|
C0 And C1 Control Codes
The C0 and C1 control code or control character sets define control codes for use in text by computer systems that use ASCII and derivatives of ASCII. The codes represent additional information about the text, such as the position of a cursor, an instruction to start a new line, or a message that the text has been received. C0 codes are the range 00 HEX–1FHEX and the default C0 set was originally defined in ISO 646 (ASCII). C1 codes are the range 80HEX–9FHEX and the default C1 set was originally defined in ECMA-48 (harmonized later with ISO 6429). The ISO/IEC 2022 system of specifying control and graphic characters allows other C0 and C1 sets to be available for specialized applications, but they are rarely used. C0 controls ASCII defined 32 control characters, plus a necessary extra character for the DEL character, 7FHEX or 01111111BIN (needed to punch out all the holes on a paper tape and erase it). This large number of codes was desirable at the time, as multi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percent-encoding
Percent-encoding, also known as URL encoding, is a method to encode arbitrary data in a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) using only the limited US-ASCII characters legal within a URI. Although it is known as ''URL encoding'', it is also used more generally within the main Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) set, which includes both Uniform Resource Locator (URL) and Uniform Resource Name (URN). As such, it is also used in the preparation of data of the application/x-www-form-urlencoded media type, as is often used in the submission of HTML form data in HTTP requests. Percent-encoding in a URI Types of URI characters The characters allowed in a URI are either ''reserved'' or ''unreserved'' (or a percent character as part of a percent-encoding). ''Reserved'' characters are those characters that sometimes have special meaning. For example, forward slash characters are used to separate different parts of a URL (or more generally, a URI). ''Unreserved'' characters have no suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Configuration And Power Interface
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) is an open standard that operating systems can use to discover and configure computer hardware components, to perform power management (e.g. putting unused hardware components to sleep), auto configuration (e.g. Plug and Play and hot swapping), and status monitoring. First released in December 1996, ACPI aims to replace Advanced Power Management (APM), the MultiProcessor Specification, and the Plug and Play BIOS (PnP) Specification. ACPI brings power management under the control of the operating system, as opposed to the previous BIOS-centric system that relied on platform-specific firmware to determine power management and configuration policies. The specification is central to the Operating System-directed configuration and Power Management (OSPM) system. ACPI defines hardware abstraction interfaces between the device's firmware (e.g. BIOS, UEFI), the computer hardware components, and the operating systems. Internally, ACPI a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differentiability Class
In mathematical analysis, the smoothness of a function is a property measured by the number of continuous derivatives it has over some domain, called ''differentiability class''. At the very minimum, a function could be considered smooth if it is differentiable everywhere (hence continuous). At the other end, it might also possess derivatives of all orders in its domain, in which case it is said to be infinitely differentiable and referred to as a C-infinity function (or C^ function). Differentiability classes Differentiability class is a classification of functions according to the properties of their derivatives. It is a measure of the highest order of derivative that exists and is continuous for a function. Consider an open set U on the real line and a function f defined on U with real values. Let ''k'' be a non-negative integer. The function f is said to be of differentiability class ''C^k'' if the derivatives f',f'',\dots,f^ exist and are continuous on U. If f is k- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centralwings
Centralwings was a charter airline based in Warsaw, Poland. The airline operated as a low-cost airline and then became a charter-only operation in October 2008. It was a subsidiary of LOT Polish Airlines, operating international services in Europe, using Boeing 737 aircraft. Its main base was Warsaw Frederic Chopin Airport, with hubs at Gdańsk Lech Wałęsa Airport and John Paul II International Airport Kraków-Balice. On 26 March 2009 the board of LOT Polish Airlines decided to close Centralwings with no information about what was to happen to its employees. History The airline was established in December 2004 and started operations in February 2005. Centralwings, as its name suggests, competed in the Central European market, namely Poland, with a fleet of LOT Boeing 737 aircraft. Centralwings operated scheduled services from Gdańsk, Katowice, Kraków, Łódź, Poznań, Szczecin, Warsaw and Wrocław. For most of this time around 60% of its capacity was allocated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
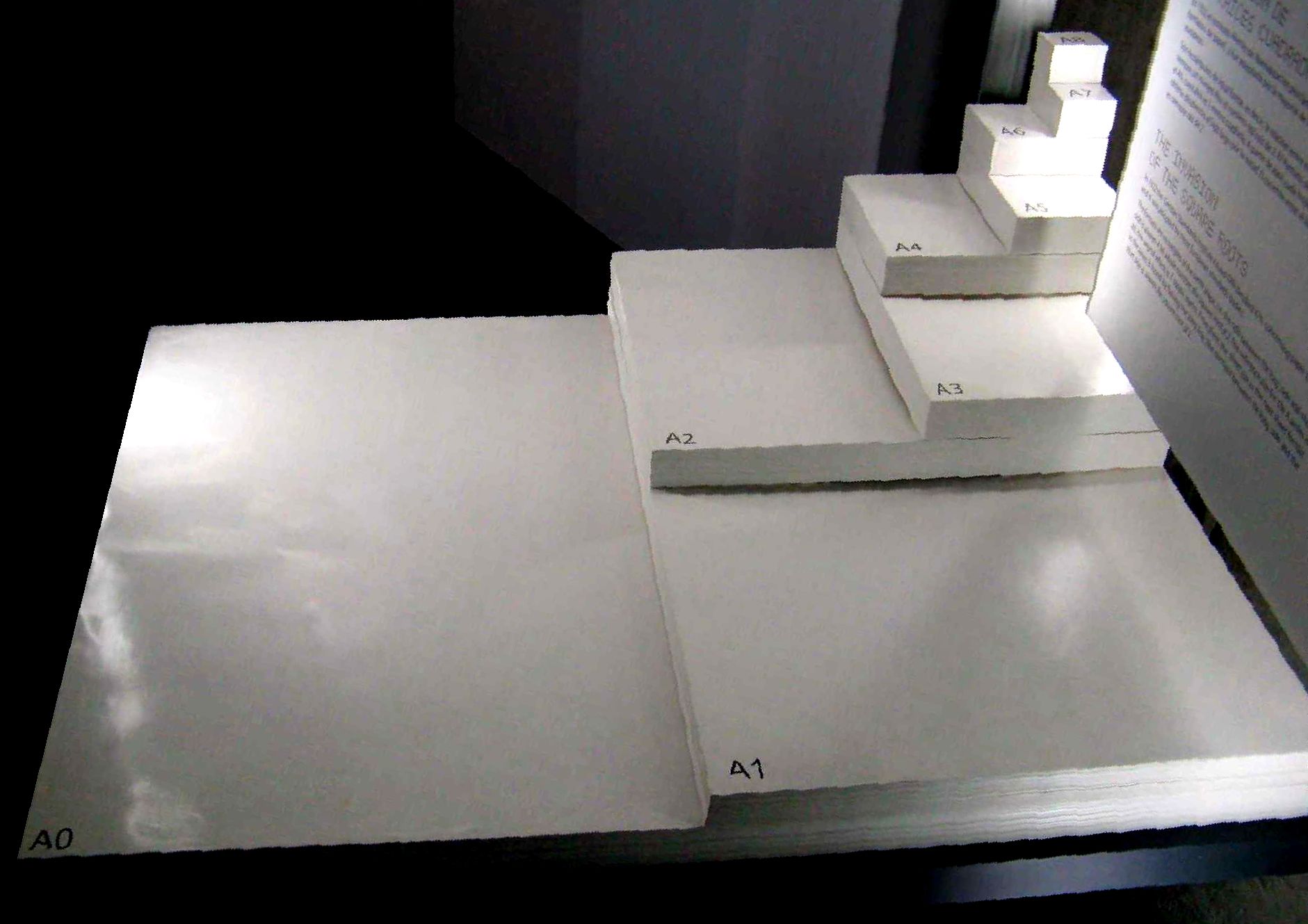
ISO 216
ISO 216 is an international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, including A4, the most commonly available paper size worldwide. Two supplementary standards, ISO 217 and ISO 269, define related paper sizes; the ISO 269 "C" series is commonly listed alongside the A and B sizes. All ISO 216, ISO 217 and ISO 269 paper sizes (except some envelopes) have the same aspect ratio, , within rounding to millimetres. This ratio has the unique property that when cut or folded in half widthways, the halves also have the same aspect ratio. Each ISO paper size is one half of the area of the next larger size in the same series. Dimensions of A, B and C series History The oldest known mention of the advantages of basing a paper size on an aspect ratio of is found in a letter written on 25 October 1786 by the German scientist Georg Christoph Lichtenberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crt0
(also known as ) is a set of execution startup routines linked into a C program that performs any initialization work required before calling the program's main function. Form and usage Crt0 generally takes the form of an object file called , often written in assembly language, which is automatically included by the linker into every executable file it builds. contains the most basic parts of the runtime library. As such, the exact work it performs depends on the program's compiler, operating system and C standard library implementation. Beside the initialization work required by the environment and toolchain, can perform additional operations defined by the programmer, such as executing C++ global constructors and C functions carrying GCC's attribute. "crt" stands for "C runtime", and the zero stands for "the very beginning". However, when programs are compiled using GCC, it is also used for languages other than C. Alternative versions of are available for spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C0-semigroup
In mathematics, a ''C''0-semigroup, also known as a strongly continuous one-parameter semigroup, is a generalization of the exponential function. Just as exponential functions provide solutions of scalar linear constant coefficient ordinary differential equations, strongly continuous semigroups provide solutions of linear constant coefficient ordinary differential equations in Banach spaces. Such differential equations in Banach spaces arise from e.g. delay differential equations and partial differential equations. Formally, a strongly continuous semigroup is a representation of the semigroup (R+,+) on some Banach space ''X'' that is continuous in the strong operator topology. Thus, strictly speaking, a strongly continuous semigroup is not a semigroup, but rather a continuous representation of a very particular semigroup. Formal definition A strongly continuous semigroup on a Banach space X is a map T : \mathbb_+ \to L(X) such that # T(0) = I , (identity operator on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C0 Space
In functional analysis and related areas of mathematics, a sequence space is a vector space whose elements are infinite sequences of real or complex numbers. Equivalently, it is a function space whose elements are functions from the natural numbers to the field ''K'' of real or complex numbers. The set of all such functions is naturally identified with the set of all possible infinite sequences with elements in ''K'', and can be turned into a vector space under the operations of pointwise addition of functions and pointwise scalar multiplication. All sequence spaces are linear subspaces of this space. Sequence spaces are typically equipped with a norm, or at least the structure of a topological vector space. The most important sequence spaces in analysis are the spaces, consisting of the -power summable sequences, with the ''p''-norm. These are special cases of L''p'' spaces for the counting measure on the set of natural numbers. Other important classes of sequences like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebraically Closed Field
In mathematics, a field is algebraically closed if every non-constant polynomial in (the univariate polynomial ring with coefficients in ) has a root in . Examples As an example, the field of real numbers is not algebraically closed, because the polynomial equation ''x''2 + 1 = 0 has no solution in real numbers, even though all its coefficients (1 and 0) are real. The same argument proves that no subfield of the real field is algebraically closed; in particular, the field of rational numbers is not algebraically closed. Also, no finite field ''F'' is algebraically closed, because if ''a''1, ''a''2, ..., ''an'' are the elements of ''F'', then the polynomial (''x'' − ''a''1)(''x'' − ''a''2) ⋯ (''x'' − ''a''''n'') + 1 has no zero in ''F''. By contrast, the fundamental theorem of algebra states that the field of complex numbers is algebraically closed. Another example of an algebraica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant that is important in many areas of physics. The speed of light is exactly equal to ). According to the special theory of relativity, is the upper limit for the speed at which conventional matter or energy (and thus any signal carrying information) can travel through space. All forms of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, travel at the speed of light. For many practical purposes, light and other electromagnetic waves will appear to propagate instantaneously, but for long distances and very sensitive measurements, their finite speed has noticeable effects. Starlight viewed on Earth left the stars many years ago, allowing humans to study the history of the universe by viewing distant objects. When communicating with distant space probes, it can take minutes to hours for signals to travel from Earth to the spacecraft and vice versa. In computing, the speed of light fixes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |