|
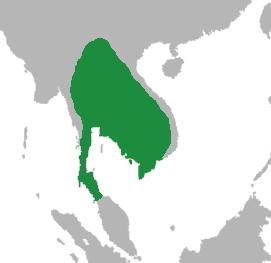
Cambodian Irredentism
Cambodian irredentism is a nationalist movement in Cambodia that refer to the land that used to be part of the Khmer Empire. The irredentist movement in Cambodia is aimed against the control by Thailand, Vietnam and Laos. Irredentist, official and unofficial Cambodian claims on territories viewed by Cambodians as having been under some form of Cambodian sovereignty, are rhetorically tied back to an accused expansionism. History Up until the establishment of the Thai and Laotian states, the Khmer Empire was the major land power and a dominant force in mainland Southeast Asia. The territory of Cambodia encompassed most of what would be now Thailand, Laos, part of Myanmar and Southern Vietnam; in an extent, it encroached to even mainland Malaysia. However, subsequent problems and turmoils, as well as the rapid advance by the Vietnamese, Laotians and Thais brought Cambodia's empire into a declining state. Among all, the Thais and the Vietnamese were seen to have done the most harm t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khmer Empire1
Khmer(s) may refer to: Cambodia *''Srok Khmer'' (lit. "Khmer land" or "Land of the Khmer(s)"), a colloquial exonym used to refer to Cambodia by Cambodians; see * *Khmer people, the ethnic group to which the great majority of Cambodians belong **Khmer Americans, Americans of Khmer (Cambodian) ancestry **Khmer Krom, Khmer people living in the Mekong Delta and Southeast Vietnam **Khmer Loeu, the Mon-Khmer highland tribes in Cambodia **Northern Khmer people, ethnic Khmer people of Northeast Thailand *Khmer (Unicode block), a block of Unicode characters of the Khmer script *Khmer architecture, the architecture of Cambodia *Khmer cuisine, the dominant cuisine in Cambodia * Khmer Empire, which ruled much of Indochina from the 9th to the 13th centuries *Khmer Issarak, anti-French, Khmer nationalist political movement formed in 1945 *Khmer language, the language of the Khmers, also the official and national language of Cambodia **Khmer Khe dialect, a Khmeric language spoken in Stung Treng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambodian–Vietnamese War
The Cambodian–Vietnamese War ( km, សង្គ្រាមកម្ពុជា-វៀតណាម, vi, Chiến tranh Campuchia–Việt Nam), known in Vietnam as the Counter-offensive on the Southwestern border ( vi, Chiến dịch Phản công Biên giới Tây-Nam), and by Cambodian nationalists as the Vietnamese invasion of Cambodia ( km, ការឈ្លានពានរបស់វៀតណាមមកកម្ពុជា), was an armed conflict between Democratic Kampuchea, controlled by the Khmer Rouge, and the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. The war began with repeated attacks by the Liberation Army of Kampuchea on the southwestern border of Vietnam, particularly the Ba Chuc massacre which resulted in the deaths of over 3,000 Vietnamese civilians. On 25 December 1978, Vietnam launched a full-scale invasion of Kampuchea, and subsequently occupied the country and removed the government of the Communist Party of Kampuchea from power. During the Vietnam War, Vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam Under Chinese Rule
Vietnam under Chinese rule or ''Bắc thuộc'' (北屬, lit. "belonging to the north") (111 BC-939, 1407-1427) refers to four historical periods when several portions of modern-day Northern Vietnam was under the rule of various Chinese dynasties. ''Bắc thuộc'' in Vietnamese historiography is traditionally considered to have started in 111 BC, when the Han dynasty conquered Nanyue and lasted after the fall of the Tang dynasty in the 10th century. A fourth, relatively brief, 20-year rule by the Ming dynasty during the 15th century is usually excluded by historians in their discussion of the main, almost continuous, period of Chinese rule from 111 BC to 939 AD. These periods are largely modern reconstructions, however, and are often twisted to serve various nationalist and irredentist causes in China, Vietnam, and other countries. Periods of Chinese rule The four periods of Chinese rule in Vietnam: Geographical extent and impact The four periods of Chinese rule did not corresp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Diplomat
''The Diplomat'' is an international online news magazine covering politics, society, and culture in the Indo-Pacific region. It is based in Washington, D.C. It was originally an Australian bi-monthly print magazine, founded by Minh Bui Jones, David Llewellyn-Smith and Sung Lee in 2001, but due to financial reasons it was converted into an online magazine in 2009 and moved to Japan and later Washington, D.C. The magazine is currently owned by MHT Corporation. History ''The Diplomat'' was originally an Australian bi-monthly print magazine, founded by Minh Bui Jones, David Llewellyn-Smith and Sung Lee in 2001. The first edition was published in April 2002, with Bui Jones as the founding editor and Llewellyn-Smith the founding publisher. The magazine was acquired by James Pach through his company Trans-Asia Inc. in December 2007. Pach assumed the role of executive publisher and hired former ''Penthouse'' editor Ian Gerrard to update its presentation. Nonetheless, the print ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hun Sen
Hun Sen (; km, ហ៊ុន សែន, ; born 5 August 1952) is a Cambodian politician and former military commander who has served as the prime minister of Cambodia since 1985. He is the longest-serving head of government of Cambodia, and one of the longest-serving leaders in the world. He is also the president of the Cambodian People's Party (CPP) and a member of the National Assembly for Kandal. His full honorary title is Samdech Akka Moha Sena Padei Techo Hun Sen ( km, សម្តេចអគ្គមហាសេនាបតី តេជោ ហ៊ុន សែន; ; meaning "Lord Prime Minister and Supreme Military Commander Hun Sen"). Born Hun Bunal,; he changed his name to Hun Sen in 1972, two years after joining the Khmer Rouge as a soldier. He fought for the Khmer Rouge in the Cambodian Civil War and was a Battalion Commander in Democratic Kampuchea until defecting in 1977 and fighting alongside Vietnamese forces in the Cambodian–Vietnamese War. From 1979 to 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2013–2014 Cambodian Protests
Anti-government protests ( km, បាតុកម្មប្រឆាំងរាជរដ្ឋាភិបាល) were a series of protests in Cambodia from July 2013 to July 2014. Popular demonstrations in Phnom Penh took place against the government of Prime Minister Hun Sen, triggered by widespread allegations of electoral fraud during the Cambodian general election of 2013. Demands to raise the minimum wage to $160 a month and resentment at Vietnamese influence in Cambodia have also contributed to the protests. The main opposition party refused to participate in parliament after the elections, and major demonstrations took place throughout December 2013. A government crackdown in January 2014 led to the deaths of 4 people and the clearing of the main protest camp. Cambodian protests may have been partly precipitated by the perception of corruption, lack of freedom and poor quality of life in the country. Cambodia is near the bottom of international rankings in the measur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pol Pot
Pol Pot; (born Saloth Sâr;; 19 May 1925 – 15 April 1998) was a Cambodian revolutionary, dictator, and politician who ruled Cambodia as Prime Minister of Democratic Kampuchea between 1976 and 1979. Ideologically a Marxist–Leninist and a Khmer nationalist, he was a leading member of Cambodia's communist movement, the Khmer Rouge, from 1963 until 1997 and served as the General Secretary of the Communist Party of Kampuchea from 1963 to 1981. Under his administration, Cambodia was converted into a one-party communist state and perpetrated the Cambodian genocide. Born to a prosperous farmer in Prek Sbauv, French Cambodia, Pol Pot was educated at some of Cambodia's most elite schools. While in Paris during the 1940s, he joined the French Communist Party. Returning to Cambodia in 1953, he involved himself in the Marxist–Leninist Khmer Việt Minh organisation and its guerrilla war against King Norodom Sihanouk's newly independent government. Following the Khmer Việt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Washington University
, mottoeng = "God is Our Trust" , established = , type = Private federally chartered research university , academic_affiliations = , endowment = $2.8 billion (2022) , president = Mark S. Wrighton , provost = Christopher Bracey , students = 27,159 (2016) , undergrad = 11,244 (2016) , postgrad = 15,486 (2016) , other = 429 (2016) , faculty = 2,663 , city = Washington, D.C. , country = U.S. , campus = Urban, , former_names = Columbian College (1821–1873)Columbian University (1873–1904) , sports_nickname = Colonials , mascot = George , colors = Buff & blue , sporting_affiliations = NCAA Division I – A-10 , website = , free_label = Newspaper , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Journal Of Asian Studies
''The Journal of Asian Studies'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of the Association for Asian Studies, covering Asian studies, ranging from history, the arts, social sciences, to philosophy and cultural studies of East, South, Inner, and Southeast Asia. In addition to research, current interest, and state-of-the-field articles, a large section of the journal is devoted to book reviews. The journal was established in 1941 as ''The Far Eastern Quarterly'', changing to its current title in September 1956. Editors-in-chief The following are or have been editor-in-chief of the journal: * Donald Shively (1956–1959) * Roger F. Hackett (1959–1962, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor) * David D. Buck (1990–1994, University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee) * Anand A. Yang (1995–2000, University of Utah) * Ann Waltner (2001–2004, University of Minnesota) * Kenneth M. George (2005–2008, University of Wisconsin–Madison) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Asia Forum
East Asia Forum (EAF) is an English-language international policy forum directed by Peter Drysdale and based at the Australian National University's Crawford School of Public Policy. It was launched in 2006 by then Australian Treasurer Peter Costello. It is a platform for dialogue on Asian economic and public policy, publishing two articles a day online. EAF also releases a quarterly magazine, the ''East Asia Forum Quarterly'' (EAFQ), published by ANU Press. EAF offers peer-reviewed daily analysis of economics, politics and public policy in the Asia Pacific. Articles focus on policy issues including trade, economic and social policy, governance, international relations and political developments. Content includes Australian, East Asian and Asia Pacific regional perspectives, with specialist contributors from around the region. An editorial is issued every Monday. East Asia Forum is an initiative by the East Asian Bureau of Economic Research (EABER). Its articles are archived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indosphere
Indosphere is a term coined by the linguist James Matisoff for areas of Indian linguistic and cultural influence in South Asia and Southeast Asia. It is commonly used in areal linguistics in contrast with Sinosphere. Influence The Tibeto-Burman family of languages, which extends over a huge geographic range, is characterized by great typological diversity, comprising languages that range from the highly tonal, monosyllabic, analytic type with practically no affixational morphology, like the Loloish languages, to marginally tonal or atonal languages with complex systems of verbal agreement morphology, like the Kiranti group of Nepal. This diversity is partly to be explained in terms of areal influences from Chinese on the one hand and Indo-Aryan languages on the other. Matisoff proposed two large and overlapping areas combining cultural and linguistic features – the "Sinosphere" and the "Indosphere", influenced by China and India respectively.Robert M. W. Dixon, Y. Alexandra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinosphere
The East Asian cultural sphere, also known as the Sinosphere, the Sinic world, the Sinitic world, the Chinese cultural sphere, the Chinese character sphere encompasses multiple countries in East Asia and Southeast Asia that were historically influenced by Chinese culture. According to academic consensus, the East Asian cultural sphere is made up of four entities: Greater China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam. Other definitions sometimes include Mongolia and Singapore, because of limited historical Chinese influences or increasing modern-day Chinese diaspora. The East Asian cultural sphere is not to be confused with the Sinophone world, which includes countries where the Chinese-speaking population is dominant. Imperial China was a regional power and exerted influence on tributary states and neighboring states, among which were Japan, Korea, and Vietnam. These interactions brought ideological and cultural influences rooted in Confucianism, Buddhism, and Taoism. During classical his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |