|
CMOS Amplifier
CMOS amplifiers ( complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor amplifiers) are ubiquitous analog circuits used in computers, audio systems, smartphones, cameras, telecommunication systems, biomedical circuits, and many other systems. Their performance impacts the overall specifications of the systems. They take their name from the use of MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) as opposite to bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). MOSFETs are simpler to fabricate and therefore less expensive than BJT amplifiers, still providing a sufficiently high transconductance to allow the design of very high performance circuits. In high performance CMOS (complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor) amplifier circuits, transistors are not only used to amplify the signal but are also used as active loads to achieve higher gain and output swing in comparison with resistive loads. CMOS technology was introduced primarily for digital circuit design. In the last few dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complementary Metal–oxide–semiconductor
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips (including CMOS BIOS), and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensors), data converters, RF circuits ( RF CMOS), and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. The CMOS process was originally conceived by Frank Wanlass at Fairchild Semiconductor and presented by Wanlass and Chih-Tang Sah at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference in 1963. Wanlass later filed US patent 3,356,858 for CMOS circuitry and it was granted in 1967. commercialized the technology with the trademark "COS-M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moore’s Law
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empirical relationship linked to gains from experience in production. The observation is named after Gordon Moore, the co-founder of Fairchild Semiconductor and Intel (and former CEO of the latter), who in 1965 posited a doubling every year in the number of components per integrated circuit, and projected this rate of growth would continue for at least another decade. In 1975, looking forward to the next decade, he revised the forecast to doubling every two years, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41%. While Moore did not use empirical evidence in forecasting that the historical trend would continue, his prediction held since 1975 and has since become known as a "law". Moore's prediction has been used in the semiconductor industry to gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor (chemistry), precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is biosynthesis, synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons (nerve cells) to send signals to other nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in specific regions of the brain, but affect many regions systemically. The brain includes several distinct dopaminergic pathway, dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward system, reward-motivated behavior. The anticipa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. "Carbon nanostructures for electromagnetic shielding applications", Mohammed Arif Poothanari, Sabu Thomas, et al., ''Industrial Applications of Nanomaterials'', 2019. "Carbon nanostructures include various low-dimensional allotropes of carbon including carbon black (CB), carbon fiber, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), fullerene, and graphene." The name is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, reflecting the fact that the allotrope of carbon contains numerous double bonds. Each atom in a graphene sheet is connecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slew Rate
In electronics, slew rate is defined as the change of voltage or current, or any other electrical quantity, per unit of time. Expressed in SI units, the unit of measurement is volts/second or amperes/second, but is usually expressed in terms of microseconds (μs) or nanoseconds (ns). Electronic circuits may specify minimum or maximum limits on the slew rates for their inputs or outputs, with these limits only valid under some set of given conditions (e.g. output loading). When given for the output of a circuit, such as an amplifier, the slew rate specification guarantees that the speed of the output signal transition will be at least the given minimum, or at most the given maximum. When applied to the input of a circuit, it instead indicates that the external driving circuitry needs to meet those limits in order to guarantee the correct operation of the receiving device. If these limits are violated, some error might occur and correct operation is no longer guaranteed. For exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transimpedance Amplifier
In electronics, a transimpedance amplifier (TIA) is a current to voltage converter, almost exclusively implemented with one or more operational amplifiers. The TIA can be used to amplify the current output of Geiger–Müller tubes, photo multiplier tubes, accelerometers, photo detectors and other types of sensors to a usable voltage. Current to voltage converters are used with sensors that have a current response that is more linear than the voltage response. This is the case with photodiodes where it is not uncommon for the current response to have better than 1% nonlinearity over a wide range of light input. The transimpedance amplifier presents a low impedance to the photodiode and isolates it from the output voltage of the operational amplifier. In its simplest form a transimpedance amplifier has just a large valued feedback resistor, Rf. The gain of the amplifer is set by this resistor and because the amplifier is in an inverting configuration, has a value of -Rf. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Papers
The term regular can mean normal or in accordance with rules. It may refer to: People * Moses Regular (born 1971), America football player Arts, entertainment, and media Music * "Regular" (Badfinger song) * Regular tunings of stringed instruments, tunings with equal intervals between the paired notes of successive open strings Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * Regular character, a main character who appears more frequently and/or prominently than a recurring character * Regular division of the plane, a series of drawings by the Dutch artist M. C. Escher which began in 1936 * ''Regular Show'', an animated television sitcom * ''The Regular Guys'', a radio morning show Language * Regular inflection, the formation of derived forms such as plurals in ways that are typical for the language ** Regular verb * Regular script, the newest of the Chinese script styles Mathematics There are an extremely large number of unrelated notions of "regularity" in mathematics. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
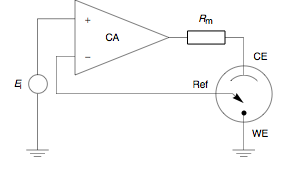
Potentiostat
A potentiostat is the electronic hardware required to control a three electrode cell and run most electroanalytical experiments. A ''Bipotentiostat'' and ''polypotentiostat'' are potentiostats capable of controlling two working electrodes and more than two working electrodes, respectively. The system functions by maintaining the potential of the working electrode at a constant level with respect to the reference electrode by adjusting the current at an auxiliary electrode. The heart of the different potentiostatic electronic circuits is an operational amplifier (op amp). It consists of an electric circuit which is usually described in terms of simple op amps. Primary use This equipment is fundamental to modern electrochemical studies using three electrode systems for investigations of reaction mechanisms related to redox chemistry and other chemical phenomena. The dimensions of the resulting data depend on the experiment. In voltammetry, electric current in amps is pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE Transactions On Biomedical Circuits And Systems
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Origins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrator
An integrator in measurement and control applications is an element whose output signal is the time integral of its input signal. It accumulates the input quantity over a defined time to produce a representative output. Integration is an important part of many engineering and scientific applications. Mechanical integrators are the oldest application, and are still used in such as metering of water flow or electric power. Electronic analogue integrators are the basis of analog computers and charge amplifiers. Integration is also performed by digital computing algorithms. In signal processing circuits :''See also Integrator at op amp applications'' An electronic integrator is a form of first-order low-pass filter, which can be performed in the continuous-time (analog) domain or approximated (simulated) in the discrete-time (digital) domain. An integrator will have a low pass filtering effect but when given an offset it will accumulate a value building it until it reaches a limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
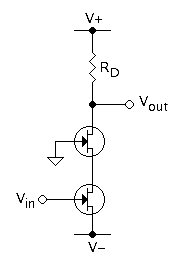
Cascode
The cascode is a two-stage amplifier that consists of a common-emitter stage feeding into a common-base stage. Compared to a single amplifier stage, this combination may have one or more of the following characteristics: higher input–output isolation, higher input impedance, high output impedance, higher bandwidth. In modern circuits, the cascode is often constructed from two transistors (BJTs or FETs), with one operating as a common emitter or common source and the other as a common base or common gate. The cascode improves input–output isolation (reduces reverse transmission), as there is no direct coupling from the output to input. This eliminates the Miller effect and thus contributes to a much higher bandwidth. History The use of a cascode (sometimes verbified to ''cascoding'') is a common technique for improving analog circuit performance, applicable to both vacuum tubes and transistors. The name "cascode" was coined in an article written by Frederick Vinton Hunt an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamental Theory And Applications
Fundamental may refer to: * Foundation of reality * Fundamental frequency, as in music or phonetics, often referred to as simply a "fundamental" * Fundamentalism, the belief in, and usually the strict adherence to, the simple or "fundamental" ideas based on faith in a system of thought * ''The Fundamentals'', a set of books important to Christian fundamentalism * Any of a number of fundamental theorems identified in mathematics, such as: ** Fundamental theorem of algebra, awe theorem regarding the factorization of polynomials ** Fundamental theorem of arithmetic, a theorem regarding prime factorization * Fundamental analysis, the process of reviewing and analyzing a company's financial statements to make better economic decisions Music * Fun-Da-Mental, a rap group * ''Fundamental'' (Bonnie Raitt album), 1998 * ''Fundamental'' (Pet Shop Boys album) * ''Fundamental'' (Puya album), 1999 * ''Fundamental'' (Mental As Anything album) * ''The Fundamentals'' (album) Other uses * " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |