|
Whitewood, Saskatchewan
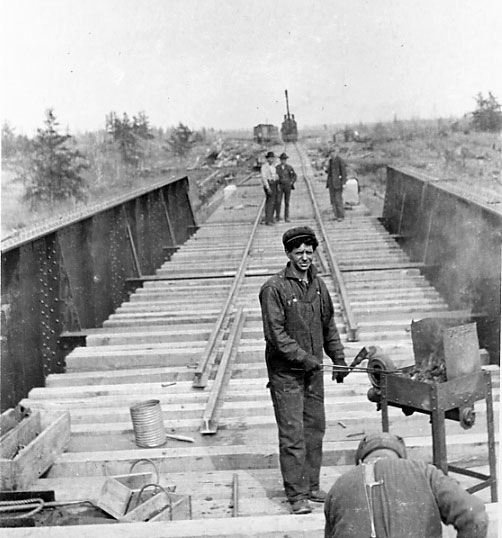
Whitewood is a town in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It is approximately east of Regina, Saskatchewan, Regina on the Trans-Canada Highway Saskatchewan Highway 1, Sk Hwy 1. It is situated at the crossroads of two major highways systems — the Trans-Canada, which runs east and west, and Saskatchewan Highway 9, Sk Hwy 9, which runs north and south from the Canada–United States border, US border to Hudson Bay, Saskatchewan. It is located midway between Brandon, Manitoba and Regina. It is administrative headquarters of the First Nations in Canada, First Nations band governments of the Ochapowace Nation, Ochapowace and the Chachacas Cree. History Before the settlement of the west, Whitewood began as a crossing of trails between the Qu'Appelle Valley to the north and the Moose Mountain Upland, Moose Mountains to the south. The Hudson's Bay Company trading post was established about the fall of 1891 to approximately the spring of 190 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces And Territories Of Canada
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Constitution of Canada, Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada (which upon Confederation was divided into Ontario and Quebec)—united to form a federation, becoming a fully Independence, independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the List of countries and dependencies by area, world's second-largest country by area. The major difference between a Canadian province and a territory is that provinces receive their power and authority from the ''Constitution Act, 1867'' (formerly called the ''British North America Acts, British North America Act, 1867''), whereas territories are federal territories whose governments a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada–United States Border
The international border between Canada and the United States is the longest in the world by total length. The boundary (including boundaries in the Great Lakes, Atlantic, and Pacific coasts) is long. The land border has two sections: Canada's border with the Northern Tier (United States), northern tier of the contiguous United States to its south, and with the U.S. state of Alaska to its west. The bi-national International Boundary Commission deals with matters relating to marking and maintaining the boundary, and the International Joint Commission deals with issues concerning boundary waters. The agencies responsible for facilitating legal passage through the international boundary are the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) and U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP). History 18th century The Treaty of Paris (1783), Treaty of Paris of 1783 ended the American Revolutionary War between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and the United States. In the second article o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
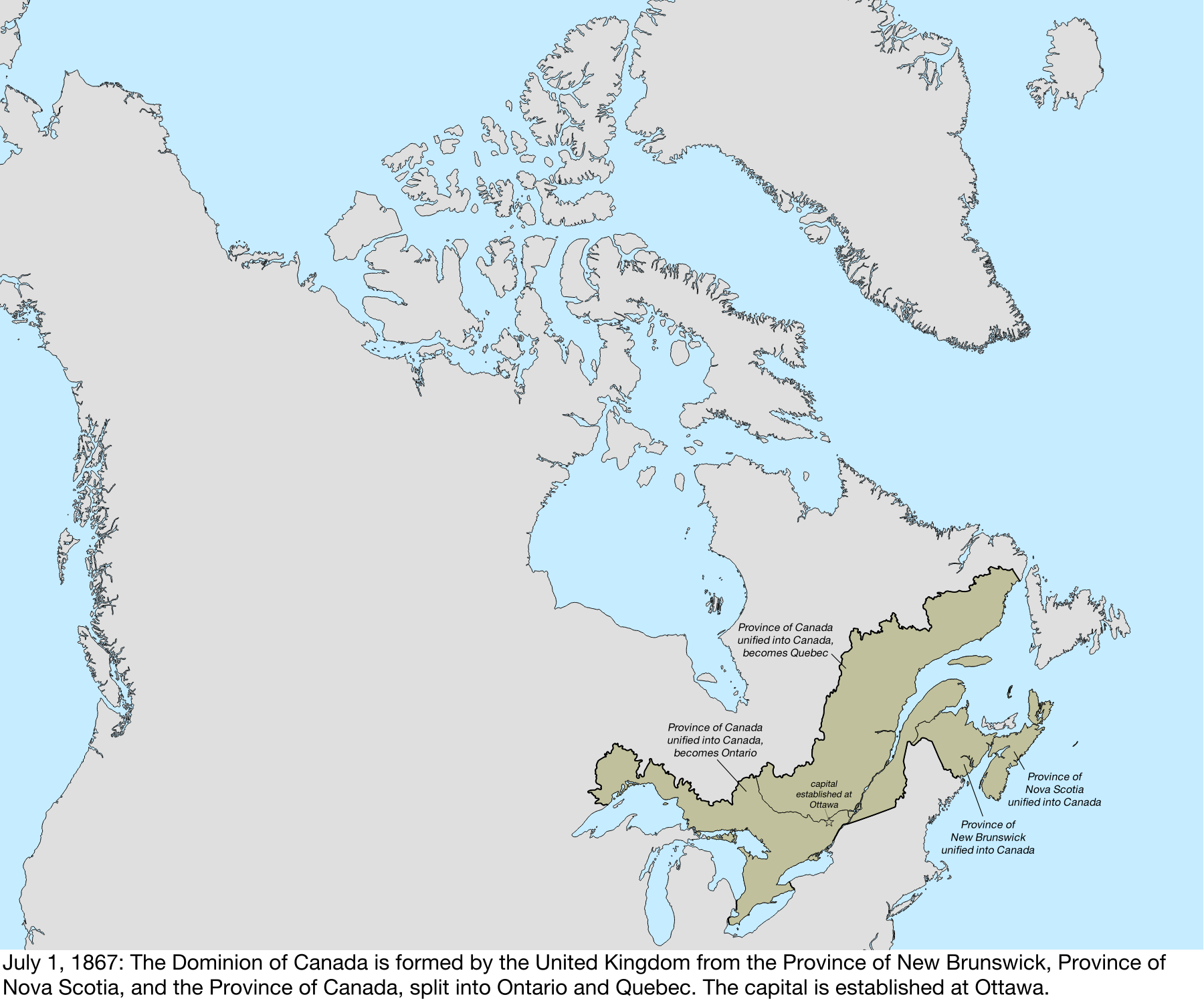
Territorial Evolution Of Canada
The history of post-confederation Canada began on July 1, 1867, when the British North American colonies of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia were united to form a single Dominion within the British Empire. Upon Confederation, the United Province of Canada was immediately split into the provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The colonies of Prince Edward Island and British Columbia joined shortly after, and Canada acquired the vast expanse of the continent controlled by the Hudson's Bay Company, which was eventually divided into new territories and provinces. Canada evolved into a fully sovereign state by 1982. Before being part of British North America, the constituents of Canada consisted of the former colonies of Canada and Acadia from within New France which had been ceded to Great Britain in 1763 as part of the Treaty of Paris. French Canadian nationality was maintained as one of the "two founding nations" and legally through the Quebec Act which ensured the maintenance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assiniboia
Assiniboia District refers to two historical districts of Canada's Northwest Territories. The name is taken from the Assiniboine First Nation. Historical usage ''For more information on the history of the provisional districts, see also Districts of the Northwest Territories'' (Old) District of Assiniboia The District of Assiniboia was a name used to describe the Red River Colony, mainly for official purposes, between 1812 and 1869. Nominally the district included all of the territory granted in the Selkirk Concession. However, much of this was ceded to the United States by the Treaty of 1818, and in 1838 the district was redefined as the circular region within of Fort Garry, which was at the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers. The actual area of settlement, centred at present-day Winnipeg, was limited to the Red River valley between Lower Fort Garry and Pembina, and the Assiniboine River valley between Winnipeg and Portage la Prairie. The district was governed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Transcontinental Railway
The National Transcontinental Railway (NTR) was a historic railway between Winnipeg, Manitoba, and Moncton, New Brunswick, in Canada. Much of the line is now operated by the Canadian National Railway. The Grand Trunk partnership The completion of construction of Canada's first transcontinental railway, the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) on November 7, 1885, preceded a tremendous economic expansion and immigration boom in western Canada during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, but the monopolistic policies of the CPR, coupled with its southerly routing (new scientific discoveries were pushing the northern boundary of cereal crops), led to increasing western discontent with the railway and federal transportation policies. The federal government had encouraged the Grand Trunk Railway (GTR) system in the 1870s to consider building the transcontinental rail line. During the same time, a government survey party under the direction of Sandford Fleming set out across Canada to sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), originally the Governor and Company of Adventurers of England Trading Into Hudson’s Bay, is a Canadian holding company of department stores, and the oldest corporation in North America. It was the owner of the namesake Hudson's Bay (department store), Hudson's Bay department stores (colloquially The Bay), and also owns or manages approximately of gross leasable real estate through its HBC Properties and Investments business unit. HBC previously owned the full-line Saks Fifth Avenue and off-price Saks Off 5th in the United States, which were spun-off into the Saks Global holding company in 2024. After incorporation by royal charter issued in 1670 by Charles II of England, King Charles II, the company was granted a right of "sole trade and commerce" over an expansive area of land known as Rupert's Land, comprising much of the Hudson Bay drainage basin. This right gave the company a monopoly, commercial monopoly over that area. The HBC functioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moose Mountain Upland
Moose Mountain Upland, Moose Mountain Uplands, or commonly Moose Mountain, is a hilly plateau located in the south-east corner of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Saskatchewan, that covers an area of about . The upland rises about above the broad, flat prairie which is about Height above sea level, above sea level. The highest peak is "Moose Mountain" at above sea level. The upland was named Moose Mountain because of the large number of moose that lived in the area. When it was originally used by fur traders, Métis, and the Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous peoples, the plateau was called ''Montagne a la Bosse'', which is French Language, French for "The Mountain of the Bump or Knob". History Before the most recent continental Laurentide Ice Sheet, glaciation 23,000 years ago, Moose Mountain was capped by Tertiary period, Tertiary-age gravels. As the ice began to retreat about 17,000 years ago from southern Saskatchewan, the highest hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qu'Appelle Valley
The Qu'Appelle River is a river in the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba that flows east from Lake Diefenbaker in south-western Saskatchewan to join the Assiniboine River in Manitoba, just south of Lake of the Prairies, near the village of St. Lazare. It is in a region called the Prairie Pothole Region of North America, which extends throughout three Canadian provinces and five U.S. states. It is also within Palliser's Triangle and the Great Plains ecoregion. With the construction of the Qu'Appelle River Dam and the Gardiner Dam upstream, water flow was significantly increased and regulated. Most of the Qu'Appelle's present flow is actually water diverted from the South Saskatchewan River. Upper and lower watersheds According to the Saskatchewan Water Security Agency, the Qu'Appelle Valley is made up of two watersheds with the dividing point being Craven Dam on the east side of Craven: Lower Qu'Appelle Watershed The Lower Qu'Appelle Valley is in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cree
The Cree, or nehinaw (, ), are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people, numbering more than 350,000 in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada, First Nations. They live primarily to the north and west of Lake Superior in the Provinces and territories of Canada, provinces of Alberta, Labrador, Manitoba, the Northwest Territories, Ontario, and Saskatchewan. Another roughly 27,000 live in Quebec. In the United States, the Cree, historically, lived from Lake Superior westward. Today, they live mostly in Montana, where they share Rocky Boy's Indian Reservation with Ojibwe (Chippewa) people. A documented westward migration, over time, has been strongly associated with their roles as traders and hunters in the North American fur trade. Sub-groups and geography The Cree are generally divided into eight groups based on dialect and region. These divisions do not necessarily represent ethnic subdivisions within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochapowace Nation
The Ochapowace Nation ( ''ocâpowês'') is a Cree First Nation in southern Saskatchewan, Canada. Reserves ; Reserves include * Ochapowace 71 * Ochapowace 71-1 * Ochapowace 71-2 * Ochapowace 71-3 * Ochapowace 71-4 * Ochapowace 71-5 * Ochapowace 71-6 * Ochapowace 71-7 * Ochapowace 71-8 * Ochapowace 71-9 * Ochapowace 71-10 * Ochapowace 71-11 * Ochapowace 71-12 * Ochapowace 71-13 * Ochapowace 71-14 * Ochapowace 71-15 * Ochapowace 71-16 * Ochapowace 71-17 * Ochapowace 71-18 * Ochapowace 71-19 * Ochapowace 71-20 * Ochapowace 71-21 * Ochapowace 71-22 * Ochapowace 71-23 * Ochapowace 71-24 * Ochapowace 71-25 * Ochapowace 71-26 * Ochapowace 71-27 * Ochapowace 71-28 * Ochapowace 71-29 * Ochapowace 71-30 * Ochapowace 71-31 * Ochapowace 71-32 * Ochapowace 71-33 * Ochapowace 71-34 * Ochapowace 71-35 * Ochapowace 71-36 * Ochapowace 71-37 * Ochapowace 71-38 * Ochapowace 71-39 * Ochapowace 71-40 * Ochapowace 71-41 * Ochapowace 71-42 * Ochapowace 71-43 * Ochapowace 71-44 Ochapowace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Government
In Canada, an Indian band (), First Nation band () or simply band, is the basic unit of government for those peoples subject to the ''Indian Act'' (i.e. status Indians or First Nations). Bands are typically small groups of people: the largest in the country, the Six Nations of the Grand River First Nation had 22,294 members in September 2005, and many have a membership below 100 people. Each First Nation is typically represented by a band council () chaired by an elected chief, and sometimes also a hereditary chief. As of 2013, there were 614 bands in Canada. Membership in a band is controlled in one of two ways: for most bands, membership is obtained by becoming listed on the Indian Register maintained by the government. As of 2013, there were 253 First Nations which had their own membership criteria, so that not all status Indians are members of a band. Bands can be united into larger regional groupings called tribal councils. A treaty council, or treaty association, has ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |