|
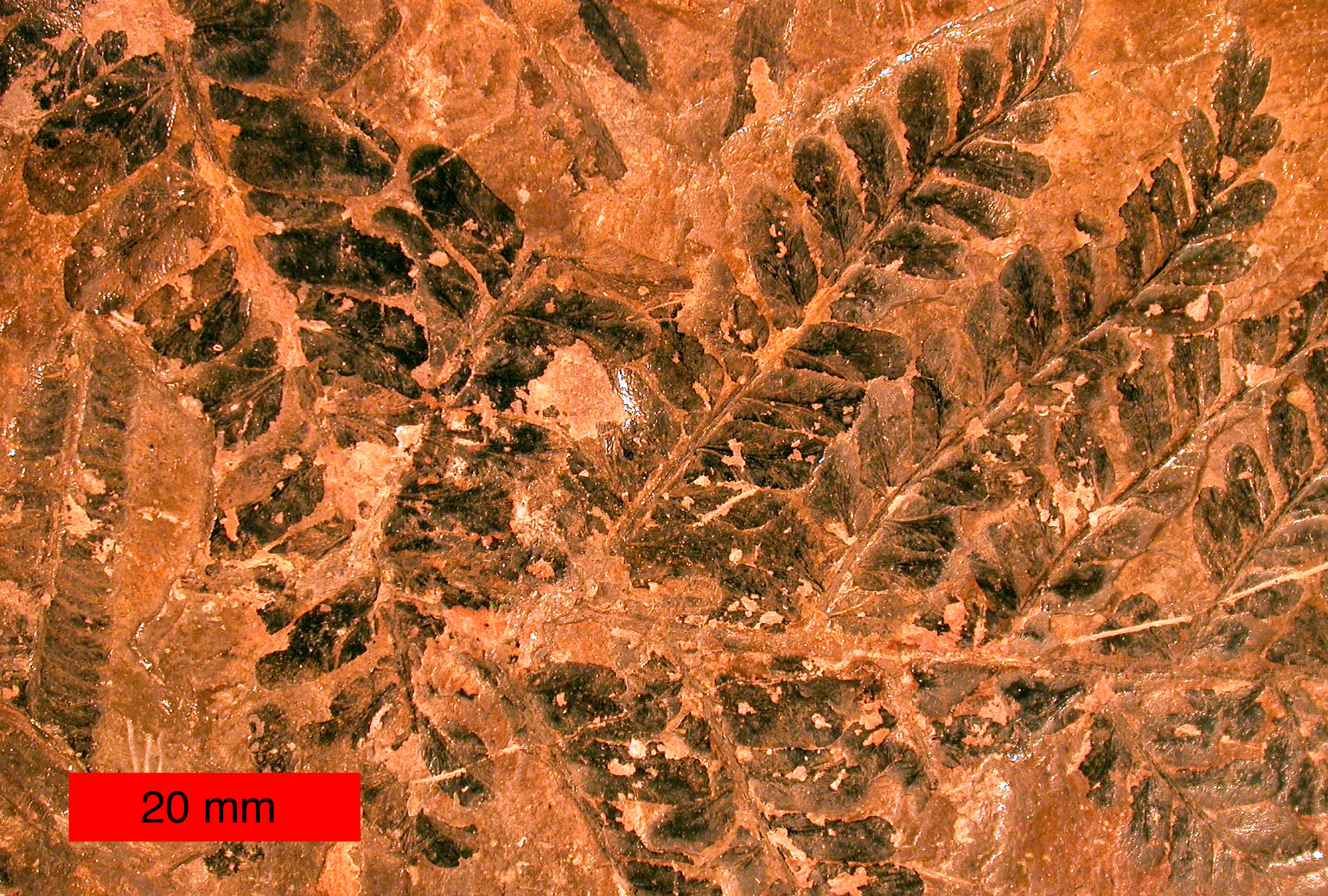
Calamopityaceae
Calamopityaceae is the largest family of the division of extinct seed-bearing plants (spermatophytes) known as Pteridospermatophyta. This family is characterized by its petioles and specific wood pattern, and it grew only in the Paleozoic era, specifically in North America and Europe. It is divided into three genera based on stem structure: '' Calamopitys'', '' Stenomyelon'', and '' Diichinia''. It was named by Solms-Laubach in 1896. Since then, its genera have been added to and grouped differently, though these three genera are currently depicted as the only genera of this family. Morphology Calamopityaceae is the largest family in Pteriodspermatophyta. This family is composed of gymnosperms, and because of their stem structure discovered through fossil rocks, they are considered to be in this division. However, nothing is known of their reproductive organs, but they are classified as seed plants based on their similarities to the Lyginopteridaceae and Medullasaceae families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteridospermatophyta
The term Pteridospermatophyta (or "seed ferns" or "Pteridospermatopsida") is a polyphyletic group of extinct seed-bearing plants (spermatophytes). The earliest fossil evidence for plants of this type is the genus ''Elkinsia'' of the late Devonian age. They flourished particularly during the Carboniferous and Permian periods. Pteridosperms declined during the Mesozoic Era and had mostly disappeared by the end of the Cretaceous Period, though some pteridosperm-like plants seem to have survived into Eocene times, based on fossil finds in Tasmania. With regard to the enduring utility of this division, many palaeobotanists still use the pteridosperm grouping in an informal sense to refer to the seed plants that are not angiosperms, coniferoids (conifers or cordaites), ginkgophytes or cycadophytes (cycads or bennettites). This is particularly useful for extinct seed plant groups whose systematic relationships remain speculative, as they can be classified as pteridosperms with no vali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, ''Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμνόσπερμος ( el, γυμνός, translit=gymnos, lit=naked, label=none and el, σπέρμα, translit=sperma, lit=seed, label=none), literally meaning 'naked seeds'. The name is based on the unenclosed condition of their seeds (called ovules in their unfertilized state). The non-encased condition of their seeds contrasts with the seeds and ovules of flowering plants (angiosperms), which are enclosed within an ovary. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or leaves, which are often modified to form cones, or solitary as in yew, ''Torreya'', ''Ginkgo''. Gymnosperm lifecycles involve alternation of generations. They have a dominant diploid sporophyte phase and a reduced haploid gametophyte phase which is dependent on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian Life
{{Disambiguation ...
Mississippian may refer to: * Mississippian (geology), a subperiod of the Carboniferous period in the geologic timescale, roughly 360 to 325 million years ago *Mississippian culture, a culture of Native American mound-builders from 900 to 1500 AD * Mississippian Railway, a short line railroad *A native of Mississippi See also *Mississippi (other) Mississippi is a state of the United States of America. Mississippi may also refer to: Places * Mississippi River, a river in central United States * Mississippi River System, a system of rivers in the Mississippi River watershed * Mississippi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Plant Families
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous Plants
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' ("coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian lineages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringian Forest
The Thuringian Forest (''Thüringer Wald'' in German), is a mountain range in the southern parts of the German state of Thuringia, running northwest to southeast. Skirting from its southerly source in foothills to a gorge on its north-west side is the Werra valley. On the other side of the Forest is an upper outcrop of the North German Plain, the Thuringian Basin, which includes the city Erfurt. The south and south-east continuation of the range is the highland often called the Thuringian-Vogtlandian Slate Mountains. Among scattered foothills at its northern foot are the towns Eisenach, Gotha, Arnstadt and Ilmenau. The town of Suhl sits in a slight dip on the range itself. In October 1806, Napoleon Bonaparte invaded Saxony with his "Grande Armée," fighting the Battle of Jena–Auerstedt near the wood. This battle, part of the War of the Fourth Coalition, is generally regarded as the basis of Napoleon's success over the Alliance. Geography and communications The Thuringia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Unger
Franz Joseph Andreas Nicolaus Unger (30 November 1800 in ''Gut Amthof'' near village Leutschach in Styria, Austria – 13 February 1870 in Graz) was an Austrian botanist, paleontologist and plant physiologist. Life and work Initially, Unger studied law at the University of Graz. In 1820 he moved to Vienna to study medicine, in 1822 he enrolled at the Charles University in Prague. In 1823 Unger returned to Vienna and completed his medical studies in 1827. From 1827 Unger practiced as a doctor in Stockerau near Vienna, then from 1830 as a court physician in Kitzbühel, Tyrol. In 1832, botanists Schott & Endl. published ''Ungeria'' is a genus of flowering plants from Norfolk Island belonging to the family Malvaceae. It was named in Franz Unger's honour. In 1836 he was named professor of botany at the University of Graz and also taught at the Joanneum (which became the Universalmuseum Joanneum and the Graz University of Technology); in 1850 professor of plant physiology in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek (, "old, ancient"), (, ( gen. ), "being, creature"), and (, "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics, and engineering. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Albany Shale
The New Albany Shale is an organic-rich geologic formation of Devonian and Mississippian age in the Illinois Basin of the United States. It is a major source of hydrocarbons. Stratigraphy The New Albany formation consists of brown, black, and green shale with minor beds of dolomite and sandstone. It was deposited under anoxic marine conditions. Pyrite is a common accessory mineral, and parts of the shale have greater than 4% by weight of organic carbon. The black shale layers have anomalously high radioactivity (due to uranium), phosphorus, and heavy metals. The formation was named for outcrops near New Albany, Indiana. It is one of a number of organic-rich shales of upper Devonian and lower Mississippian age in North America. It is correlative with the Antrim Shale of the Michigan Basin, the Ohio Shale of Ohio and eastern Kentucky, and the Chattanooga Shale of Tennessee and central Kentucky. The formation is composed of six members. These members in ascending strat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calciferous Sandstone
Calciferous sandstone is a geological term relating to strata at the base of the Carboniferous formation, below the entire sequence of coal measures. This term may be unique to the UK. Typically this part of the geological sequence, as in the Touch Hills and Fintry Hills to the west of Stirling tends to contain a mixture of lavas and sedimentary rocks, including sandstone Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ... and mudstone, and lies unconformably on top of older Devonian strata. Carboniferous geology {{UK-geologic-formation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



_(2).jpg)


