|
CIE 141 Class
The CIE 141 Class locomotives were built in 1962 by General Motors Electro Motive Division (EMD) in the United States. Numbered B141 to B177, they were an updated version of the 121 Class locomotives, mechanically very similar but with cabs at each end. They are EMD model JL8 (J = Double Ended Cabs, L = Lightweight Frame, 8= 8-cylinder 567 engine) and although originally fitted with an EMD 8-567CR engine of , all were later fitted with 645 type "power packs" (piston & liner assemblies) for parts standardisation. The original power output was kept for reliability reasons. They weighed 67 tonnes and had a maximum speed of . Many of these locomotives were later rebuilt with a GM 8-645E engine of (as used in the re-engined Class C locomotives), though some have since had the original engine refitted. The locomotives were delivered in the CIE livery of brown/black/white. Service Following crew training trials between Inchicore and Monasterevin (passenger trains), Kildare (goo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limerick Colbert Railway Station
Limerick Station ( ga, Stáisiún Luimnigh) also known as Colbert Station ( ga, Stáisiún Uí Cholbáird) or Limerick Colbert serves the city of Limerick in County Limerick. It is on Parnell Street and is the main station on the Limerick Suburban Rail network. It has approximately 2,500 rail passengers a day travelling on four rail routes. The Bus Éireann bus station on site services approximately one million passengers a year, with 125 buses departing each day. Services The station is the terminus of the Dublin–Limerick, Limerick–Nenagh–Ballybrophy and Limerick–Ennis–Galway lines. Connections for Cork, Clonmel, Carrick-on-Suir, Waterford and Kerry stations, such as Killarney, Farranfore and Tralee can be made at Limerick Junction. Bus Éireann's Limerick depot is adjacent and offers Intercity, Express and Eurolines services. Connecting to Shannon Airport Buses connect the railway station to Shannon Airport. History The station opened on 28 August 1858, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIE 201 Class
The Córas Iompair Éireann 201 Class was a class of 34 diesel electric locomotives manufactured by Metropolitan-Vickers at their Dukinfield Works in Manchester. They were a smaller, lighter and less powerful version of the 001 Class and were originally intended for branch line passenger and freight (mixed traffic) duties. They were introduced in 1956 and, although their duties changed over the years, were in regular service on the Irish railway network until the mid-1980s. Six were sold to Northern Ireland Railways (NIR) in 1986. Service history Unfortunately, these locomotives suffered from two distinct problems: * During the late 1950s and early 1960s, following the publication of the Andrews Report (mimicking the widescale the Beeching Axe in Britain), CIÉ undertook large-scale closures of branch lines, leaving the engines without a purpose. *The locomotives were of insufficient power for their duties and their Crossley engines suffered reliability problems. The exist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobh Railway Station
Cobh railway station serves the town of Cobh, County Cork. It is located in a red brick building adjacent to the town's Cobh Heritage Centre. It is the terminus of the on Cork-Cobh section of the Cork Suburban Rail line. Travel to Glounthaune station to transfer to Midleton. Description The station is staffed part-time and has a single platform. The station is accessible only via a steep ramp. History The station opened 10 March 1862 and was closed for goods traffic on 3 November 1975. It began life as the terminus of the Cobh (then Queenstown) section of the Cork, Youghal & Queenstown Railway. The present station occupies only a small part of the old station building. The original station was expanded greatly during the latter part of the 19th century as it served what was then Ireland's largest emigration port which was also an important way-point as the last port between Western Europe and North America. The station was also the main receiving centre for mails for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork Kent Railway Station
Kent Station ( ga, Stáisiún Cheannt) is an Iarnród Éireann railway station in Cork (city), Cork, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Originally opened in 1893, the station operates as a hub for Intercity services to Dublin Heuston railway station, Dublin and Tralee railway station, Tralee and Cork Suburban Rail, commuter services to Mallow, County Cork, Mallow, Cobh and Midleton. In 2016, Kent Station was the fifth busiest station in the Republic of Ireland, as well as the busiest outside of Dublin. Background Name The station was originally called ''Glanmire Road Station'', but was renamed after Thomas Kent in 1966 on the 50th anniversary of the Easter Rising. History The station opened on 2 February 1893 and the current building was built in the same year. The station replaced two earlier stations that served as separate termini for the Great Southern and Western Railway (GS&WR) and Cork and Youghal Railway, Cork & Youghal Railway (C&Y). The original GS&WR station, Penros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIE 181 Class
The Córas Iompair Éireann 181 Class locomotives were built in 1966 by General Motors Electro-Motive Division (EMD) and numbered B181 to B192. These locomotives were virtually identical to the earlier 141 Class locomotives, but fitted with the more powerful 645 engine and thermostatically controlled engine cooling fan and inlet shutters. Delivery took place in 1966, with introduction into service happening a short time later. They were fitted with an EMD 8-645E engine of 1100 hp, weighed , and had a maximum design speed of which was restricted to in service. Number 186 was later fitted with an EMD 8-567CR engine of , as used in the 141 Class locomotives. Withdraw and preservation All of the 181 class have been withdrawn, the first being 191 in 1991 after a runaway incident at Clonsilla; it was later scrapped in 1998. The last was 190 in November 2009 and has been preserved by the Irish Traction Group The Irish Traction Group is a railway preservation society dedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limerick–Rosslare Railway Line
The Limerick–Rosslare Main Line is a railway route in the Republic of Ireland that linked the city of Limerick on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast with Rosslare Europort on the coast of the Irish Sea. It also serves the city of Waterford, and at it connects with the Dublin–Cork railway line. Since 2010 there has been no service between Waterford and Rosslare Europort, and all trains terminate at . Rosslare (Europort and Strand) and Wexford have still at least three trains a day to Dublin, and three back (morning, afternoon and evening). The line between Rosslare and Waterford is closed to passenger trains since September 2010, though it is still maintained by Iarnród Éireann. History Construction of the route was begun in 1848 for the Waterford, Limerick and Western Railway, Waterford and Limerick Railway and completed in 1854. It is one of the oldest railways in Ireland, and the first to have been authorised by the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK Parliament. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise (train Service)
''Enterprise'' is the cross-border inter-city train service between in the Republic of Ireland and in Northern Ireland, jointly operated by Iarnród Éireann (IE) and NI Railways (NIR). It operates on the Belfast–Dublin railway line. History The Great Northern Railway (Ireland) (GNR(I)) introduced the service as the "Enterprise Express" on Monday 11 August 1947 in an attempt to compete with air and road transport which were challenging the railways. In particular, business travel was and is an important market. Customs checks were limited to the Belfast and Dublin terminals to reduce journey times by ensuring that journeys were non-stop, and advance booking was available. The name of the train comes from the "enterprising" approach that the GNR(I) took to make journeys more convenient for passengers despite the requirement for customs checks. The initial service ran between and Dublin Amiens Street Junction (renamed in 1966). Locomotives of GNRI Class V were initially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-heading
In railroad terminology, double heading indicates the use of two locomotives at the front of a train, each operated individually by its own crew. The practice of triple-heading involves the use of three locomotives. The practice of multi-heading involves the use of multiple locomotives and so on. Double heading is most common with steam locomotives, but is also practised with diesel locomotives. It is not strictly the same practice as two or more diesel or electric locomotives working ' in multiple' (or 'multiple-working'), where both (or all) locomotives are controlled by a single driver in the cab of the leading locomotive. Advantages Double heading is practised for a number of reasons: * In the UK it was usually to gain traction on steep inclines, twice the amount of driven wheels - twice the amount of grip. * The need for additional motive power when a single locomotive is unable to haul the train due to uphill grades, excessive train weight, or a combination of the two. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arklow
Arklow (; ; , ) is a town in County Wicklow on the southeast coast of Ireland. The town is overlooked by Ballymoyle Hill. It was founded by the Vikings in the ninth century. Arklow was the site of one of the bloodiest battles of the 1798 rebellion. Its proximity to Dublin led to it becoming a commuter town with a population of 13,163 as of the 2016 census. Arklow is at the mouth of the River Avoca, the longest river wholly within County Wicklow. The town is divided by the river, which is crossed by the Nineteen Arches Bridge, a stone arch bridge linking the southern or main part of the town with the northern part, called Ferrybank. The Nineteen Arches Bridge is the longest handmade stone bridge in Ireland, and a plaque on the south end of the bridge acknowledges this. History The town's English name derives from ''Arnkell's Lág'' (Arnkell was a Viking leader; a "lág" (low) was an area of land). Its Irish name, ''Inbhear Mór'' or ''An tInbhear Mór'', means ''the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin Pearse Railway Station
Pearse railway station ( ga, Stáisiún na bPiarsach) or Dublin Pearse is a railway station on Westland Row on the Southside of Dublin, Ireland. It is Ireland's busiest commuter station and second busiest station overall (behind Dublin Connolly railway station) with 9 million passenger journeys through the station in 2016. Services All DART services stop at the station. Additionally Pearse is on the South Eastern Commuter (Dublin Connolly to Gorey) and South Western Commuter (Grand Canal Dock to Newbridge) routes, and is a terminus for the Northern Commuter (to Balbriggan / Dundalk) and Western Commuter (to Maynooth / Longford) services. It also services the InterCity (from Dublin Connolly to Rosslare Europort) route. Facilities The station has two through platforms, 1 and 2, the former on the Boyne Street side for northbound "up" services towards Connolly station, the other on the Pearse Street side for southbound "down" services towards Bray. It also has a café and pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
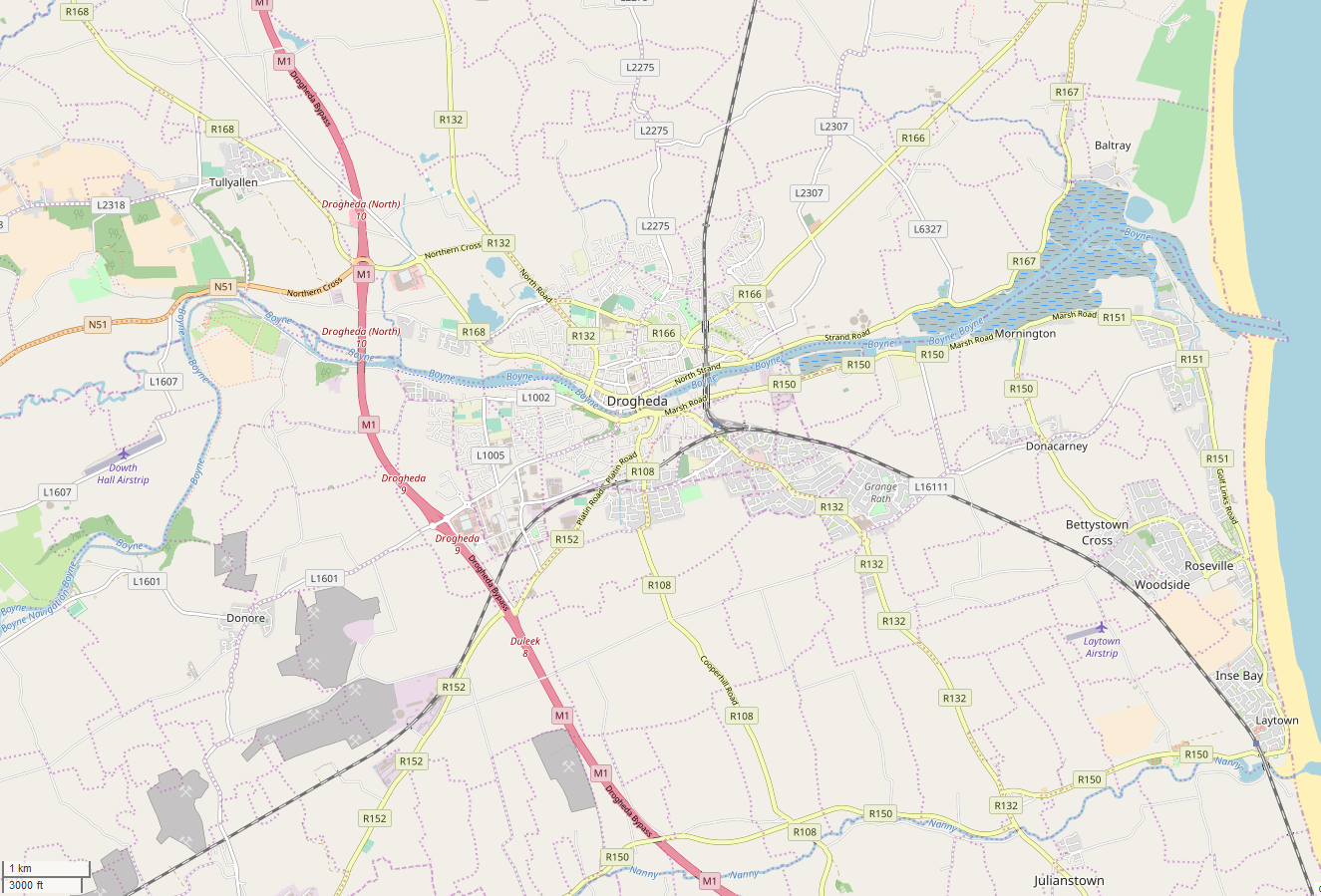
Drogheda
Drogheda ( , ; , meaning "bridge at the ford") is an industrial and port town in County Louth on the east coast of Ireland, north of Dublin. It is located on the Dublin–Belfast corridor on the east coast of Ireland, mostly in County Louth but with the south fringes of the town in County Meath, north of Dublin. Drogheda has a population of approximately 41,000 inhabitants (2016), making it the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, eleventh largest settlement by population in all of Ireland, and the largest town in the Republic of Ireland by both population and area. It is the last bridging point on the River Boyne before it enters the Irish Sea. The UNESCO World Heritage Site of Newgrange is located west of the town. Drogheda was founded as two separately administered towns in two different territories: Drogheda-in-Kingdom of Meath, Meath (i.e. the Lordship of Meath, Lordship and Liberty of Meath, from which a charter was granted in 1194) and Drogheda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin Connolly Railway Station
Connolly station ( ga, Stáisiún Uí Chonghaile) or Dublin Connolly is one of the busiest railway stations in Dublin and Ireland, and is a focal point in the Irish route network. On the North side of the River Liffey, it provides InterCity, Enterprise and commuter services to the north, north-west, south-east and south-west. The north–south Dublin Area Rapid Transit (DART) and Luas light rail services also pass through the station. The station offices are the headquarters of Irish Rail, Iarnród Éireann. Opened in 1844 as ''Dublin Station'', the ornate facade has a distinctive Italianate tower at its centre. History On 24 May 1844 the Dublin and Drogheda Railway (DDR) began public operations from an interim terminus at the Royal Canal, and on the same day the foundation stone for what is now Connolly station was laid by Earl de Grey, Lord Lieutenant of Ireland. The station was opened for operations on 29 November 1844 as ''Dublin Station'', but was renamed ''Amie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |