|
CEBPA
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha is a protein encoded by the ''CEBPA'' gene in humans. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha is a transcription factor involved in the differentiation of certain blood cells. For details on the CCAAT structural motif in gene enhancers and on CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Proteins see the specific page. Function The protein encoded by this intronless gene is a bZIP transcription factor which can bind as a homodimer to certain promoters and gene enhancers. It can also form heterodimers with the related proteins CEBP-beta and CEBP-gamma, as well as distinct transcription factors such as c-Jun. The encoded protein is a key regulator of adipogenesis (the process of forming new fat cells) and the accumulation of lipids in those cells, as well as in the metabolism of glucose and lipids in the liver. The protein has been shown to bind to the promoter and modulate the expression of the gene encoding leptin, a protein that plays an important role in body wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipogenesis
Adipogenesis is the formation of adipocytes (fat cells) from stem cells. It involves 2 phases, determination, and terminal differentiation. Determination is mesenchymal stem cells committing to the adipocyte precursor cells, also known as preadipocytes which lose the potential to differentiate to other types of cells such as chondrocytes, myocytes, and osteoblasts. Terminal differentiation is that preadipocytes differentiate into mature adipocytes. Adipocytes can arise either from preadipocytes resident in adipose tissue, or from bone-marrow derived progenitor cells that migrate to adipose tissue. Introduction Adipocytes play a vital role in energy homeostasis and process the largest energy reserve as triglycerol in the body of animals. Adipocytes stay in a dynamic state, they start expanding when the energy intake is higher than the expenditure and undergo mobilization when the energy expenditure exceeds the intake. This process is highly regulated by counter regulatory hormones t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, easy bruising and bleeding, and increased risk of infection. Occasionally, spread may occur to the brain, skin, or gums. As an acute leukemia, AML progresses rapidly, and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated. Risk factors include smoking, previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, myelodysplastic syndrome, and exposure to the chemical benzene. The underlying mechanism involves replacement of normal bone marrow with leukemia cells, which results in a drop in red blood cells, platelets, and normal white blood cells. Diagnosis is generally based on bone marrow aspiration and specific blood tests. AML has several subtypes for which treatments and outcomes may vary. The fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult person, approximately – new blood cells are produced daily in order to maintain steady state levels in the peripheral circulation.Semester 4 medical lectures at Uppsala University 2008 by Leif Jansson Process Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside in the medulla of the bone (bone marrow) and have the unique ability to give rise to all of the different mature blood cell types and tissues. HSCs are self-renewing cells: when they differentiate, at least some of their daughter cells remain as HSCs so the pool of stem cells is not depleted. This phenomenon is called asymmetric division. The other daughters of HSCs ( myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells) can follow any of the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDK2
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, also known as cell division protein kinase 2, or Cdk2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CDK2'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family of Ser/Thr protein kinases. This protein kinase is highly similar to the gene products of ''S. cerevisiae'' cdc28, and ''S. pombe'' cdc2, also known as Cdk1 in humans. It is a catalytic subunit of the cyclin-dependent kinase complex, whose activity is restricted to the G1-S phase of the cell cycle, where cells make proteins necessary for mitosis and replicate their DNA. This protein associates with and is regulated by the regulatory subunits of the complex including cyclin E or A. Cyclin E binds G1 phase Cdk2, which is required for the transition from G1 to S phase while binding with Cyclin A is required to progress through the S phase. Its activity is also regulated by phosphorylation. Multiple alternatively spliced variants and multiple transcription initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclin-dependent Kinase 2
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, also known as cell division protein kinase 2, or Cdk2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CDK2'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family of Ser/Thr protein kinases. This protein kinase is highly similar to the gene products of ''S. cerevisiae'' cdc28, and ''S. pombe'' cdc2, also known as Cdk1 in humans. It is a catalytic subunit of the cyclin-dependent kinase complex, whose activity is restricted to the G1-S phase of the cell cycle, where cells make proteins necessary for mitosis and replicate their DNA. This protein associates with and is regulated by the regulatory subunits of the complex including cyclin E or A. Cyclin E binds G1 phase Cdk2, which is required for the transition from G1 to S phase while binding with Cyclin A is required to progress through the S phase. Its activity is also regulated by phosphorylation. Multiple alternatively spliced variants and multiple transcription initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclin-dependent Kinase 4
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 also known as cell division protein kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CDK4'' gene. CDK4 is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This protein is highly similar to the gene products of ''S. cerevisiae'' cdc28 and ''S. pombe'' cdc2. It is a catalytic subunit of the protein kinase complex that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression. The activity of this kinase is restricted to the G1-S phase, which is controlled by the regulatory subunits D-type cyclins and CDK inhibitor p16INK4a. This kinase was shown to be responsible for the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product ( Rb). Ser/Thr-kinase component of cyclin D-CDK4 (DC) complexes that phosphorylate and inhibit members of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein family including RB1 and regulate the cell-cycle during G1/S transition. Phosphorylation of RB1 allows dissociati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDK4
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 also known as cell division protein kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CDK4'' gene. CDK4 is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This protein is highly similar to the gene products of ''S. cerevisiae'' cdc28 and ''S. pombe'' cdc2. It is a catalytic subunit of the protein kinase complex that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression. The activity of this kinase is restricted to the G1-S phase, which is controlled by the regulatory subunits D-type cyclins and CDK inhibitor p16INK4a. This kinase was shown to be responsible for the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product ( Rb). Ser/Thr-kinase component of cyclin D-CDK4 (DC) complexes that phosphorylate and inhibit members of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein family including RB1 and regulate the cell-cycle during G1/S transition. Phosphorylation of RB1 allows dissociati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ccaat-enhancer-binding Proteins
CCAAT-enhancer-binding proteins (or C/EBPs) is a family of transcription factors composed of six members, named from C/EBPα to C/EBPζ. They promote the expression of certain genes through interaction with their promoters. Once bound to DNA, C/EBPs can recruit so-called co-activators (such as CBP) that in turn can open up chromatin structure or recruit basal transcription factors. Function C/EBP proteins interact with the CCAAT (cytosine-cytosine- adenosine-adenosine-thymidine) box motif, which is present in several gene promoters. They are characterized by a highly conserved basic-leucine zipper (bZIP) domain at the C-terminus. This domain is involved in dimerization and DNA binding, as are other transcription factors of the leucine zipper domain-containing family ('' c-Fos'' and '' c-jun''). The bZIP domain structure of C/EBPs is composed of an α-helix that forms a "coiled coil" structure when it dimerizes. Members of the C/EBP family can form homodimers or heterodime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BZIP Domain
The Basic Leucine Zipper Domain (bZIP domain) is found in many DNA binding eukaryotic proteins. One part of the domain contains a region that mediates sequence specific DNA binding properties and the leucine zipper that is required to hold together (dimerize) two DNA binding regions. The DNA binding region comprises a number of basic amino acids such as arginine and lysine. Proteins containing this domain are transcription factors. bZIP transcription factors bZIP transcription factors are found in all eukaryotes and form one of the largest families of dimerizing TFs. An evolutionary study from 2008 revealed that 4 bZIP genes were encoded by the genome of the most recent common ancestor of all plants. Interactions between bZIP transcription factors are numerous and complex and play important roles in cancer development in epithelial tissues, steroid hormone synthesis by cells of endocrine tissues, factors affecting reproductive functions, and several other phenomena that aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
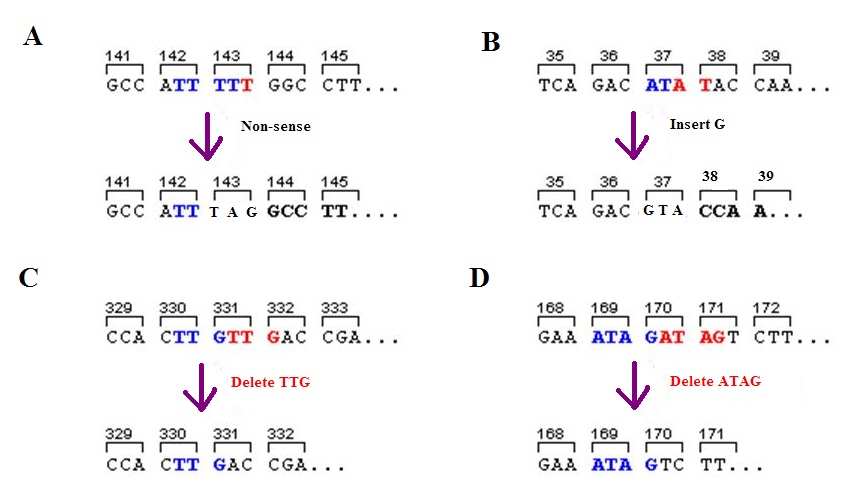
Frameshift Mutation
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels ( insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon ("UAA", "UGA" or "UAG") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulocyte
Granulocytes are cells in the innate immune system characterized by the presence of specific granules in their cytoplasm. Such granules distinguish them from the various agranulocytes. All myeloblastic granulocytes are polymorphonuclear. They have varying shapes (morphology) of the nucleus (segmented, irregular; often lobed into three segments); and are referred to as polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN, PML, or PMNL). In common terms, ''polymorphonuclear granulocyte'' refers specifically to "neutrophil granulocytes", the most abundant of the granulocytes; the other types (eosinophils, basophils, and mast cells) have varying morphology. Granulocytes are produced via granulopoiesis in the bone marrow. Types There are four types of granulocytes (full name polymorphonuclear granulocytes): * Basophils * Eosinophils * Neutrophils * Mast cells Except for the mast cells, their names are derived from their staining characteristics; for example, the most abundant granulocyte is the neut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Suppressor
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or reduction in its function. In combination with other genetic mutations, this could allow the cell to grow abnormally. The loss of function for these genes may be even more significant in the development of human cancers, compared to the activation of oncogenes. TSGs can be grouped into the following categories: caretaker genes, gatekeeper genes, and more recently landscaper genes. Caretaker genes ensure stability of the genome via DNA repair and subsequently when mutated allow mutations to accumulate. Meanwhile, gatekeeper genes directly regulate cell growth by either inhibiting cell cycle progression or inducing apoptosis. Lastly landscaper genes regulate growth by contributing to the surrounding environment, when mutated can cause an envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |