|
CHRNE
Acetylcholine receptor subunit epsilon is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CHRNE'' gene. Acetylcholine receptors at mature mammalian neuromuscular junctions are pentameric protein complexes composed of four subunits in the ratio of two alpha subunits to one beta, one epsilon, and one delta subunit. The achetylcholine receptor changes subunit composition shortly after birth when the epsilon subunit replaces the gamma subunit seen in embryonic receptors. Mutations in the epsilon subunit are associated with congenital myasthenic syndrome. Role in health and disease Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is associated with genetic defects that affect proteins of the neuromuscular junction. Postsynaptic defects are the most frequent cause of CMS and often result in abnormalities in the acetylcholine receptor (AChR). The majority of mutations causing CMS are found in the AChR subunits genes. Out of all mutations associated with CMS, more than half are mutations in one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome
Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is an inherited neuromuscular disorder caused by defects of several types at the neuromuscular junction. The effects of the disease are similar to Lambert-Eaton Syndrome and myasthenia gravis, the difference being that CMS is not an autoimmune disorder. There are only 600 known family cases of this disorder and it is estimated that its overall frequency in the human population is 1 in 200,000. Types The types of CMS are classified into three categories: presynaptic, postsynaptic, and synaptic. * ''Presynaptic'' symptoms include brief stops in breathing, weakness of the eye, mouth, and throat muscles. These symptoms often result in double vision and difficulty chewing and swallowing. * ''Postsynaptic'' symptoms in infants include severe muscle weakness, feeding and respiratory problems, and delays in the ability to sit, crawl, and walk. * ''Synaptic'' symptoms include early childhood feeding and respiratory problems, reduced mobility, curva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome
Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is an inherited neuromuscular disorder caused by defects of several types at the neuromuscular junction. The effects of the disease are similar to Lambert-Eaton Syndrome and myasthenia gravis, the difference being that CMS is not an autoimmune disorder. There are only 600 known family cases of this disorder and it is estimated that its overall frequency in the human population is 1 in 200,000. Types The types of CMS are classified into three categories: presynaptic, postsynaptic, and synaptic. * ''Presynaptic'' symptoms include brief stops in breathing, weakness of the eye, mouth, and throat muscles. These symptoms often result in double vision and difficulty chewing and swallowing. * ''Postsynaptic'' symptoms in infants include severe muscle weakness, feeding and respiratory problems, and delays in the ability to sit, crawl, and walk. * ''Synaptic'' symptoms include early childhood feeding and respiratory problems, reduced mobility, curva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
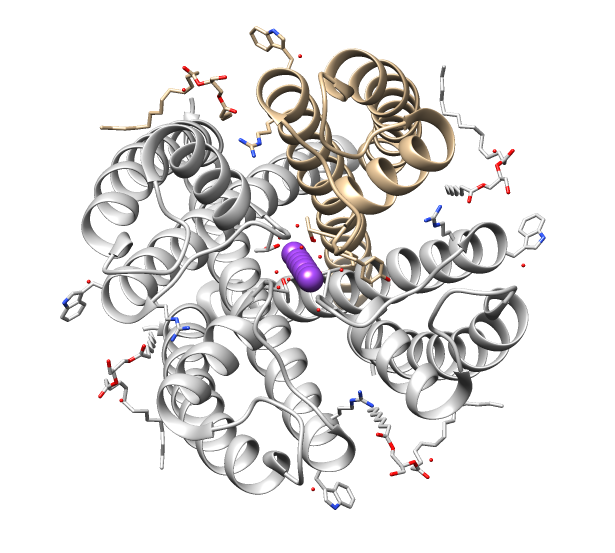
Acetylcholine Receptor
An acetylcholine receptor (abbreviated AChR) is an integral membrane protein that responds to the binding of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Classification Like other transmembrane receptors, acetylcholine receptors are classified according to their "pharmacology," or according to their relative affinities and sensitivities to different molecules. Although all acetylcholine receptors, by definition, respond to acetylcholine, they respond to other molecules as well. *Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (''nAChR'', also known as "ionotropic" acetylcholine receptors) are particularly responsive to nicotine. The nicotine ACh receptor is also a Na+, K+ and Ca2+ ion channel. *Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (''mAChR'', also known as "metabotropic" acetylcholine receptors) are particularly responsive to muscarine. Nicotinic and muscarinic are two main kinds of "cholinergic" receptors. Receptor types Molecular biology has shown that the nicotinic and muscarinic receptors belong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral nervous system, muscle, and many other tissues of many organisms. At the neuromuscular junction they are the primary receptor in muscle for motor nerve-muscle communication that controls muscle contraction. In the peripheral nervous system: (1) they transmit outgoing signals from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic cells within the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, and (2) they are the receptors found on skeletal muscle that receive acetylcholine released to signal for muscular contraction. In the immune system, nAChRs regulate inflammatory processes and signal through distinct intracellular pathways. In insects, the cholinergic system is limited to the central nervous system. The nicotinic receptors are considered cholinergi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentameric Protein
A pentameric protein is a quaternary protein structure that consists of five protein subunits. Examples Ligand-gated ion channels Five sub-units come together to form a channel. Each channel consist of two alpha chain, one beta, one gamma and one delta chain. These five chains assemble together (along with certain receptors like protons or acetylcholine) forming the structure of the channel. A ligand-gated ion channel on the post-synaptic junction of the muscle-end plate is an example of such a channel. They are acetylcholine-operated ion channels, which means that acetylcholine brings about a conformational change. The channel allows the free movement of the cations like Na and K when acetylcholine binds to its receptors. Viral capsids Many viral capsids are formed by hexameric and pentameric proteins. Such capsids are assigned a triangulation number (T-number) which describe relation between the number of pentagons and hexagons. Carboxysomes Protein enclosing bacterial organe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuromuscular Junction
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction. Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. In the neuromuscular system nerves from the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system are linked and work together with muscles. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-gated calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmins) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the amino and guanidino groups are protonated, resulting in a cation. Only the -arginine (symbol Arg or R) enantiomer is found naturally. Arg residues are common components of proteins. It is encoded by the codons CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG. The guanidine group in arginine is the precursor for the biosynthesis of nitric oxide. Like all amino acids, it is a white, water-soluble solid. History Arginine was first isolated in 1886 from yellow lupin seedlings by the German chemist Ernst Schulze and his assistant Ernst Steiger. He named it from the Greek ''árgyros'' (ἄργυρος) meaning "silver" due to the silver-white appearance of arginine nitrate crystals. In 1897, Schulze and Ernst Winterstein (1865–1949) determined the structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channels
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion transporter proteins: #The rate of ion transport through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |