|
CPU Design
Processor design is a subfield of computer science and computer engineering (fabrication) that deals with creating a processor (computing), processor, a key component of computer hardware. The design process involves choosing an instruction set and a certain execution paradigm (e.g. Very long instruction word, VLIW or Reduced instruction set computing, RISC) and results in a microarchitecture, which might be described in e.g. VHDL or Verilog. For microprocessor design, this description is then manufactured employing some of the various semiconductor device fabrication processes, resulting in a Die (integrated circuit), die which is bonded onto a chip carrier. This chip carrier is then soldered onto, or inserted into a CPU socket, socket on, a printed circuit board (PCB). The mode of operation of any processor is the execution of lists of instructions. Instructions typically include those to compute or manipulate data values using Processor register, registers, change or retrieve va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuits (ICs) such as microprocessors, microcontrollers, and memories (such as RAM and flash memory). It is a multiple-step photolithographic and physico-chemical process (with steps such as thermal oxidation, thin-film deposition, ion-implantation, etching) during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer, typically made of pure single-crystal semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications. This article focuses on the manufacture of integrated circuits, however steps such as etching and photolithography can be used to manufacture other devices such as LCD and OLED displays. The fabrication process is performed in highly specialized semiconductor fabrication plants, also called foundries or "fabs", with the central part being the " clean room". In more advanced semi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library (electronics)
In semiconductor design, standard-cell methodology is a method of designing application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) with mostly digital-logic features. Standard-cell methodology is an example of design abstraction, whereby a low-level very-large-scale integration ( VLSI) layout is encapsulated into an abstract logic representation (such as a NAND gate). Cell-based methodology – the general class to which standard cells belong – makes it possible for one designer to focus on the high-level (logical function) aspect of digital design, while another designer focuses on the implementation (physical) aspect. Along with semiconductor manufacturing advances, standard-cell methodology has helped designers scale ASICs from comparatively simple single-function ICs (of several thousand gates), to complex multi-million gate system-on-a-chip (SoC) devices. Construction of a standard cell A standard cell is a group of transistor and interconnect structures that provides a boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic Gate
A logic gate is a device that performs a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has, for instance, zero rise time and unlimited fan-out, or it may refer to a non-ideal physical device (see ideal and real op-amps for comparison). The primary way of building logic gates uses diodes or transistors acting as electronic switches. Today, most logic gates are made from MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors). ''From Integrated circuit'' They can also be constructed using vacuum tubes, electromagnetic relays with relay logic, fluidic logic, pneumatic logic, optics, molecules, acoustics, or even mechanical or thermal elements. Logic gates can be cascaded in the same way that Boolean functions can be composed, allowing the construction of a physical model of all of Boolean logic, and therefore, all o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock Distribution Network
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions. A clock signal is produced by an electronic oscillator called a clock generator. The most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of sufficien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase-locked Loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is fixed relative to the phase of an input signal. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and output frequencies the same, thus a phase-locked loop can also track an input frequency. Furthermore, by incorporating a frequency divider, a PLL can generate a stable frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency. These properties are used for clock synchronization, demodulation, frequency synthesis, clock multipliers, and signal recovery from a noisy communication channel. Since 1969, a single integrated circuit can provide a complete PLL building block, and nowadays have output frequencies from a fraction of a hertz up to many gigahertz. Thus, PLLs are widely employed in radio, telecommunications, computers (e.g. to distribute precisely timed clock signals in microprocessors), grid-tie inverters (electronic power converters used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
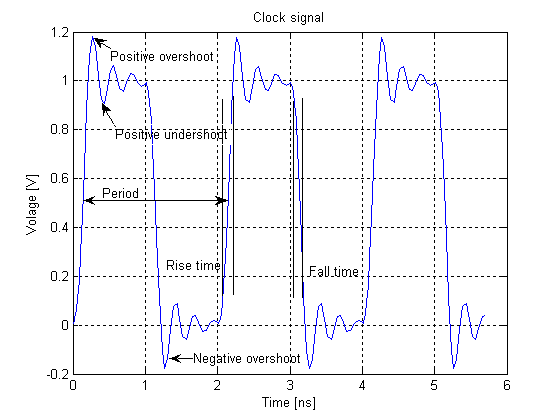
Clock Signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions. A clock signal is produced by an electronic oscillator called a clock generator. The most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cache (computing)
In computing, a cache ( ) is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster; the data stored in a cache might be the result of an earlier computation or a copy of data stored elsewhere. A cache hit occurs when the requested data can be found in a cache, while a cache miss occurs when it cannot. Cache hits are served by reading data from the cache, which is faster than recomputing a result or reading from a slower data store; thus, the more requests that can be served from the cache, the faster the system performs. To be cost-effective, caches must be relatively small. Nevertheless, caches are effective in many areas of computing because typical Application software, computer applications access data with a high degree of locality of reference. Such access patterns exhibit temporal locality, where data is requested that has been recently requested, and spatial locality, where data is requested that is stored near dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Register File
A register file is an array of processor registers in a central processing unit (CPU). The instruction set architecture of a CPU will almost always define a set of registers which are used to stage data between memory and the functional units on the chip. The register file is part of the architecture and visible to the programmer, as opposed to the concept of transparent caches. In simpler CPUs, these ''architectural registers'' correspond one-for-one to the entries in a physical register file (PRF) within the CPU. More complicated CPUs use register renaming, so that the mapping of which physical entry stores a particular architectural register changes dynamically during execution. Modern integrated circuit-based register files are usually implemented by way of fast static RAMs with multiple ports. Such RAMs are distinguished by having dedicated read and write ports, whereas ordinary multiported SRAMs will usually read and write through the same ports. Register banking is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory (computing)
Computer memory stores information, such as data and programs, for immediate use in the computer. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the terms '' RAM,'' ''main memory,'' or ''primary storage.'' Archaic synonyms for main memory include ''core'' (for magnetic core memory) and ''store''. Main memory operates at a high speed compared to mass storage which is slower but less expensive per bit and higher in capacity. Besides storing opened programs and data being actively processed, computer memory serves as a mass storage cache and write buffer to improve both reading and writing performance. Operating systems borrow RAM capacity for caching so long as it is not needed by running software. If needed, contents of the computer memory can be transferred to storage; a common way of doing this is through a memory management technique called ''virtual memory''. Modern computer memory is implemented as semiconductor memory, where data is stored within memory cells built from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Unit
The control unit (CU) is a component of a computer's central processing unit (CPU) that directs the operation of the processor. A CU typically uses a binary decoder to convert coded instructions into timing and control signals that direct the operation of the other units (memory, arithmetic logic unit and input and output devices, etc.). Most computer resources are managed by the CU. It directs the flow of data between the CPU and the other devices. John von Neumann included the control unit as part of the von Neumann architecture. In modern computer designs, the control unit is typically an internal part of the CPU with its overall role and operation unchanged since its introduction. Multicycle control units The simplest computers use a multicycle microarchitecture. These were the earliest designs. They are still popular in the very smallest computers, such as the embedded systems that operate machinery. In a computer, the control unit often steps through the instructio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipeline (computing)
In computing, a pipeline, also known as a data pipeline, is a set of data processing elements connected in series, where the output of one element is the input of the next one. The elements of a pipeline are often executed in parallel or in time-sliced fashion. Some amount of buffer storage is often inserted between elements. Concept and motivation Pipelining is a commonly used concept in everyday life. For example, in the assembly line of a car factory, each specific task—such as installing the engine, installing the hood, and installing the wheels—is often done by a separate work station. The stations carry out their tasks in parallel, each on a different car. Once a car has had one task performed, it moves to the next station. Variations in the time needed to complete the tasks can be accommodated by "buffering" (holding one or more cars in a space between the stations) and/or by "stalling" (temporarily halting the upstream stations), until the next station becomes avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |