|
Camelpox Virus
Camelpox is a disease of camels caused by the camelpox virus (CMPV) of the family ''Poxviridae'', subfamily ''Chordopoxvirinae'', and the genus ''Orthopoxvirus''. It causes skin lesions and a generalized infection. Approximately 25% of young camels that become infected will die from the disease, while infection in older camels is generally more mild. Although rare, the infection may spread to the hands of those that work closely with camels. Cause The camelpox virus that causes camelpox is an orthopoxvirus that is very closely related to the variola virus that causes smallpox. It is a large, brick-shaped, enveloped virus that ranges in size from 265–295 nm. The viral genetic material is contained in a linear double-stranded DNA consisting of 202,182 tightly packed base pairs. The DNA is encased in the viral core. Two lateral bodies are found outside the viral core, and are believed to hold the enzymes required for viral reproduction. The camelpox virus most often aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
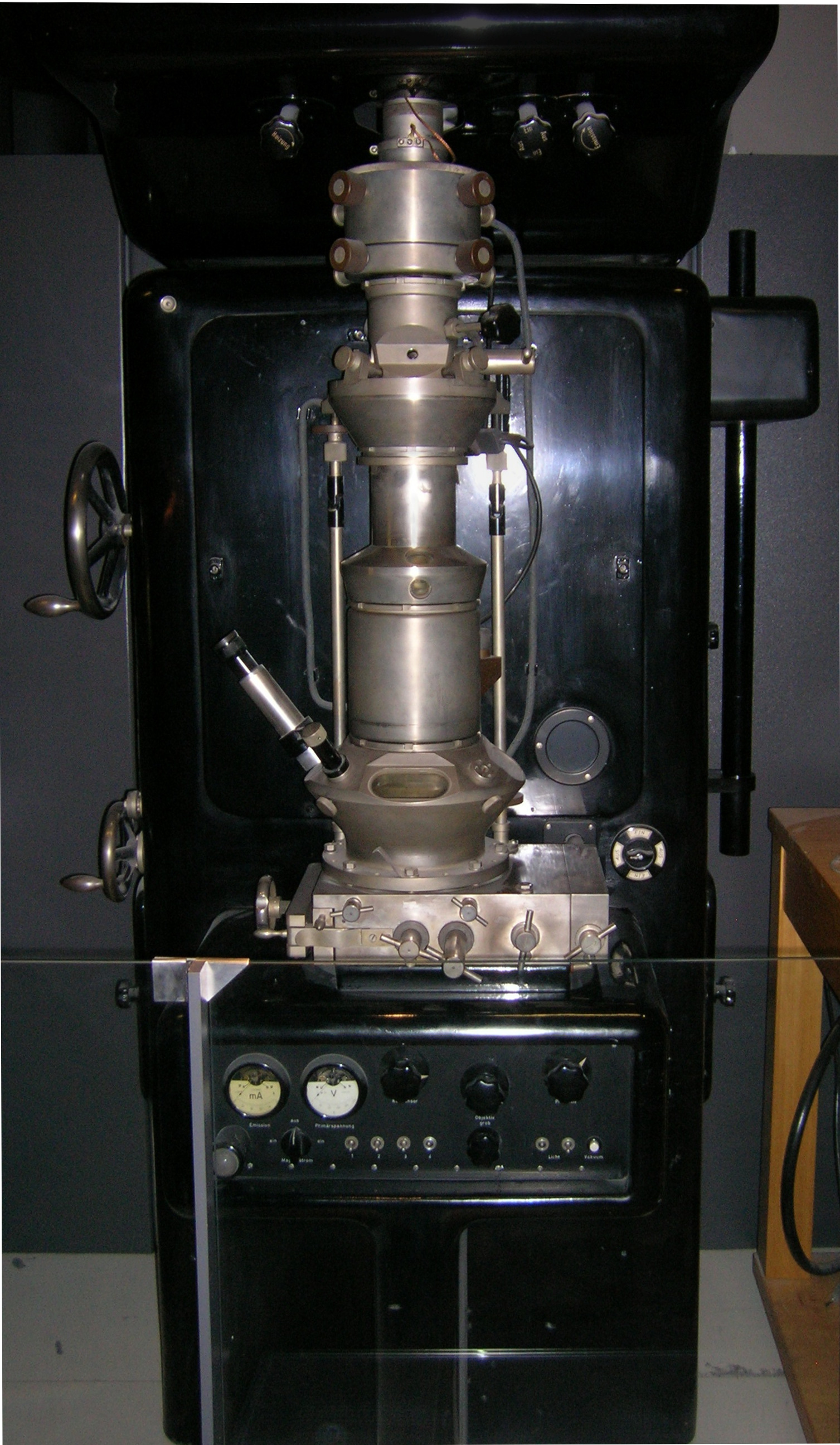
Transmission Electron Micrograph
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. An image is formed from the interaction of the electrons with the sample as the beam is transmitted through the specimen. The image is then magnified and focused onto an imaging device, such as a fluorescent screen, a layer of photographic film, or a sensor such as a scintillator attached to a charge-coupled device. Transmission electron microscopes are capable of imaging at a significantly higher resolution than light microscopes, owing to the smaller de Broglie wavelength of electrons. This enables the instrument to capture fine detail—even as small as a single column of atoms, which is thousands of times smaller than a resolvable object seen in a light microscope. Transmission electron microscopy is a major analytical method i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cidofovir
Cidofovir, brand name Vistide, is a topical or injectable antiviral medication primarily used as a treatment for cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis (an infection of the retina of the eye) in people with AIDS. Cidofovir was approved for medical use in 1996. Medical use DNA virus Its only indication that has received regulatory approval worldwide is cytomegalovirus retinitis. Cidofovir has also shown efficacy in the treatment of aciclovir-resistant HSV infections. Cidofovir has also been investigated as a treatment for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy with successful case reports of its use. Despite this, the drug failed to demonstrate any efficacy in controlled studies. Cidofovir might have anti-smallpox efficacy and might be used on a limited basis in the event of a bioterror incident involving smallpox cases. Brincidofovir, a cidofovir derivative with much higher activity against smallpox that can be taken orally has been developed. It has inhibitory effects on var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-viral Medication
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do not destroy their target pathogen; instead they inhibit its development. Antiviral drugs are one class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic (also termed antibacterial), antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to treat infections. They should be distinguished from viricides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural viricides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees. Medical uses Most of the antiviral drugs now available are designed to help deal with HIV, herpes viruses, the he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) to a large enough amount to study in detail. PCR was invented in 1983 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation; Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serological
Serology is the scientific study of serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given microorganism), against other foreign proteins (in response, for example, to a mismatched blood transfusion), or to one's own proteins (in instances of autoimmune disease). In either case, the procedure is simple. Serological tests Serological tests are diagnostic methods that are used to identify antibodies and antigens in a patient's sample. Serological tests may be performed to diagnose infections and autoimmune illnesses, to check if a person has immunity to certain diseases, and in many other situations, such as determining an individual's blood type. Serological tests may also be used in forensic serology to investigate crime scene evidence. Several methods can be used to detect antibodies and antigens, including ELISA, agglutinati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Electron Microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. An image is formed from the interaction of the electrons with the sample as the beam is transmitted through the specimen. The image is then magnified and focused onto an imaging device, such as a fluorescent screen, a layer of photographic film, or a sensor such as a scintillator attached to a charge-coupled device. Transmission electron microscopes are capable of imaging at a significantly higher resolution than light microscopes, owing to the smaller de Broglie wavelength of electrons. This enables the instrument to capture fine detail—even as small as a single column of atoms, which is thousands of times smaller than a resolvable object seen in a light microscope. Transmission electron microscopy is a major analytical method i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papillomatosis
Papillomatosis of skin is skin surface elevation caused by hyperplasia and enlargement of contiguous dermal papillae.Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) ''Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease'' (7th ed.). Saunders. Page 1230. . These papillary projections of the epidermis form an undulating surface under microscopic examination. See also * Skin lesion * Skin disease * List of skin diseases * Papilloma * Laryngeal papillomatosis Laryngeal papillomatosis, also known as recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) or glottal papillomatosis, is a rare medical condition in which benign tumors (papilloma) form along the aerodigestive tract. There are two variants based on the ag ... References External links {{Clinical and histological nomenclature for skin lesions Dermatologic terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecthyma
Ecthyma( ec·thy·ma , \ ek-ˈthī-mə )is a variation of impetigo, presenting at a deeper level of tissue. It is usually associated with Group A (beta-hemolytic) Streptococcus (abbreviated GAS). See also * Ecthyma gangrenosum Ecthyma gangrenosum is a type of skin lesion characterized by vesicles or blisters which rapidly evolve into pustules and necrotic ulcers with undermined tender erythematous border. "Ecthyma" means a pus forming infection of the skin with an ulcer ... References External links {{Bacterial cutaneous infections Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pustule
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. Conditions of the human integumentary system constitute a broad spectrum of diseases, also known as dermatoses, as well as many nonpathologic states (like, in certain circumstances, melanonychia and racquet nails). While only a small number of skin diseases account for most visits to the physician, thousands of skin conditions have been described. Classification of these conditions often presents many nosological challenges, since underlying causes and pathogenetics are often not known. Therefore, most current textbooks present a classification based on location (for example, conditions of the mucous membrane), morphology ( chronic blistering conditions), cause (skin conditions result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papule
A papule is a small, well-defined bump in the skin. It may have a rounded, pointed or flat top, and may have a dip. It can appear with a stalk, be thread-like or look warty. It can be soft or firm and its surface may be rough or smooth. Some have crusts or scales. A papule can be flesh colored, yellow, white, brown, red, blue or purplish. There may be just one or many, and they may occur irregularly in different parts of the body or appear in clusters. It does not contain fluid but may progress to a pustule or vesicle. A papule is smaller than a nodule; it can be as tiny as a pinhead and is typically less than 1 cm in width, according to some sources, and 0.5 cm according to others. When merged together, it appears as a plaque. Its color might indicate its cause, such as white in milia, red in eczema, yellowish in xanthoma and black in melanoma. They may open when scratched and become infected and crusty. Definition A papule is a small, well-defined bump in the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


