Industrial Revolution, Plymouth grew as a commercial shipping port, handling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weston Mill Halt Railway Station
Weston Mill Halt railway station was named after a mill and quay with its lime kiln sitting on Weston Mill Lake next to the River Tamar. The small settlement of Weston Mill also lay near by and the halt was opened as part of Plymouth's suburban network development, together with other halts such as the nearby Camels Head Halt, by the London and South Western Railway in 1906, closing in 1921 or Sunday 4 May 1942. It was located on the outskirts of the city not far from the Great Western Railway main line's Weston Mill Bridge. Infrastructure As stated the halt, with the entrance on Bridewell Road, was named after a well known local mill where housing developments had taken place and although it officially opened on 1 November 1906 it may have had services from Wednesday 26 September when suburban service was launched. Some disagreement exists over its closure date that is variously recorded as being from the 27 June 1921, 14 September 1921 or even Sunday 4 May 1942. Like Came ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Closed In 1942
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Opened In 1906
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Railway (Great Britain)
The Southern Railway (SR), sometimes shortened to 'Southern', was a British railway company established in the 1923 Grouping. It linked London with the Channel ports, South West England, South coast resorts and Kent. The railway was formed by the amalgamation of several smaller railway companies, the largest of which were the London and South Western Railway (LSWR), the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR) and the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR).Bonavia (1987) pp. 26-28 The construction of what was to become the Southern Railway began in 1838 with the opening of the London and Southampton Railway, which was renamed the London & South Western Railway. The railway was noted for its astute use of public relations and a coherent management structure headed by Sir Herbert Walker. At , the Southern Railway was the smallest of the '' Big Four'' railway companies and, unlike the others, the majority of its revenue came from passenger traffic rather than freight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
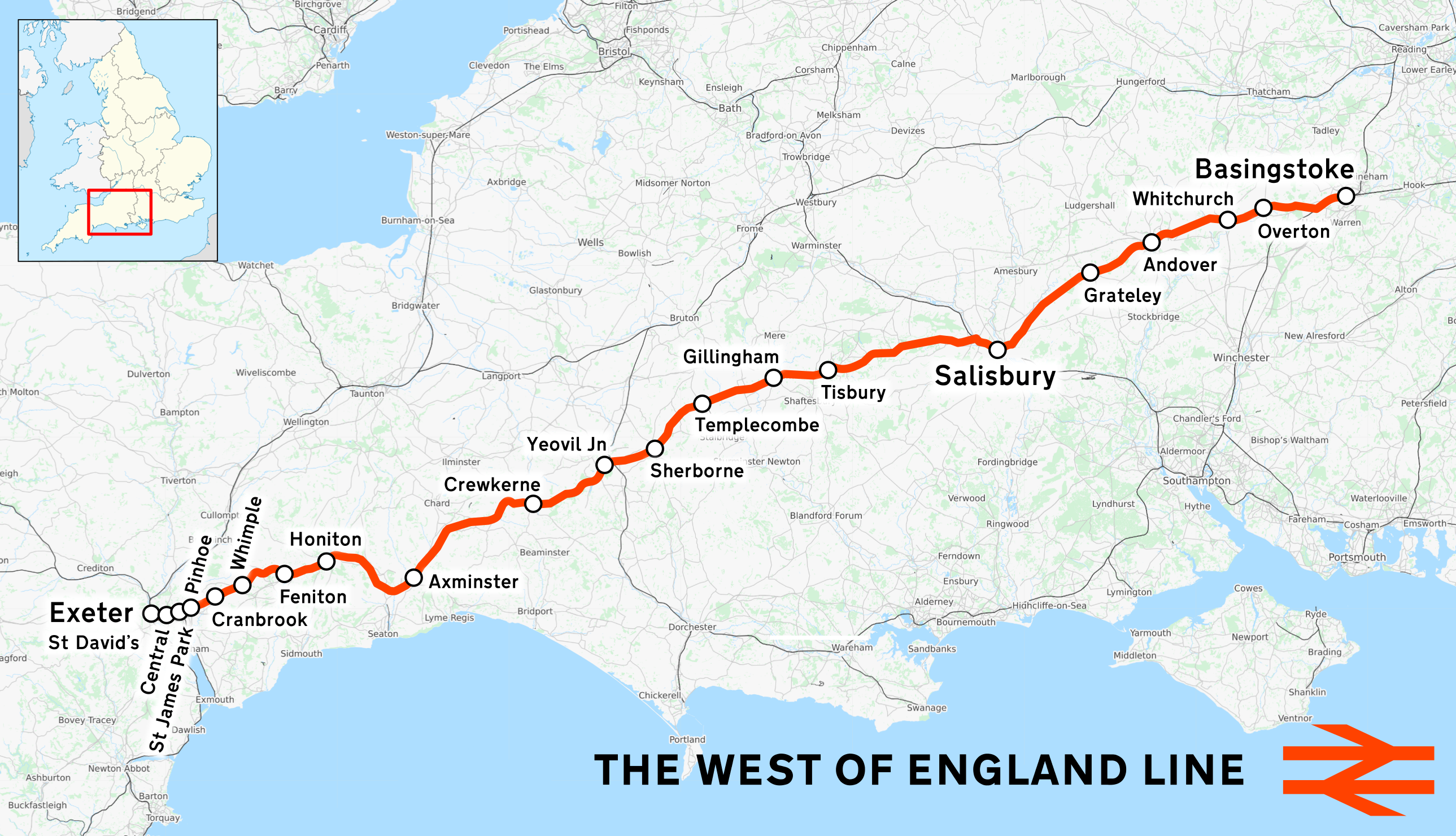
West Of England Main Line
The West of England line (also known as the West of England Main Line) is a British railway line from , Hampshire, to in Devon, England. Passenger services run between London Waterloo station and Exeter; the line intersects with the Wessex Main Line at . Despite its historic title, it is not today's principal route from London to the West of England: Exeter and everywhere further west are reached more quickly from London Paddington via the Reading–Taunton line. History Once all sections had been incorporated into the London and South Western Railway, the sections and branches were: * Basingstoke to Salisbury ** Basingstoke to Andover, opened 3 July 1854 ** Andover to Salisbury, opened 1 May 1857 ** Branches: ***''Basingstoke and Alton Light Railway'' opened June 1901, closed 30 May 1936 *** From Hurstbourne and Andover to Romsey and on to Eastleigh and Southampton: both closed. Link via Longparish opened 1 June 1885; closed 6 July 1931. *** At Andover, junction with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford (Devon) Railway Station
Ford (Devon) railway station was originally named Ford railway station and stood at the eastern end of Station Road, Keyham Barton in Plymouth, South Devon. History Ford station was built by the Plymouth, Devonport and South Western Junction Railway Company and came into use when the line from Lydford to Plymouth was opened on Monday 2 June 1890. Ford was joined by a number of new halts in 1906 such as Weston Mill Halt and Camels Head Halt that were constructed to allow a suburban service to be operated between Plymouth Friary and St Budeaux for Saltash station in response to competition from tram lines. William Brown, from Gosport, was the first station master and for 30 years served at the station, retiring in 1920. The station's name in the public timetables was changed to Ford (Devon) in July 1923 to prevent confusion with Ford station in Sussex, however the name board was never altered. In 1932 one goods train, the 8:12am from Friary to Exmouth Junction Goods Yard, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonport, Plymouth
Devonport ( ), formerly named Plymouth Dock or just Dock, is a district of Plymouth in the English county of Devon, although it was, at one time, the more important settlement. It became a county borough in 1889. Devonport was originally one of the "Three Towns" (along with Plymouth and East Stonehouse); these merged in 1914 to form what would become in 1928 the City of Plymouth. It is represented in the Parliament of the United Kingdom as part of the Plymouth Sutton and Devonport constituency. Its elected Member of Parliament (MP) is Luke Pollard, who is a member of the Labour Party. The population of the ward at the 2011 census was 14,788. History Plymouth Dock In 1690 the Admiralty gave a contract to Robert Waters from Portsmouth to build a stone dock at Point Froward on the east bank of the Hamoaze at the mouth of the River Tamar. Plymouth Dock, as Devonport was originally called, began around 1700 as a small settlement to house workers employed on the new naval base tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth Friary Railway Station
Plymouth Friary railway station was the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) terminus in Plymouth, Devon, England. History London and South Western Railway trains first arrived at Plymouth on 17 May 1876, entering the town from the east. To get there trains had travelled over the company's line as far as Lydford railway station, then over the Great Western Railway (GWR) Launceston branch via Tavistock and the South Devon main line to Mutley. They then continued over the new Cornwall Loop Viaduct (now known as Pennycomequick Viaduct) and a short section of the Cornwall Railway before reaching the company's line to its Devonport station. A new joint LSWR and GWR station at Plymouth North Road, a short distance to the west of Mutley, was opened on 28 March 1877. Friary Goods Station had opened on 1 February 1878 at the end of a short branch from Friary Junction near Laira on the GWR's Sutton Harbour branch. On 22 October 1879 an extension was opened through a short tunn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
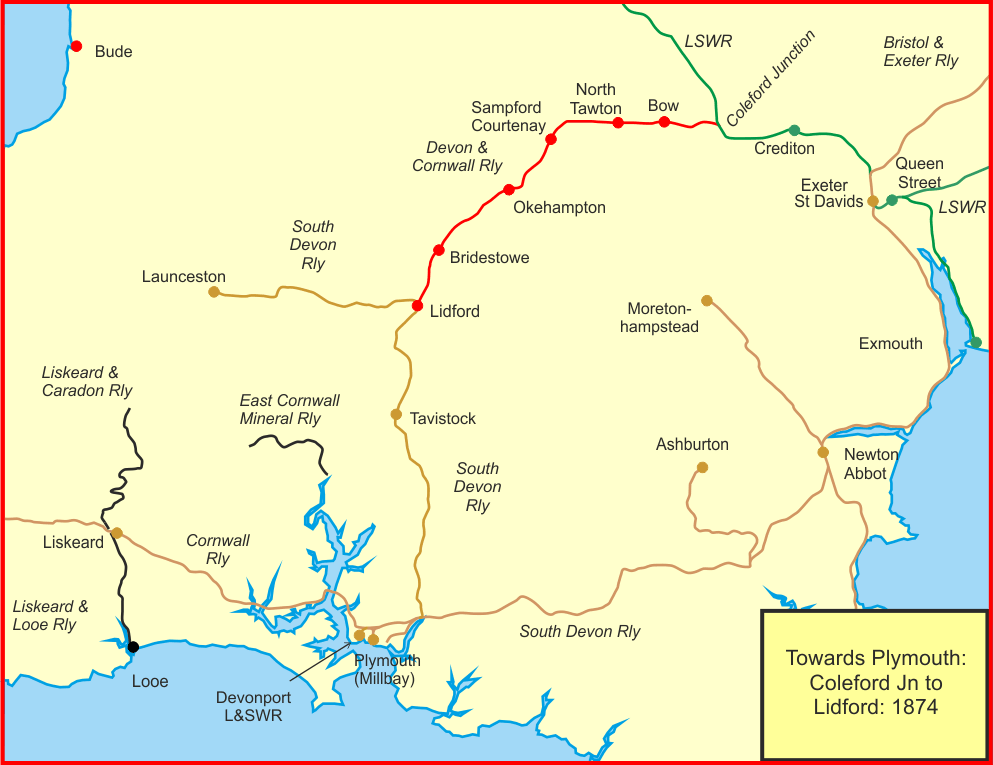
Exeter To Plymouth Railway Of The LSWR
The Exeter to Plymouth railway of the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) was the westernmost part of a route competing with that of the Great Western Railway (GWR) and its 'associated companies' from London and Exeter to Plymouth in Devon, England. Whereas the GWR route from Exeter followed the coast to Newton Abbot and then went around the southern edge of Dartmoor, the LSWR route followed the northern and western margins of Dartmoor, passing through the towns of Crediton, Okehampton, and Tavistock. The route was constructed piecemeal by independent companies, in most cases supported by the LSWR. LSWR trains first reached Plymouth in 1876 and the route took on its final form in 1891. The central part of the line closed in 1968, leaving just local services at either end. History Railways to Exeter The broad gauge Bristol and Exeter Railway (B&ER) was the first line to reach Exeter. It had reached St Davids station in Exeter in 1844 and was allied with the Great We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Budeaux Victoria Road
St Budeaux Victoria Road railway station is a suburban station in St Budeaux, Plymouth, Devon, England. The station is managed and served by Great Western Railway. History The Plymouth, Devonport and South Western Junction Railway opened its St Budeaux station on 2 June 1890 with its main line from to Devonport, which gave the London and South Western Railway a route into Plymouth that was independent of the Great Western Railway. The station was close to the road to the Saltash ferry across the River Tamar. A connection to the Great Western Railway was installed east of the station on 21 March 1941 to offer the two companies alternative routes between Plymouth and St Budeaux should either line be closed due to bombing during World War II. On 7 September 1964 the original line into Devonport was closed, and all trains use the former Great Western route and the wartime connection to reach St Budeaux, renamed St Budeaux Victoria Road to differentiate it from , opened by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is a coastal county with cliffs and sandy beaches. Home to the largest open space in southern England, Dartmoor (), the county is predominately rural and has a relatively low population density for an English county. The county is bordered by Somerset to the north east, Dorset to the east, and Cornwall to the west. The county is split into the non-metropolitan districts of East Devon, Mid Devon, North Devon, South Hams, Teignbridge, Torridge, West Devon, Exeter, and the unitary authority areas of Plymouth, and Torbay. Combined as a ceremonial county, Devon's area is and its population is about 1.2 million. Devon derives its name from Dumnonia (the shift from ''m'' to ''v'' is a typical Celtic consonant shift). During the Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |