|
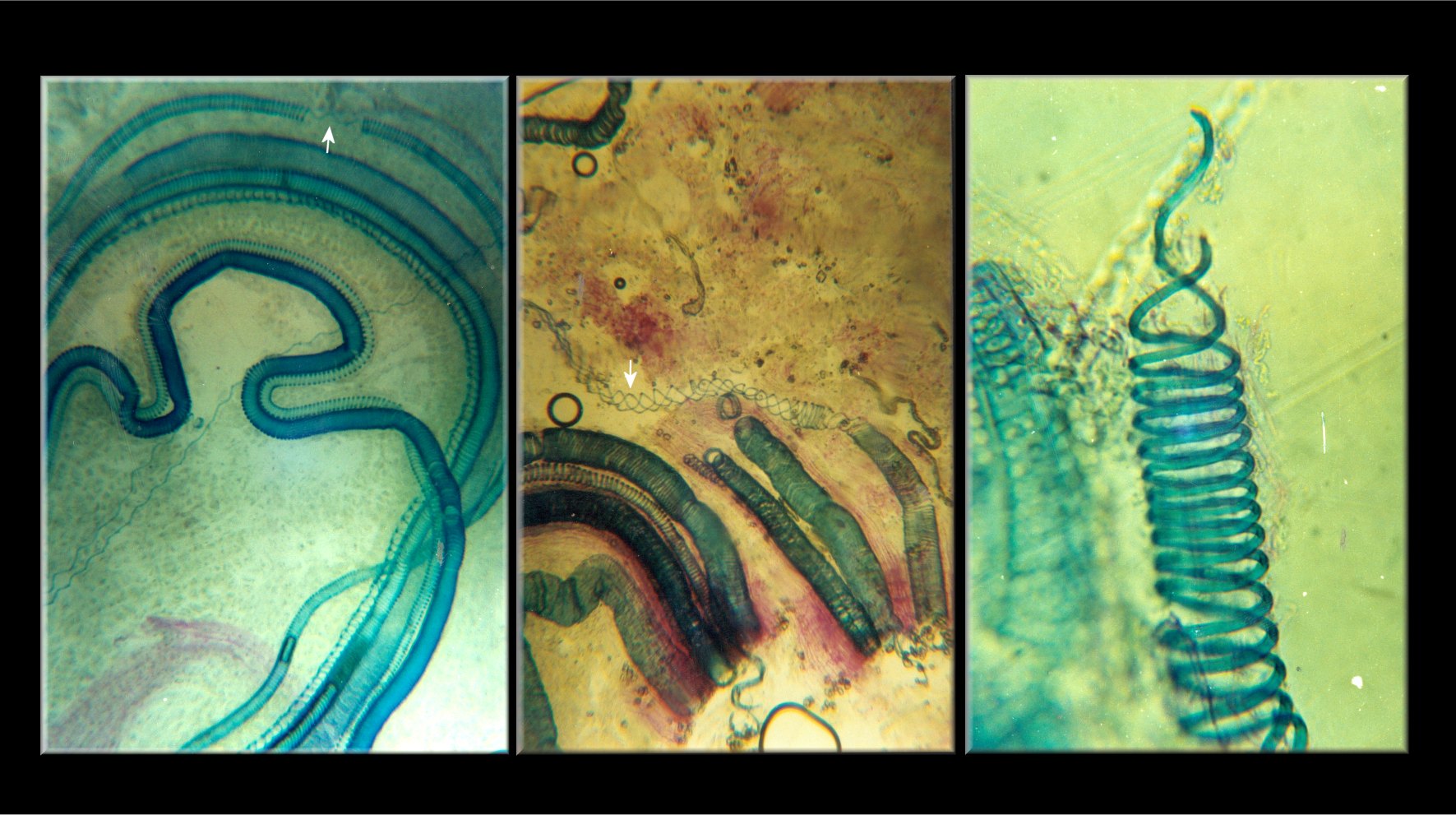
Calliarthron
''Calliarthron'' is a genus containing two species of thalloid intertidal alga. Specimens can reach around 30 cm in size. The thalli take a crustose form. The organisms lack secondary pit connections. ''Calliarthron'' reproduces by means of conceptacles; it produces tetraspores, dispores and carpospores. The genus has lignin and contains secondary cell walls, traits which are normally associated with the vascular plants. It is similar to the genus ''Bossiella''. ''Calliarthron'' is calcified, but also has uncalcified joints that allow it to flex in response to the waves to which it is subjected. These joints start out calcified, and decalcify as they grow older. After decalcifying they grow much longer, then fatten themselves up in the same way as xylem formation, resulting in secondary walls. Species The 2 species currently recognised are:Paul W. Gabrielson, Kathy Ann Miller, and Patrick T. Martone (2011) Morphometric and molecular analyses confirm two distinct species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calliarthron Cheilosporioides
''Calliarthron'' is a genus containing two species of thalloid intertidal alga. Specimens can reach around 30 cm in size. The thalli take a crustose form. The organisms lack secondary pit connections. ''Calliarthron'' reproduces by means of conceptacles; it produces tetraspores, dispores and carpospores. The genus has lignin and contains secondary cell walls, traits which are normally associated with the vascular plants. It is similar to the genus ''Bossiella''. ''Calliarthron'' is calcified, but also has uncalcified joints that allow it to flex in response to the waves to which it is subjected. These joints start out calcified, and decalcify as they grow older. After decalcifying they grow much longer, then fatten themselves up in the same way as xylem formation, resulting in secondary walls. Species The 2 species currently recognised are:Paul W. Gabrielson, Kathy Ann Miller, and Patrick T. Martone (2011) Morphometric and molecular analyses confirm two distinct species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calliarthron Tuberculosum
''Calliarthron tuberculosum'' is a species of thalloid intertidal alga. Distribution and habitat ''Calliarthron tuberculosum'' is found on the west coast of North America, from the Baja California Peninsula to the Alaska Panhandle Southeast Alaska, colloquially referred to as the Alaska(n) Panhandle, is the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Alaska, bordered to the east and north by the northern half of the Canadian province of British Columbia (and a small part .... South of Monterey Bay, California, ''C. tuberculosum'' overlaps with ''C. cheilosporioides''; as the two species are quite similar, distinguishing the two can be quite hard. Molecular sequencing or detailed measurements are required to separate them. It is commonly found in "low intertidal tidepools in moderate to exposed habitats". References Corallinaceae Algae {{Rhodophyta-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity and do not rot easily. Chemically, lignins are polymers made by cross-linking phenolic precursors. History Lignin was first mentioned in 1813 by the Swiss botanist A. P. de Candolle, who described it as a fibrous, tasteless material, insoluble in water and alcohol but soluble in weak alkaline solutions, and which can be precipitated from solution using acid. He named the substance “lignine”, which is derived from the Latin word '' lignum'', meaning wood. It is one of the most abundant organic polymers on Earth, exceeded only by cellulose. Lignin constitutes 30% of non-fossil organic carbon on Earth, and 20 to 35% of the dry mass of wood. Lignin is present in red algae, which suggest that the common ancestor of plants and red algae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corallinaceae
The Corallinaceae are one of the two extant Coralline families of red algae; they are differentiated from the morphologically similar Sporolithaceae by their formation of grouped sporangial chambers, clustered into sori. The Corallinoideae is monophyletic; the other subfamilies form another monophyletic group. Genera The following genera are listed in the World Register of Marine Species: *Subfamily Amphiroideae **Genus '' Amphiroa'' J.V. Lamouroux, 1812 **Genus '' Lithothrix'' J.E. Gray, 1867 *Subfamily Corallinoideae **Genus '' Alatocladia'' (Yendo) Johansen, 1969 **Genus '' Arthrocardia'' Decaisne, 1842 **Genus ''Bossiella'' P.C. Silva, 1957 **Genus ''Calliarthron'' Manza, 1937 **Genus ''Cheilosporum'' (Decaisne) Zanardini, 1844 **Genus '' Chiharaea'' Johansen, 1966 **Genus ''Corallina'' Linnaeus, 1758 **Genus '' Ellisolandia'' **Genus '' Haliptilon'' (Decaisne) Lindley, 1846 **Genus '' Jania'' J.V. Lamouroux, 1812 **Genus '' Marginisporum'' (Yendo) Ganesan, 1968 ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alga
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as ''Chlorella,'' ''Prototheca'' and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to in length. Most are aquatic and autotrophic (they generate food internally) and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the ''Charophyta'', a division of green algae which includes, for example, ''Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. No definition of algae is generally accepted. One definition is that algae "have chlorophyll ''a'' as their primary photosynthetic pigment and lack a sterile covering of cells around t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pit Connection
In algal anatomy, a pit connection is a hole in the septum between two algal cells, and is found only in the red algae − specifically, all orders except the Porphyridiales and haploid Bangiales. They are often stoppered with proteinaceous "pit plugs". By contrast, many fungi A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ... (only ascomycetes and basidiomycetes, as most other groups lack septa) contain septal pores − an unrelated phenomenon. Characteristics A sieve-like membrane may cover the pit in living algae, but in the majority of algae a plug forms, they likely limit the transfer of metabolites between neighbouring cells. Formation Primary pit connections are formed between cells in the same filament, derived from the same parent cell by its division. Such connections ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conceptacle
Conceptacles are specialized cavities of marine and freshwater algae that contain the reproductive organs. They are situated in the receptacle and open by a small ostiole.Boney, A.D. (1969). ''A Biology of Marine Algae''. Hutchinson Educational Ltd, London Conceptacles are present in Corallinaceae,Irvine, L.M. and Chamberlain, Y.M. (1994). ''Seaweeds of the British Isles''. Volume 1, Part 2B. Natural History Museum, London. and Hildenbrandiales, as well as the brown Fucales. In the Fucales there is no haploid phase in the reproductive cycle and therefore no alternation of generations.Fritsch, F.E. (1945). ''The Structure and Reproduction of the Algae''. Vol 2. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge The thallus is a sporophyte.Smith, G.M. (1938). ''Cryptogamic Botany. Algae and Fungi''. Second edition, Volume ''1'', McGraw-Hill Bok Company, Inc. The diploid plants produce male (antheridia) and female (oogonia) gametangia by meiosis. The gametes are released into the surrounding wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpospore
A carpospore is a diploid spore produced by red algae. After fertilization, the alga's carpogonium subdivides into carpospores, and generally the largest type of spore (larger than bispores, which are larger again than tetraspores Tetraspores are red algae spores produced by the tetrasporophytic ( diploid) phase in the life history of algae in the Rhodophyta as a result of meiosis.Jones, W.E. Revised and reprinted 1964. A Key to the genera of the British seaweeds.''Field ...). The wall of the carposporangium then breaks down, releasing the spores into the environment. References Red algae {{rhodophyta-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue (the phloem) to conduct products of photosynthesis. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers), and angiosperms (flowering plants). Scientific names for the group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida ''sensu lato''. Some early land plants (the rhyniophytes) had less developed vascular tissue; the term eutracheophyte has been used for all other vascular plants, including all living ones. Historically, vascular plants were known as "higher plants", as it was believed that they were further evolved than other plants due to being more complex organisms. However, this is an antiquated remnant of the obsolete scala naturae, and the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bossiella
''Bossiella'' is a genus of coralline algae with 5 recognised species. It reproduces via conceptacles; individual thalli only produce conceptacles of a single sex. Species The valid species currently considered to belong to this genus are: *''Bossiella californica'' *''Bossiella chiloensis'' *''Bossiella compressa'' *'' Bossiella orbigniana'' *'' Bossiella plumosa'' References * External linksImagesof ''Bossiella'' at Algaebase AlgaeBase is a global species database of information on all groups of algae, both marine and freshwater, as well as sea-grass. History AlgaeBase began in March 1996, founded by Michael Guiry. Text was copied from this source, which is avai ... Corallinaceae Red algae genera {{Rhodophyta-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AlgaeBase
AlgaeBase is a global species database of information on all groups of algae, both marine and freshwater, as well as sea-grass. History AlgaeBase began in March 1996, founded by Michael Guiry. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)licence. (Sehere. By 2005, the database contained about 65,000 names. In 2013, AlgaeBase and the Flanders Marine Institute (VLIZ) signed an end-user license agreement regarding the Electronic Intellectual Property of AlgaeBase. This allows the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) to include taxonomic names of algae in WoRMS, thereby allowing WoRMS, as part of the Aphia database, to make its overview of all described marine species more complete. Synchronisation of the AlgaeBase data with Aphia and WoRMS was undertaken manually until March 2015, but this was very time-consuming, so an online application was developed to semi-automate the synchronisation, launching in 2015 in conju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algaebase
AlgaeBase is a global species database of information on all groups of algae, both marine and freshwater, as well as sea-grass. History AlgaeBase began in March 1996, founded by Michael Guiry. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)licence. (Sehere. By 2005, the database contained about 65,000 names. In 2013, AlgaeBase and the Flanders Marine Institute (VLIZ) signed an end-user license agreement regarding the Electronic Intellectual Property of AlgaeBase. This allows the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) to include taxonomic names of algae in WoRMS, thereby allowing WoRMS, as part of the Aphia database, to make its overview of all described marine species more complete. Synchronisation of the AlgaeBase data with Aphia and WoRMS was undertaken manually until March 2015, but this was very time-consuming, so an online application was developed to semi-automate the synchronisation, launching in 2015 in conju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |