|
Cadmium Stearate
Cadmium stearate is a salt with the formula Cd(O2CC17H35)2. Classified as a metallic soap, this a white solid is used as a lubricant and as a heat- and light-stabilizer in polyvinyl chloride. The use of cadmium stearate is being phased out because of its toxicity. Synthesis The compound is produced by the reaction of cadmium chloride with sodium stearate or heating stearic acid and cadmium oxide or hydroxide. Also, an exchange reaction between cadmium sulfate and sodium stearate: ::\mathsf Safety Like other cadmium compounds, cadmium stearate is toxic. Cadmium stearate is also carcinogen A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substan .... References {{Cadmium compounds Cadmium compounds Stearates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallic Soap
A metallic soap is a metallic salt of a fatty acid. Theoretically, soaps can be made of any metal, although not all enjoy practical uses. Varying the metal can strongly affect the properties of the compound, particularly its solubility. Alkali, alkaline earth soaps Alkali metal and alkaline earth soaps are white solids. The most commonly encountered are traditional household soaps, which are the fatty acid salts of sodium (hard soap) and potassium (soft soap). Lithium soap or greases, such as lithium stearate, are insoluble in water and find use in lubricating grease. Calcium and magnesium soaps are most commonly encountered as soap scum but the pure materials have a variety of uses. Magnesium stearate and calcium stearate are used as excipients, lubricants, release agents, and food additives, with the later use being covered be the generic E numbers of E470b and E470 respectively. Other metal soaps Aluminium soaps are used as thickening agents, in the production of cosmetics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubricant
A lubricant (sometimes shortened to lube) is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, transporting foreign particles, or heating or cooling the surfaces. The property of reducing friction is known as lubricity. In addition to industrial applications, lubricants are used for many other purposes. Other uses include cooking (oils and fats in use in frying pans, in baking to prevent food sticking), bioapplications on humans (e.g. lubricants for artificial joints), ultrasound examination, medical examination, and sexual intercourse. It is mainly used to reduce friction and to contribute to a better and efficient functioning of a mechanism. History Lubricants have been in some use for thousands of years. Calcium soaps have been identified on the axles of chariots dated to 1400 BC. Building stones were slid on oil-impregrated lumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Chloride
Cadmium chloride is a white crystalline compound of cadmium and chloride, with the formula CdCl2. This salt is a hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The crystal structure of cadmium chloride (described below), is a reference for describing other crystal structures. Also known are CdCl2•H2O and CdCl2•5H2O. Structure Cadmium chloride forms a layered structure consisting of octahedral Cd2+ centers linked with chloride ligands. Cadmium iodide, CdI2, has a similar structure, but the iodide ions are arranged in a HCP lattice, whereas in CdCl2 the chloride ions are arranged in a CCP lattice.N. N. Greenwood, A. Earnshaw, ''Chemistry of the Elements'', 2nd ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, UK, 1997. Chemical properties Cadmium chloride dissolves well in water and other polar solvents. It is a mild Lewis acid. :CdCl2 + 2 Cl− → dCl4sup>2− Solutions of equimolar cadmium chloride and potassium chloride give potassium cadmium trichlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Stearate
Sodium stearate is the sodium salt of stearic acid. This white solid is the most common soap. It is found in many types of solid deodorants, rubbers, latex paints, and inks. It is also a component of some food additives and food flavorings.Klaus Schumann, Kurt Siekmann, "Soaps" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. {{doi, 10.1002/14356007.a24_247 Use Characteristic of soaps, sodium stearate has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts, the carboxylate and the long hydrocarbon chain, respectively. These two chemically different components induce the formation of micelles, which present the hydrophilic heads outwards and their hydrophobic (hydrocarbon) tails inwards, providing a lipophilic environment for hydrophobic compounds. The tail part dissolves the grease (or) dirt and forms the micelle. It is also used in the pharmaceutical industry as a surfactant to aid the solubility of hydrophobic compounds in the production of various mouth foa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Oxide
Cadmium oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdO. It is one of the main precursors to other cadmium compounds. It crystallizes in a cubic rocksalt lattice like sodium chloride, with octahedral cation and anion centers. It occurs naturally as the rare mineral monteponite. Cadmium oxide can be found as a colorless amorphous powder or as brown or red crystals.Lewis, Richard J. Sr., Hawley's condensed chemical dictionary, 13th ed., 1997, p. 189 Cadmium oxide is an n-type semiconductor with a band gap of 2.18 eV (2.31 eV) at room temperature (298 K). Production and structure Since cadmium compounds are often found in association with zinc ores, cadmium oxide is a common by-product of zinc refining. It is produced by burning elemental cadmium in air. Pyrolysis of other cadmium compounds, such as the nitrate or the carbonate, also affords this oxide. When pure, it is red, but CdO is unusual in being available in many differing colours due to its tendency to form defect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
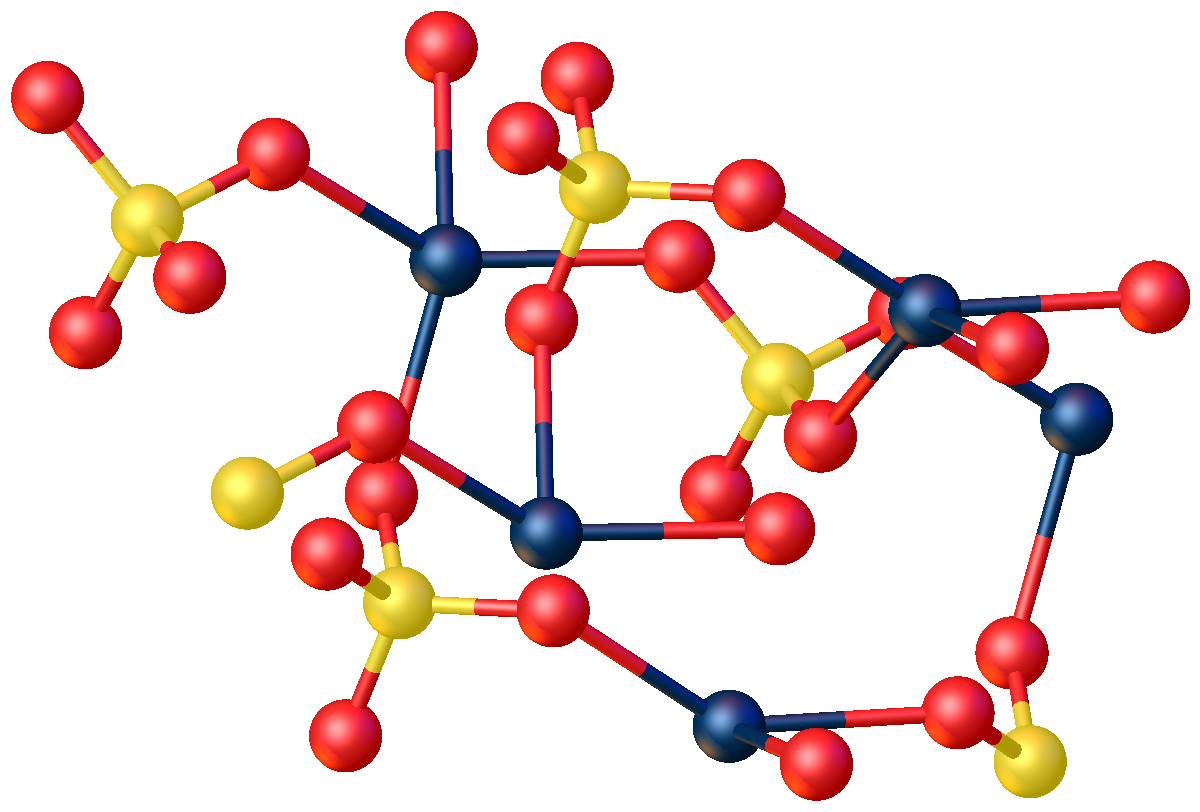
Cadmium Sulfate
Cadmium sulfate is the name of a series of related inorganic compounds with the formula CdSO4·H2O. The most common form is the monohydrate CdSO4·H2O, but two other forms are known CdSO4·H2O and the anhydrous salt (CdSO4). All salts are colourless and highly soluble in water. Structure, preparation, and occurrence X-ray crystallography shows that CdSO4·H2O is a typical coordination polymer. Each Cd2+ center has octahedral coordination geometry, being surrounded by four oxygen centers provided by four sulfate ligands and two oxygen centers from the bridging water ligands. Cadmium sulfate hydrate can be prepared by the reaction of cadmium metal or its oxide or hydroxide with dilute sulfuric acid: : CdO + H2SO4 → CdSO4 + H2O : Cd + H2SO4 → CdSO4 + H2 The anhydrous material can be prepared using sodium persulfate: : Cd + Na2S2O8 → CdSO4 + Na2SO4 Cadmium sulfates occur as the following rare minerals drobecite (CdSO4·4H2O), voudourisite (monohydrate), and lazaridisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Government Publishing Office
The United States Government Publishing Office (USGPO or GPO; formerly the United States Government Printing Office) is an agency of the legislative branch of the United States Federal government. The office produces and distributes information products and services for all three branches of the Federal Government, including U.S. passports for the Department of State as well as the official publications of the Supreme Court, the Congress, the Executive Office of the President, executive departments, and independent agencies. An act of Congress changed the office's name to its current form in 2014. History The Government Printing Office was created by congressional joint resolution () on June 23, 1860. It began operations March 4, 1861, with 350 employees and reached a peak employment of 8,500 in 1972. The agency began transformation to computer technology in the 1980s; along with the gradual replacement of paper with electronic document distribution, this has led to a stea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of non-radioactive carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke. Although the public generally associates carcinogenicity with synthetic chemicals, it is equally likely to arise from both natural and synthetic substances. Carcinogens are not necessarily immediately toxic; thus, their effect can be insidious. Carcinogens, as mentioned, are agents in the environment capable of contributing to cancer growth. Carcinogens can be categorized into two different types: activation-dependent and activation-independent, and each nature impacts their level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Compounds
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds, and like mercury, it has a lower melting point than the transition metals in groups 3 through 11. Cadmium and its congeners in group 12 are often not considered transition metals, in that they do not have partly filled ''d'' or ''f'' electron shells in the elemental or common oxidation states. The average concentration of cadmium in Earth's crust is between 0.1 and 0.5 parts per million (ppm). It was discovered in 1817 simultaneously by Stromeyer and Hermann, both in Germany, as an impurity in zinc carbonate. Cadmium occurs as a minor component in most zinc ores and is a byproduct of zinc production. Cadmium was used for a long time as a corrosion-resistant plating on steel, and cadmium compounds are used as red, orange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |