|
Caisse De La Dette
The Caisse de la Dette Publique ("Public Debt Commission") was an international commission established by a decree issued by Khedive Ismail of Egypt on 2 May 1876 to supervise the payment by the Egyptian government of the loans to the European governments following the construction of the Suez Canal. It was initially led by a secretary and three commissioners representing the governments of Austria-Hungary, France and Italy; from 1877 the United Kingdom and from 1885 Russia and Germany. One of the Commissioners would serve as the President, or Chairman, of the Commission. "This system was under the control of two main countries, France and Britain. This system of 'dual control' represented Europeans direct intervention in Egypt's financial affairs." The Public Debt Commission was abolished by a bilateral agreement between the British and the Egyptian governments, signed on 17 July 1940,Text in ''League of Nations Treaty Series'', vol. 202, pp. 98-105. due to Allied interest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khedive Ismail
Isma'il Pasha ( ar, إسماعيل باشا ; 12 January 1830 – 2 March 1895), was the Khedive of Egypt and conqueror of Sudan from 1863 to 1879, when he was removed at the behest of Great Britain. Sharing the ambitious outlook of his grandfather, Muhammad Ali Pasha, he greatly modernized Egypt and Sudan during his reign, investing heavily in industrial and economic development, urbanization, and the expansion of the country's boundaries in Africa. His philosophy can be glimpsed in a statement that he made in 1879: "My country is not longer only in Africa; we are now part of Europe, too. It is therefore natural for us to abandon our former ways and to adopt a new system adapted to our social conditions". In 1867 he also secured Ottoman and international recognition for his title of '' Khedive'' (Viceroy) in preference to '' Wāli'' (Governor) which was previously used by his predecessors in the Eyalet of Egypt and Sudan (1517–1867). However, Isma'il's policies placed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
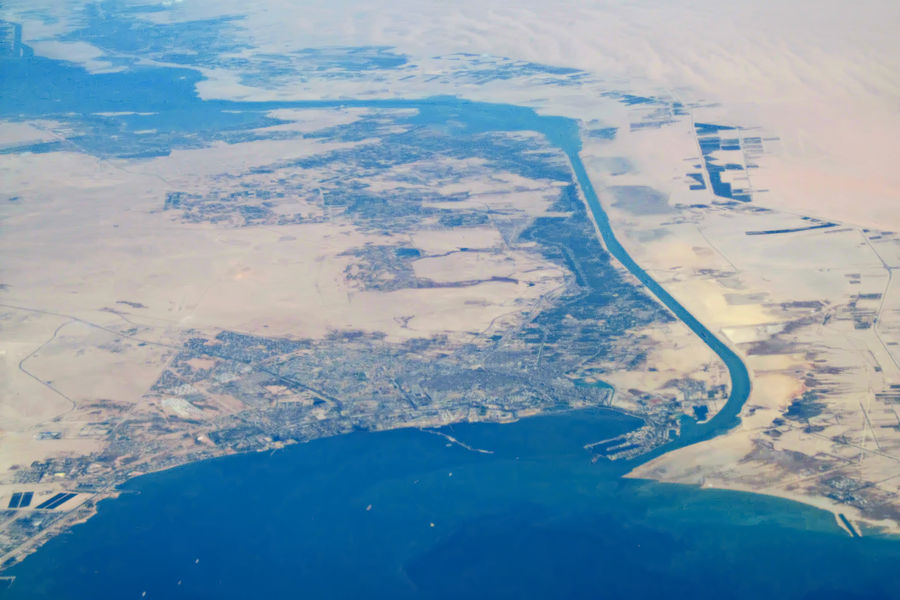
Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular trade route between Europe and Asia. In 1858, Ferdinand de Lesseps formed the Suez Canal Company for the express purpose of building the canal. Construction of the canal lasted from 1859 to 1869. The canal officially opened on 17 November 1869. It offers vessels a direct route between the North Atlantic and northern Indian oceans via the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea, avoiding the South Atlantic and southern Indian oceans and reducing the journey distance from the Arabian Sea to London by approximately , or 10 days at to 8 days at . The canal extends from the northern terminus of Port Said to the southern terminus of Port Tewfik at the city of Suez. In 2021, more than 20,600 vessels traversed the canal (an average of 56 per day) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Public Debt Administration
The Ottoman Public Debt Administration (OPDA) ( ota, دیون عمومیهٔ عثمانیه واردات مخصصه ادارهسی, script=Arab, Düyun-u Umumiye-i Osmaniye Varidat-ı Muhassasa İdaresi, or simply as it was popularly known), was a European-controlled organization that was established in 1881 to collect the payments which the Ottoman Empire owed to European companies in the Ottoman public debt. The OPDA became a vast, essentially independent bureaucracy within the Ottoman bureaucracy, run by the creditors and its governing council was packed with European government officials https://www.economist.com/news/international/21595928-countries-have-started-outsource-public-services-each-other-unbundling-nation Government-to-government trade: Unbundling the nation state- including one representative each from British, French, German, Austrian, Italian, Dutch, and Ottoman creditors, and one representative from the Ottoman state. It employed 5,000 officials who collec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Financial Control
The International Financial Control ( el, Διεθνής Οικονομικός Έλεγχος) was the supervision of the public finances of Greece which was imposed by European powers, who had lent Greece in autumn of 1897 when the country bankrupted four years earlier. The goal was the payment of the country's debts to its creditors. The control was exercised by a six-person commission, the ''International Financial Commission'' (official name, in french: Commission Internationale Financière de la Grèce). Background and precedent international practice Between 1857 and 1859, UK, France and Russia created the International Financial Commission of Inquiry, a commission whose goal was reporting Greece's capability of repaying the debt of 1833. This commission, by the intervention of Russia, did not have the role of controlling the economy and ensuring payments; it was restricted to an advisory role. The result from the work of this commission was the payment of an instalment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Greece
The Kingdom of Greece ( grc, label= Greek, Βασίλειον τῆς Ἑλλάδος ) was established in 1832 and was the successor state to the First Hellenic Republic. It was internationally recognised by the Treaty of Constantinople, where Greece also secured its full independence from the Ottoman Empire after nearly four centuries. The Kingdom of Greece was dissolved in 1924 and the Second Hellenic Republic was established following Greece's defeat by Turkey in the Asia Minor Campaign. A military ''coup d'état'' restored the monarchy in 1935 and Greece became a Kingdom again until 1973. The Kingdom was finally dissolved in the aftermath of a seven-year military dictatorship (1967–1974) and the Third Hellenic Republic was established following a referendum held in 1974. Background The Greek-speaking Eastern Roman Empire, also known as Byzantine Empire, which ruled most of the Eastern Mediterranean region for over 1100 years, had been fatally weakened since the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moroccan Debt Administration
The Moroccan Debt Administration (french: administration de la dette marocaine), formally known as the ''Contrôle de la dette'' from 1904 to 1910 and after that as the ''Administration du Contrôle de la dette publique mahghzénienne'' (referring to the Moroccan monarchy as the Makhzen), was an entity set up by the French government in 1904 to administer the sovereign debt of the Moroccan Monarchy. History The Moroccan Debt Administration originated in 1904, as Morocco's sovereign debt, which had increased significantly following the Hispano-Moroccan War (1859–1860) and the First Melillan campaign of 1894, was restructured by the Banque de Paris et des Pays-Bas (BPPB) in coordination with the French government. as a consequence, France became the only creditor of the Moroccan government. The loan contract was signed on by Moroccan Foreign Minister Si Abdelkrim Ben Slimane, Moroccan Finance Minister Si Mohammed Tazi, and the BPPB's representative Georges Zangarussiano. The loa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th Century In Egypt
19 (nineteen) is the natural number following 18 and preceding 20. It is a prime number. Mathematics 19 is the eighth prime number, and forms a sexy prime with 13, a twin prime with 17, and a cousin prime with 23. It is the third full reptend prime, the fifth central trinomial coefficient, and the seventh Mersenne prime exponent. It is also the second Keith number, and more specifically the first Keith prime. * 19 is the maximum number of fourth powers needed to sum up to any natural number, and in the context of Waring's problem, 19 is the fourth value of g(k). * The sum of the squares of the first 19 primes is divisible by 19. *19 is the sixth Heegner number. 67 and 163, respectively the 19th and 38th prime numbers, are the two largest Heegner numbers, of nine total. * 19 is the third centered triangular number as well as the third centered hexagonal number. : The 19th triangular number is 190, equivalently the sum of the first 19 non-zero integers, that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizations Established In 1876
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose. The word is derived from the Greek word ''organon'', which means tool or instrument, musical instrument, and organ. Types There are a variety of legal types of organizations, including corporations, governments, non-governmental organizations, political organizations, international organizations, armed forces, charities, not-for-profit corporations, partnerships, cooperatives, and educational institutions, etc. A hybrid organization is a body that operates in both the public sector and the private sector simultaneously, fulfilling public duties and developing commercial market activities. A voluntary association is an organization consisting of volunteers. Such organizations may be able to operate without legal formalities, depending on jurisdiction, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizations Disestablished In 1940
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose. The word is derived from the Greek word ''organon'', which means tool or instrument, musical instrument, and organ. Types There are a variety of legal types of organizations, including corporations, governments, non-governmental organizations, political organizations, international organizations, armed forces, charities, not-for-profit corporations, partnerships, cooperatives, and educational institutions, etc. A hybrid organization is a body that operates in both the public sector and the private sector simultaneously, fulfilling public duties and developing commercial market activities. A voluntary association is an organization consisting of volunteers. Such organizations may be able to operate without legal formalities, depending on jurisdiction, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |