|
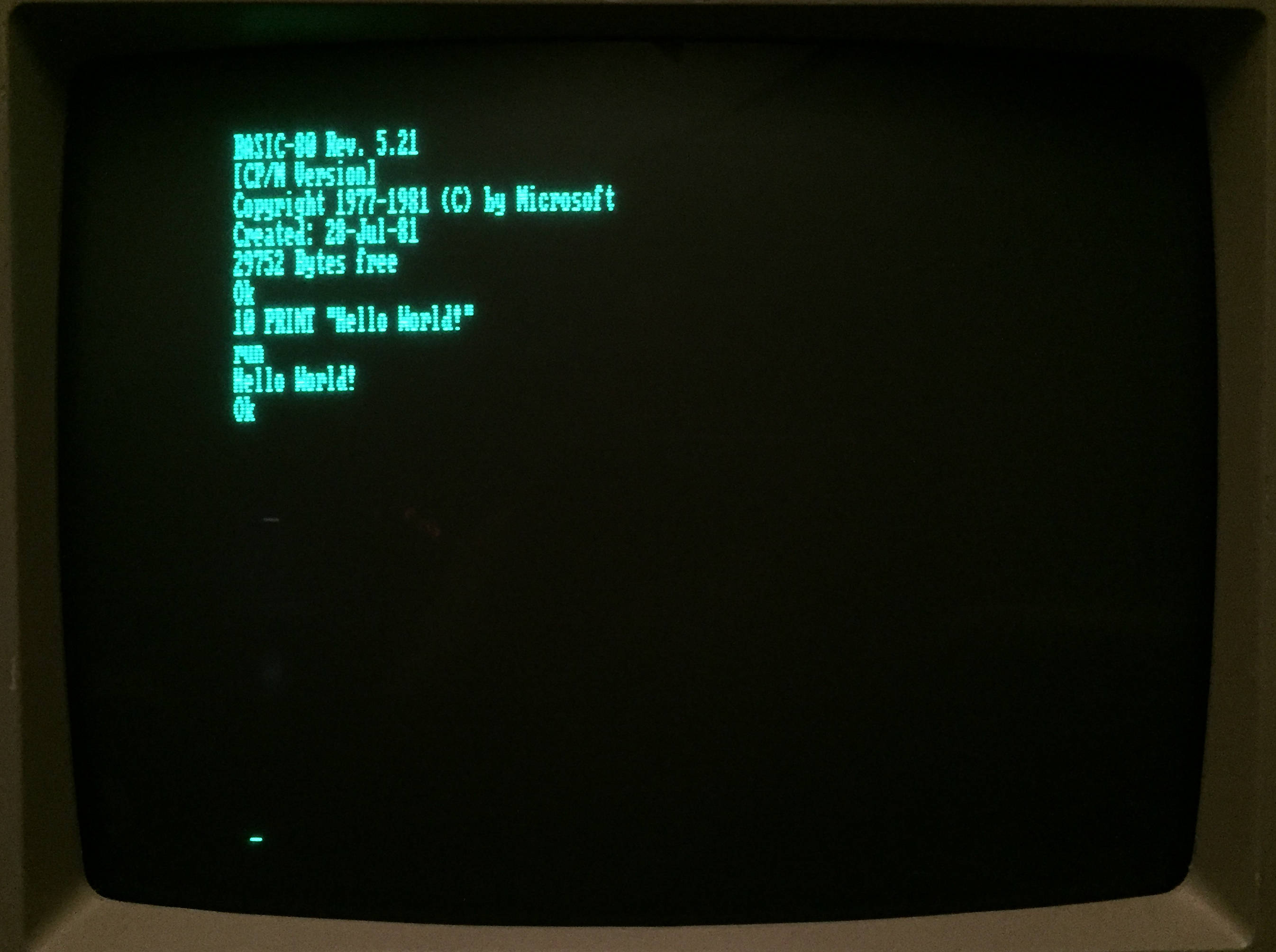
CBASIC
CBASIC is a compiled version of the BASIC programming language written for the CP/M operating system by Gordon Eubanks in 1976–1977. It is an enhanced version of BASIC-E. History BASIC-E was Eubank's master's thesis project. It was developed in PL/M by Eubanks for Gary Kildall's new CP/M operating system while both men were at the Naval Postgraduate School in Monterey, California. BASIC-E was based on a BASIC compiler originally written by Gary Kildall in 1974. Because it was developed at public expense, BASIC-E is in the public domain and could not be marketed exclusively. Seymour Rubinstein, the marketing director of IMSAI contacted Eubanks and asked him to create a saleable version under contract for the IMSAI 8080 microcomputer. p. 9, November 2000, Computerworld Honors Prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cbasic
CBASIC is a compiled version of the BASIC programming language written for the CP/M operating system by Gordon Eubanks in 1976–1977. It is an enhanced version of BASIC-E. History BASIC-E was Eubank's master's thesis project. It was developed in PL/M by Eubanks for Gary Kildall's new CP/M operating system while both men were at the Naval Postgraduate School in Monterey, California. BASIC-E was based on a BASIC compiler originally written by Gary Kildall in 1974. Because it was developed at public expense, BASIC-E is in the public domain and could not be marketed exclusively. Seymour Rubinstein, the marketing director of IMSAI contacted Eubanks and asked him to create a saleable version under contract for the IMSAI 8080 microcomputer. p. 9, November 2000, Computerworld Honors Prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon Eubanks
Gordon Edwin Eubanks, Jr. (born November 7, 1946) is an American microcomputer industry pioneer who worked with Gary Kildall in the early days of Digital Research (DRI). Eubanks attended Oklahoma State University, where he was involved as a member of Pi Kappa Alpha fraternity. Scott Kildall was his graduate thesis advisor at the Naval Postgraduate School in Monterey, California. Eubank's 1976 master's thesis was a BASIC language compiler called BASIC-E designed for Kildall's new CP/M operating system. Over the next year and a half, Eubanks wrote the popular CBASIC compiler for IMSAI while he was still a naval officer. Friends of Eubanks say he called it "CBASIC" because he wrote it while serving on a submarine (at ''sea''). Other people say the name CBASIC referred to "commercial" basic, because it incorporated BCD mathematics which eliminated MBASIC's rounding errors that were sometimes troublesome for accounting. In 1981, after Microsoft moved from programming languages int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compiler Systems (company)
Gordon Edwin Eubanks, Jr. (born November 7, 1946) is an American microcomputer industry pioneer who worked with Gary Kildall in the early days of Digital Research (DRI). Eubanks attended Oklahoma State University, where he was involved as a member of Pi Kappa Alpha fraternity. Scott Kildall was his graduate thesis advisor at the Naval Postgraduate School in Monterey, California. Eubank's 1976 master's thesis was a BASIC language compiler called BASIC-E designed for Kildall's new CP/M operating system. Over the next year and a half, Eubanks wrote the popular CBASIC compiler for IMSAI while he was still a naval officer. Friends of Eubanks say he called it "CBASIC" because he wrote it while serving on a submarine (at ''sea''). Other people say the name CBASIC referred to "commercial" basic, because it incorporated BCD mathematics which eliminated MBASIC's rounding errors that were sometimes troublesome for accounting. In 1981, after Microsoft moved from programming language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MBASIC
MBASIC is the Microsoft BASIC implementation of BASIC for the CP/M operating system. MBASIC is a descendant of the original Altair BASIC interpreters that were among Microsoft's first products. MBASIC was one of the two versions of BASIC bundled with the Osborne 1 computer. The name "MBASIC" is derived from the disk file name MBASIC.COM of the BASIC interpreter. Environment MBASIC version 5 required a CP/M system with at least 28 kB of random access memory (RAM) and at least one diskette drive. Unlike versions of Microsoft BASIC-80 that were customized by home computer manufacturers to use the particular hardware features of the computer, MBASIC relied only on the CP/M operating system calls for all input and output. Only the CP/M console (screen and keyboard), line printer, and disk devices were available. MBASIC in the uncustomized form had no functions for graphics, color, joysticks, mice, serial communications, networking, sound, or even a real-time clock function. MBASI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Research
Digital Research, Inc. (DR or DRI) was a company created by Gary Kildall to market and develop his CP/M operating system and related 8-bit, 16-bit and 32-bit systems like MP/M, Concurrent DOS, FlexOS, Multiuser DOS, DOS Plus, DR DOS and GEM. It was the first large software company in the microcomputer world. Digital Research was originally based in Pacific Grove, California, later in Monterey, California. Overview In 1972, Gary Kildall, an instructor at the Naval Postgraduate School in Monterey, California, began working at Intel as a consultant under the business name Microcomputer Applications Associates (MAA). By 1974, he had developed Control Program/Monitor, or CP/M, the first disk operating system for microcomputers. In 1974 he incorporated as Intergalactic Digital Research, with his wife handling the business side of the operation. The company soon began operating under its shortened name Digital Research. The company's operating systems, starting with CP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seymour Rubinstein
Seymour Ivan Rubinstein (born 1934) is an American businessman and software developer. With the founding of MicroPro International in 1978, he became a pioneer of personal computer software, publishing under it the extremely popular word processing package, WordStar. He grew up in Brooklyn, New York, and after a six-year stint in New Hampshire, later moved to California. Programs developed partially or entirely under his direction include WordStar, HelpDesk, Quattro Pro, and WebSleuth, among others. WordStar was the first truly successful program for the personal computer in a commercial sense and gave reasonably priced access to word processing for the general population for the first time. Rubinstein began his involvement with microcomputers as director of marketing at IMSAI. Early career During his teenage years, Rubinstein was a television repairman. After his military service he became a technical writer and continued his undergraduate studies at night. In 1964, he was gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byte (magazine)
''Byte'' (stylized as ''BYTE'') was a microcomputer magazine, influential in the late 1970s and throughout the 1980s because of its wide-ranging editorial coverage. "''Byte'' magazine, the leading publication serving the homebrew market ..." ''Byte'' started in 1975, shortly after the first personal computers appeared as kits advertised in the back of electronics magazines. ''Byte'' was published monthly, with an initial yearly subscription price of $10. Whereas many magazines were dedicated to specific systems or the home or business users' perspective, ''Byte'' covered developments in the entire field of "small computers and software", and sometimes other computing fields such as supercomputers and high-reliability computing. Coverage was in-depth with much technical detail, rather than user-oriented. The company was purchased by McGraw-Hill in 1979, a watershed event that led to the rapid purchase of many of the early computer magazines by larger publishers. By this time t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerry Pournelle
Jerry Eugene Pournelle (; August 7, 1933 – September 8, 2017) was an American scientist in the area of operations research and human factors research, a science fiction writer, essayist, journalist, and one of the first bloggers. In the 1960s and early 1970s, he worked in the aerospace industry, but eventually focused on his writing career. In an obituary in ''Gizmodo'', he is described as "a tireless ambassador for the future." Pournelle's hard science fiction writing received multiple awards. In addition to his solo writing, he wrote several novels with collaborators including Larry Niven. Pournelle served a term as President of the Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of America. Pournelle's journalism focused primarily on the computer industry, astronomy, and space exploration. From the 1970s until the early 1990s, he contributed to the computer magazine ''Byte'', writing from the viewpoint of an intelligent user, with the oft-cited credo, "We do this stuff so you won't ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preprocessor
In computer science, a preprocessor (or precompiler) is a program that processes its input data to produce output that is used as input in another program. The output is said to be a preprocessed form of the input data, which is often used by some subsequent programs like compilers. The amount and kind of processing done depends on the nature of the preprocessor; some preprocessors are only capable of performing relatively simple textual substitutions and macro expansions, while others have the power of full-fledged programming languages. A common example from computer programming is the processing performed on source code before the next step of compilation. In some computer languages (e.g., C and PL/I) there is a phase of translation known as ''preprocessing''. It can also include macro processing, file inclusion and language extensions. Lexical preprocessors Lexical preprocessors are the lowest-level of preprocessors as they only require lexical analysis, that is, they oper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InfoWorld
''InfoWorld'' (abbreviated IW) is an information technology media business. Founded in 1978, it began as a monthly magazine. In 2007, it transitioned to a web-only publication. Its parent company today is International Data Group, and its sister publications include '' Macworld'' and ''PC World''. InfoWorld is based in San Francisco, with contributors and supporting staff based across the United States. Since its founding, ''InfoWorld''s readership has largely consisted of IT and business professionals. ''InfoWorld'' focuses on how-to, analysis, and editorial content from a mixture of experienced technology journalists and working technology practitioners. The site averages 4.6 million monthly page views and 1.1 million monthly unique visitors. History The magazine was founded by Jim Warren in 1978 as ''The Intelligent Machines Journal'' (IMJ). It was sold to IDG in late 1979. On 18 February 1980, the magazine name was changed to ''InfoWorld''. In 1986, the Robert X. Cringel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Reference
The term cross-reference (abbreviation: xref) can refer to either: * An instance within a document which refers to related information elsewhere in the same document. In both printed and online dictionaries cross-references are important because they form a network structure of relations existing between different parts of data, dictionary-internal as well as dictionary external. * In an index, a cross-reference is often denoted by ''See also''. For example, under the term ''Albert Einstein'' in the index of a book about Nobel Laureates, there may be the cross-reference ''See also: Einstein, Albert''. * In hypertext, cross-referencing is maintained to a document with either in-context (XRIC) or out-of-context (''XROC'') cross-referencing. These are similar to KWIC and KWOC. * In programming, "cross-referencing" means the listing of every file name and line number where a given named identifier occurs within the program's source tree. * In a relational database management syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accounting
Accounting, also known as accountancy, is the measurement, processing, and communication of financial and non financial information about economic entities such as businesses and corporations. Accounting, which has been called the "language of business", measures the results of an organization's economic activities and conveys this information to a variety of stakeholders, including investors, creditors, management, and regulators. Practitioners of accounting are known as accountants. The terms "accounting" and "financial reporting" are often used as synonyms. Accounting can be divided into several fields including financial accounting, management accounting, tax accounting and cost accounting. Financial accounting focuses on the reporting of an organization's financial information, including the preparation of financial statements, to the external users of the information, such as investors, regulators and suppliers; and management accounting focuses on the measurement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |