|
CASP3
Caspase-3 is a caspase protein that interacts with caspase-8 and caspase-9. It is encoded by the ''CASP3'' gene. ''CASP3'' orthologs have been identified in numerous mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs are also present in birds, lizards, lissamphibians, and teleosts. The CASP3 protein is a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes that undergo proteolytic processing at conserved aspartic residues to produce two subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme. This protein cleaves and activates caspases 6 and 7; and the protein itself is processed and activated by caspases 8, 9, and 10. It is the predominant caspase involved in the cleavage of amyloid-beta 4A precursor protein, which is associated with neuronal death in Alzheimer's disease. Alternative splicing of this g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspase 7
Caspase-7, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase, also known as CASP7, is a human protein encoded by the ''CASP7'' gene. ''CASP7'' orthologs have been identified in nearly all mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs are also present in birds, lizards, lissamphibians, and teleosts. Function Caspase-7 is a member of the caspase (cysteine aspartate protease) family of proteins, and has been shown to be an executioner protein of apoptosis. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes that undergo proteolytic processing by upstream caspases (caspase-8, -9) at conserved aspartic residues to produce two subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme in the form of a heterotetramer. The precursor of this caspase is cleaved by caspase 3, caspase 10, and caspase 9. It is activated upon cell death stimuli and induces apoptosis. Alternative splicing re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspase 7
Caspase-7, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase, also known as CASP7, is a human protein encoded by the ''CASP7'' gene. ''CASP7'' orthologs have been identified in nearly all mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs are also present in birds, lizards, lissamphibians, and teleosts. Function Caspase-7 is a member of the caspase (cysteine aspartate protease) family of proteins, and has been shown to be an executioner protein of apoptosis. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes that undergo proteolytic processing by upstream caspases (caspase-8, -9) at conserved aspartic residues to produce two subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme in the form of a heterotetramer. The precursor of this caspase is cleaved by caspase 3, caspase 10, and caspase 9. It is activated upon cell death stimuli and induces apoptosis. Alternative splicing re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspase
Caspases (cysteine-aspartic proteases, cysteine aspartases or cysteine-dependent aspartate-directed proteases) are a family of protease enzymes playing essential roles in programmed cell death. They are named caspases due to their specific cysteine protease activity – a cysteine in its active site nucleophilically attacks and cleaves a target protein only after an aspartic acid residue. As of 2009, there are 12 confirmed caspases in humans and 10 in mice, carrying out a variety of cellular functions. The role of these enzymes in programmed cell death was first identified in 1993, with their functions in apoptosis well characterised. This is a form of programmed cell death, occurring widely during development, and throughout life to maintain cell homeostasis. Activation of caspases ensures that the cellular components are degraded in a controlled manner, carrying out cell death with minimal effect on surrounding tissues. Caspases have other identified roles in programmed cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term memory, remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include primary progressive aphasia, problems with language, Orientation (mental), disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and challenging behaviour, behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-sheet
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, notably Alzheimer's disease. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate models, especially since he did not then know that the peptide bond was planar. A refined versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction. An enzyme inhibitor stops ("inhibits") this process, either by binding to the enzyme's active site (thus preventing the substrate itself from binding) or by binding to another site on the enzyme such that the enzyme's catalysis of the reaction is blocked. Enzyme inhibitors may bind reversibly or irreversibly. Irreversible inhibitors form a chemical bond with the enzyme such that the enzyme is inhibited until the chemical bond is broken. By contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and may spontaneously leave the enzyme, allowing the enzyme to resume its function. Reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (biochemistry)
In chemistry, the term substrate is highly context-dependent. Broadly speaking, it can refer either to a chemical species being observed in a chemical reaction, or to a surface on which other chemical reactions or microscopy are performed. In the former sense, a reagent is added to the ''substrate'' to generate a product through a chemical reaction. The term is used in a similar sense in synthetic and organic chemistry, where the substrate is the chemical of interest that is being modified. In biochemistry, an enzyme substrate is the material upon which an enzyme acts. When referring to Le Chatelier's principle, the substrate is the reagent whose concentration is changed. ;Spontaneous reaction : :*Where S is substrate and P is product. ;Catalysed reaction : :*Where S is substrate, P is product and C is catalyst. In the latter sense, it may refer to a surface on which other chemical reactions are performed or play a supporting role in a variety of spectroscopic and microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zymogens
In biochemistry, a zymogen (), also called a proenzyme (), is an inactive precursor of an enzyme. A zymogen requires a biochemical change (such as a hydrolysis reaction revealing the active site, or changing the configuration to reveal the active site) for it to become an active enzyme. The biochemical change usually occurs in Golgi bodies, where a specific part of the precursor enzyme is cleaved in order to activate it. The inactivating piece which is cleaved off can be a peptide unit, or can be independently-folding domains comprising more than 100 residues. Although they limit the enzyme's ability, these N-terminal extensions of the enzyme or a “prosegment” often aid in the stabilization and folding of the enzyme they inhibit. The pancreas secretes zymogens partly to prevent the enzymes from digesting proteins in the cells in which they are synthesised. Enzymes like pepsin are created in the form of pepsinogen, an inactive zymogen. Pepsinogen is activated when chief cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamic Acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABA-ergic neurons. Its molecular formula is . Glutamic acid exists in three optically isomeric forms; the dextrorotatory -form is usually obtained by hydrolysis of gluten or from the waste waters of beet-sugar manufacture or by fermentation.Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, Third Edition, 1971. Its molecular structure could be idealized as HOOC−CH()−()2−COOH, with two carboxyl groups −COOH and one amino group −. However, in the solid state and mildly acidic water solutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspartic Acid
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the protonated –NH form under physiological conditions, while its α-carboxylic acid group is deprotonated −COO− under physiological conditions. Aspartic acid has an acidic side chain (CH2COOH) which reacts with other amino acids, enzymes and proteins in the body. Under physiological conditions (pH 7.4) in proteins the side chain usually occurs as the negatively charged aspartate form, −COO−. It is a non-essential amino acid in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it as needed. It is encoded by the codons GAU and GAC. D-Aspartate is one of two D-amino acids commonly found in mammals. .html" ;"title="/sup>">/sup> In proteins aspartate sidechains are often hydrogen bonded to form asx turns or asx motifs, which frequently occur at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
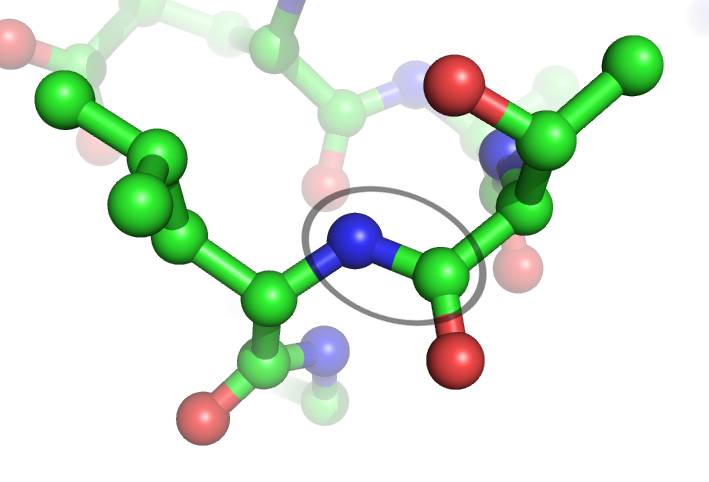
Peptide Bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein chain. It can also be called a eupeptide bond to distinguish it from an isopeptide bond, which is another type of amide bond between two amino acids. Synthesis When two amino acids form a ''dipeptide'' through a ''peptide bond'', it is a type of condensation reaction. In this kind of condensation, two amino acids approach each other, with the non-side chain (C1) carboxylic acid moiety of one coming near the non-side chain (N2) amino moiety of the other. One loses a hydrogen and oxygen from its carboxyl group (COOH) and the other loses a hydrogen from its amino group (NH2). This reaction produces a molecule of water (H2O) and two amino acids joined by a peptide bond (−CO−NH−). The two joined amino acids are called a dipeptide. The am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |