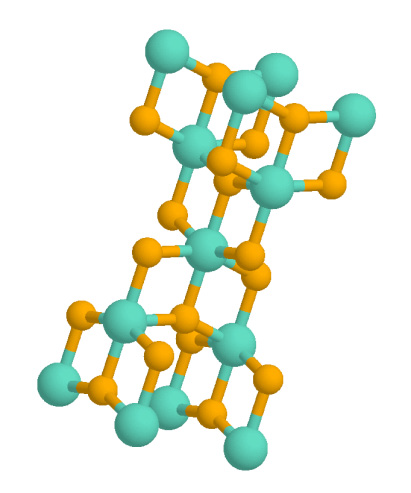
|
Cafetite
Cafetite is a rare titanium oxide mineral with formula ·. It is named for its composition, Ca-Fe-Ti. It was first described in 1959 for an occurrence in the Afrikanda Massif, Afrikanda (rural locality), Afrikanda, Kola Peninsula, Murmanskaja Oblast, Northern Region, Russia. It is also reported from the Khibiny Massif, Khibiny and Kovdor Massif, Kovdor massifs of the Kola Peninsula and from Meagher County, Montana, US. It occurs in pegmatites in a pyroxenite intrusion as crystals in Miarolitic cavity, miarolitic cavities. It occurs associated with ilmenite, titaniferous magnetite, titanite, anatase, perovskite, baddeleyite, phlogopite, Chlorite group, clinochlore and Kassite (mineral), kassite. References Oxide minerals Titanium minerals Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 14 {{oxide-mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxide Mineral
The oxide mineral class includes those minerals in which the oxide anion (O2−) is bonded to one or more metal alloys. The hydroxide-bearing minerals are typically included in the oxide class. The minerals with complex anion groups such as the silicates, sulfates, carbonates and phosphates are classed separately. Simple oxides: *XO **Periclase group ***Periclase ***Manganosite **Zincite group ***Zincite *** Bromellite ***Tenorite ***Litharge * **Cuprite **Ice * **Hematite group ***Corundum ***Hematite ***Ilmenite * **Rutile group ***Rutile ***Pyrolusite ***Cassiterite **Baddeleyite **Uraninite **Thorianite * **Spinel group ***Spinel ***Gahnite ***Magnetite ***Franklinite ***Chromite **Chrysoberyl **Columbite *Hydroxide subgroup: **Brucite **Manganite ** Romanèchite **Goethite group: ***Diaspore ***Goethite Nickel–Strunz Classification -04- Oxides IMA-CNMNC proposes a new hierarchical scheme (Mills et al., 2009). This list uses it to modify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khibiny Massif
The Khibiny Mountains (russian: Хиби́ны ; sjd, Umptek) is one of the two main mountain ranges of the Kola Peninsula, Russia, within the Arctic Circle, located between Imandra and Umbozero lakes. The range is also known as Khibiny Massif, Khibinsky Mountains, Khibinsky Tundras, Khibins or Khibiny. The Khibiny National Park was set up in 2018. Geography The Khibiny Massif are the highest mountains of the Kola Peninsula, a large peninsula extending from northern Russia into the Barents and White seas. The total land area of the peninsula is approximately . It is rich in minerals due to the removal of a layer of soil during the last ice age. The Khibiny Massif is of oval shape of about 1,300 km2. and occupies the central part of the peninsula at a relative elevation of 900–1000 m above the surrounding plain. The mountains are not particularly high; the two highest peaks are the Yudychvumchorr, which stands , and the Chasnachorr, which stands . The average elevati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlogopite
Phlogopite is a yellow, greenish, or reddish-brown member of the mica family of phyllosilicates. It is also known as magnesium mica. Phlogopite is the magnesium endmember of the biotite solid solution series, with the chemical formula KMg3AlSi3O10(F,OH)2. Iron substitutes for magnesium in variable amounts leading to the more common biotite with higher iron content. For physical and optical identification, it shares most of the characteristic properties of biotite. Paragenesis Phlogopite is an important and relatively common end-member composition of biotite. Phlogopite micas are found primarily in igneous rocks, although it is also common in contact metamorphic aureoles of intrusive igneous rocks with magnesian country rocks and in marble formed from impure dolomite (dolomite with some siliclastic sediment). The occurrence of phlogopite mica within igneous rocks is difficult to constrain precisely because the primary control is rock composition as expected, but phlogopite is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baddeleyite
Baddeleyite is a rare zirconium oxide mineral (ZrO2 or zirconia), occurring in a variety of monoclinic prismatic crystal forms. It is transparent to translucent, has high indices of refraction, and ranges from colorless to yellow, green, and dark brown. See etymology below. Baddeleyite is a refractory mineral, with a melting point of 2700 °C. Hafnium is a substituting ''impurity'' and may be present in quantities ranging from 0.1 to several percent. It can be found in igneous rocks containing potassium feldspar and plagioclase. Baddeleyite is commonly not found with zircon (ZrSiO4), because it forms in silica-undersaturated rocks, such as mafic rocks. This is because, when silica is free in the system (silica-saturated/oversaturated), zircon is the dominating phase, not baddeleyite. It belongs to the monoclinic-prismatic class, of the P21/c crystal system. It has been used for geochronology. Geologic occurrence Baddeleyite was first found in Sri Lanka in 1892. It can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perovskite
Perovskite (pronunciation: ) is a calcium titanium oxide mineral composed of calcium titanate (chemical formula ). Its name is also applied to the class of compounds which have the same type of crystal structure as (XIIA2+VIB4+X2−3), known as the perovskite structure. Many different cations can be embedded in this structure, allowing the development of diverse engineered materials. History The mineral was discovered in the Ural Mountains of Russia by Gustav Rose in 1839 and is named after Russian mineralogist Lev Perovski (1792–1856). Perovskite's notable crystal structure was first described by Victor Goldschmidt in 1926 in his work on tolerance factors. The crystal structure was later published in 1945 from X-ray diffraction data on barium titanate by Helen Dick Megaw. Occurrence Found in the Earth's mantle, perovskite's occurrence at Khibina Massif is restricted to the silica under-saturated ultramafic rocks and foidolites, due to the instability in a paragenesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatase
Anatase is a metastable mineral form of titanium dioxide (TiO2) with a tetragonal crystal structure. Although colorless or white when pure, anatase in nature is usually a black solid due to impurities. Three other polymorphs (or mineral forms) of titanium dioxide are known to occur naturally: brookite, akaogiite, and rutile, with rutile being the most common and most stable of the bunch. Anatase is formed at relatively low temperatures and found in minor concentrations in igneous and metamorphic rocks. Thin films of TiO2-coated glass show antifogging and self-cleaning properties under ultraviolet radiation. Anatase is always found as small, isolated, and sharply developed crystals, and like rutile, it crystallizes in a tetragonal system. Anatase is metastable at all temperatures and pressures, with rutile being the equilibrium polymorph. Nevertheless, anatase is often the first titanium dioxide phase to form in many processes due to its lower surface energy, with a transforma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanite
Titanite, or sphene (from the Greek ''sphenos'' (σφηνώ), meaning wedge), is a calcium titanium nesosilicate mineral, Ca Ti Si O5. Trace impurities of iron and aluminium are typically present. Also commonly present are rare earth metals including cerium and yttrium; calcium may be partly replaced by thorium. Nomenclature The International Mineralogical Association Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names (CNMMN) adopted the name titanite and "discredited" the name sphene as of 1982, although commonly papers and books initially identify the mineral using both names. Sphene was the most commonly used name until the IMA decision, although both were well known. Some authorities think it is less confusing as the word is used to describe any chemical or crystal with oxidized titanium such as the rare earth titanate pyrochlores series and many of the minerals with the perovskite structure. The name sphene continues to be publishable in peer-reviewed scientific literature, e.g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With the exception of extremely rare native iron deposits, it is the most magnetic of all the naturally occurring minerals on Earth. Naturally magnetized pieces of magnetite, called lodestone, will attract small pieces of iron, which is how ancient peoples first discovered the property of magnetism. Magnetite is black or brownish-black with a metallic luster, has a Mohs hardness of 5–6 and leaves a black streak. Small grains of magnetite are very common in igneous and metamorphic rocks. The chemical IUPAC name is iron(II,III) oxide and the common chemical name is ''ferrous-ferric oxide''. Properties In addition to igneous rocks, magnetite also occurs in sedimentary rocks, including banded iron formations and in lake and marine sediments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilmenite
Ilmenite is a titanium-iron oxide mineral with the idealized formula . It is a weakly magnetic black or steel-gray solid. Ilmenite is the most important ore of titanium and the main source of titanium dioxide, which is used in paints, printing inks, fabrics, plastics, paper, sunscreen, food and cosmetics. Structure and properties Ilmenite is a heavy (specific gravity 4.7), moderately hard (Mohs hardness 5.6 to 6), opaque black mineral with a submetallic luster. It is almost always massive, with thick tabular crystals being quite rare. It shows no discernible cleavage, breaking instead with a conchoidal to uneven fracture. Ilmenite crystallizes in the trigonal system with space group ''R''. The ilmenite crystal structure consists of an ordered derivative of the corundum structure; in corundum all cations are identical but in ilmenite Fe2+ and Ti4+ ions occupy alternating layers perpendicular to the trigonal c axis. Pure ilmenite is paramagnetic (showing only very weak attrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miarolitic Cavity
Miarolitic cavities (or ''miarolitic texture'') are typically crystal-lined irregular cavities or vugs most commonly found in granitic pegmatites, and also in a variety of igneous rocks. The central portions of pegmatites are often miarolitic as the pegmatite dike crystallizes from the outside walls toward the center. The volatile portion of the magma is gradually excluded from the forming crystal phases until it becomes trapped within the body and forms the cavities which often contain minerals of elements incompatible with the typical silicate granitic mineralogy. The miarolitic cavities and miarolitic pegmatites are sources of rare and unusual minerals containing elements not found in abundance in normal igneous rocks. Minerals containing lithium, rubidium, beryllium, boron, niobium, tantalum, tin, bismuth, fluorine and other elements can be found. The term ''miarolitic'' comes from the Italian Italian(s) may refer to: * Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroxenite
Pyroxenite is an ultramafic igneous rock consisting essentially of minerals of the pyroxene group, such as augite, diopside, hypersthene, bronzite or enstatite. Pyroxenites are classified into clinopyroxenites, orthopyroxenites, and the websterites which contain both types of pyroxenes (see diagram below). Closely allied to this group are the hornblendites, consisting essentially of hornblende and other amphiboles. They are essentially of igneous origin, though some pyroxenites are included in the metamorphic Lewisian complex of Scotland. The pyroxene-rich rocks, which result from the type of contact metamorphism known as pyroxene-hornfels facies, have siliceous sediment or basaltic protoliths, and are respectively metapelites and metabasites. Intrusive and mantle pyroxenites Igneous pyroxenites are closely allied to gabbros and norites, from which they differ by the absence of feldspar, and to peridotites, which are distinguished from them by containing more than 40% olivine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pegmatite
A pegmatite is an igneous rock showing a very coarse texture, with large interlocking crystals usually greater in size than and sometimes greater than . Most pegmatites are composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silicic composition to granite. However, rarer intermediate composition and mafic pegmatites are known. Many of the world's largest crystals are found within pegmatites. These include crystals of microcline, quartz, mica, spodumene, beryl, and tourmaline. Some individual crystals are over long. Most pegmatites are thought to form from the last fluid fraction of a large crystallizing magma body. This residual fluid is highly enriched in volatiles and trace elements, and its very low viscosity allows molecules to migrate rapidly to join an existing crystal rather than coming together to form new crystals. This allows a few very large crystals to form. While most pegmatites have a simple composition of minerals common in ordinary igneous rock, a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


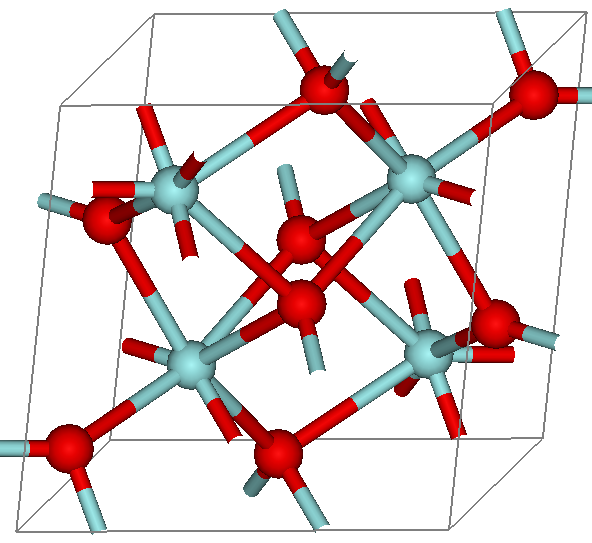
_crystallographic_standard_alignment.png)