|
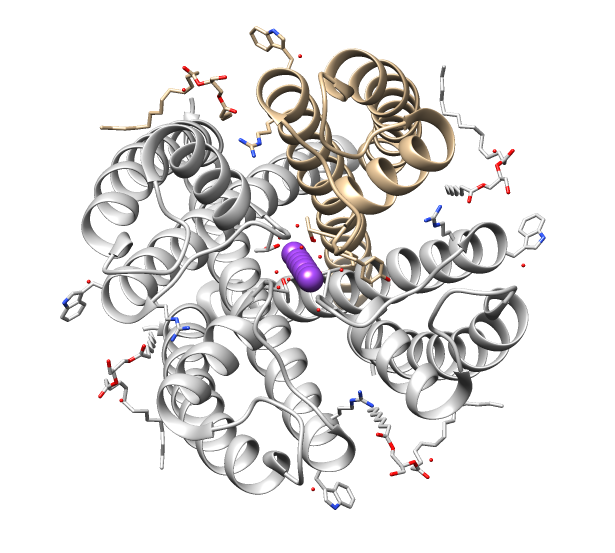
CACNA1G
Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, alpha 1G subunit, also known as CACNA1G or Cav3.1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CACNA1G'' gene. It is one of the primary targets in the pharmacology of absence seizure. Function Cav3.1 is a type of low-voltage-activated calcium channel, also known as "T-type" for its transient on and off. It is expressed in Thalamocortical_radiations#Relay_cells, thalamocortical relay nucleus, and is responsible for the slow-wave sleep and absence seizure. During a slow-wave sleep, Cav3.1 is put into burst mode, and a self-sustaining synchronous cycle between cortex and thalamus is formed, sensory inputs are isolated from cortex; while awake the thalamus should instead relay sensory inputs from outside the central nervous system. The mechanism of absence seizure has a lot in common with slow-wave sleep. Therefore, a blocker that inhibits the burst mode activation of Cav3.1 is effective in treating absence seizures. Common drugs includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-type Calcium Channel
T-type calcium channels are low voltage activated calcium channels that become inactivated during cell membrane hyperpolarization but then open to depolarization. The entry of calcium into various cells has many different physiological responses associated with it. Within cardiac muscle cell and smooth muscle cells voltage-gated calcium channel activation initiates contraction directly by allowing the cytosolic concentration to increase. Not only are T-type calcium channels known to be present within cardiac and smooth muscle, but they also are present in many neuronal cells within the central nervous system. Different experimental studies within the 1970s allowed for the distinction of T-type calcium channels (transient opening calcium channels) from the already well-known L-type calcium channels (Long-Lasting calcium channels). The new T-type channels were much different from the L-type calcium channels due to their ability to be activated by more negative membrane potentials, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-dependent Calcium Channel
Voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), also known as voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs), are a group of voltage-gated ion channels found in the membrane of excitable cells (''e.g.'', muscle, glial cells, neurons, etc.) with a permeability to the calcium ion Ca2+. These channels are slightly permeable to sodium ions, so they are also called Ca2+-Na+ channels, but their permeability to calcium is about 1000-fold greater than to sodium under normal physiological conditions. At physiologic or resting membrane potential, VGCCs are normally closed. They are activated (''i.e.'': opened) at depolarized membrane potentials and this is the source of the "voltage-gated" epithet. The concentration of calcium (Ca2+ ions) is normally several thousand times higher outside the cell than inside. Activation of particular VGCCs allows a Ca2+ influx into the cell, which, depending on the cell type, results in activation of calcium-sensitive potassium channels, muscular contraction, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethosuximide
Ethosuximide, sold under the brand name Zarontin among others, is a medication used to treat absence seizures. It may be used by itself or with other antiseizure medications such as valproic acid. Ethosuximide is taken by mouth. Ethosuximide is usually well tolerated. Common side effects include loss of appetite, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and feeling tired. Serious side effects include suicidal thoughts, low blood cell levels, and lupus erythematosus. It is unclear if it is safe for the baby during pregnancy. Ethosuximide is in the succinimide family of medications. Its mechanism of action is thought to be due to antagonism of the postsynaptic T-type voltage-gated calcium channel. Ethosuximide was approved for medical use in the United States in 1960. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Ethosuximide is available as a generic medication. As of 2019 its availability was limited in many countries with concerns of price fixing in the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalamocortical Radiations
In neuroanatomy, thalamocortical radiations are the fibers between the thalamus and the cerebral cortex. Structure Thalamocortical (TC) fibers have been referred to as one of the two constituents of the isothalamus, the other being micro neurons. Thalamocortical fibers have a bush or tree-like appearance as they extend into the internal capsule and project to the layers of the cortex. The main thalamocortical fibers extend from different nuclei of the thalamus and project to the visual cortex, somatosensory (and associated sensori-motor) cortex, and the auditory cortex in the brain. Thalamocortical radiations also innervate gustatory and olfactory pathways, as well as pre-frontal motor areas. Visual input from the optic tract is processed by the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus, auditory input in the medial geniculate nucleus, and somatosensory input in the ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus. Thalamic nuclei project to cortical areas of distinct architectural or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
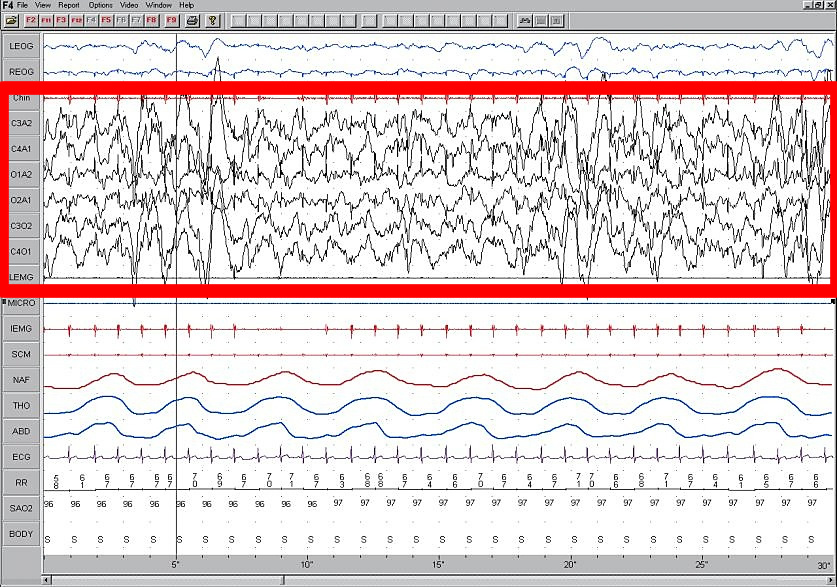
Slow-wave Sleep
Slow-wave sleep (SWS), often referred to as deep sleep, consists of stage three of non-rapid eye movement sleep. It usually lasts between 70 and 90 minutes and takes place during the first hours of the night. Initially, SWS consisted of both Stage 3, which has 20–50 percent delta wave activity, and Stage 4, which has more than 50 percent delta wave activity. Overview This period of sleep is called slow-wave sleep because the EEG activity is synchronized, characterised by slow waves with a frequency range of 0.5–4.5 Hz, relatively high amplitude power with peak-to-peak amplitude greater than 75µV. The first section of the wave signifies a "down state", an inhibition or hyperpolarizing phase in which the neurons in the neocortex are silent. This is the period when the neocortical neurons are able to rest. The second section of the wave signifies an "up state", an excitation or depolarizing phase in which the neurons fire briefly at a high rate. The principal characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absence Seizure
Absence seizures are one of several kinds of generalized seizures. These seizures are sometimes referred to as petit mal seizures (from the French for "little illness", a term dated in the late 18th century). Absence seizures are characterized by a brief loss and return of consciousness, generally not followed by a period of lethargy (i.e. without a notable postictal state). Absence seizure is very common in children. It affects both sides of the brain. Epidemiology Absence seizures affect between 0.7 and 4.6 per 100,000 in the general population and 6% to 8% in children younger than 15 years. Childhood absence seizures account for 10% to 17% of all absence seizures. Onset is between 4 and 10 years and peaks at 5 to 7 years. It is more common in girls than in boys. Etiology An absence seizure is specifically caused by multifactorial inheritance. The voltage-gated T-type calcium channel is regulated by GABRG2, GABRG3, and CACNA1A2 genes. Inheritance of these genes is involved in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethadione
Trimethadione (Tridione) is an oxazolidinedione anticonvulsant. It is most commonly used to treat epileptic conditions that are resistant to other treatments. It is primarily effective in treating absence seizures, but can also be used in refractory temporal lobe epilepsy. It is usually administered 3 or 4 times daily, with the total daily dose ranging from 900 mg to 2.4 g. Treatment is most effective when the concentration of its active metabolite, dimethadione, is above 700 µg/mL. Severe adverse reactions are possible, including Steven Johnson syndrome, nephrotoxicity, hepatitis, aplastic anemia, neutropenia, or agranulocytosis. More common adverse effects include drowsiness, hemeralopia, and hiccups. Fetal trimethadione syndrome If administered during pregnancy, fetal trimethadione syndrome may result causing facial dysmorphism (short upturned nose, slanted eyebrows), cardiac defects, intrauterine growth restriction Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or fetal grow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channels
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion transporter proteins: #The rate of ion transport through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |