|
Votians
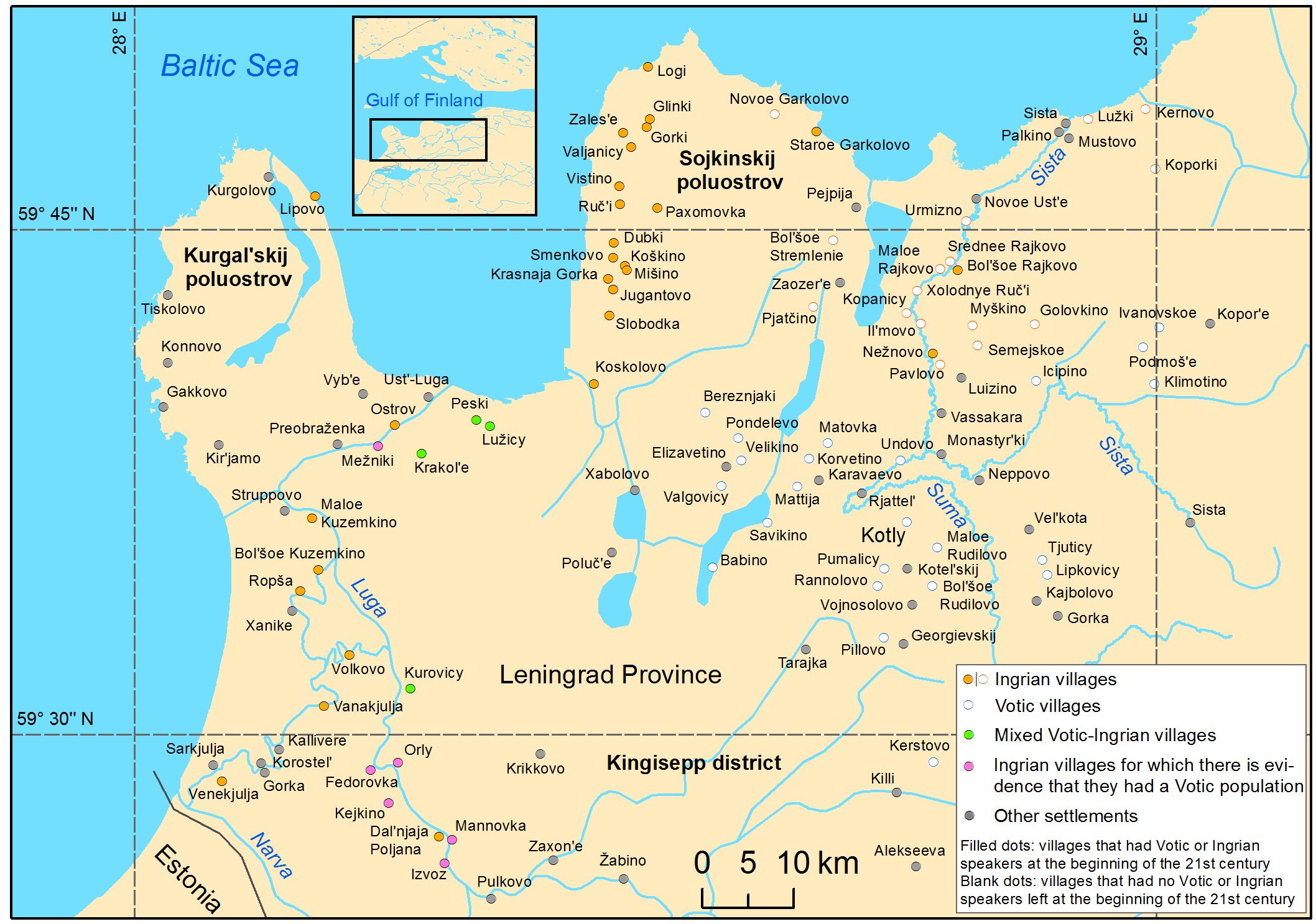
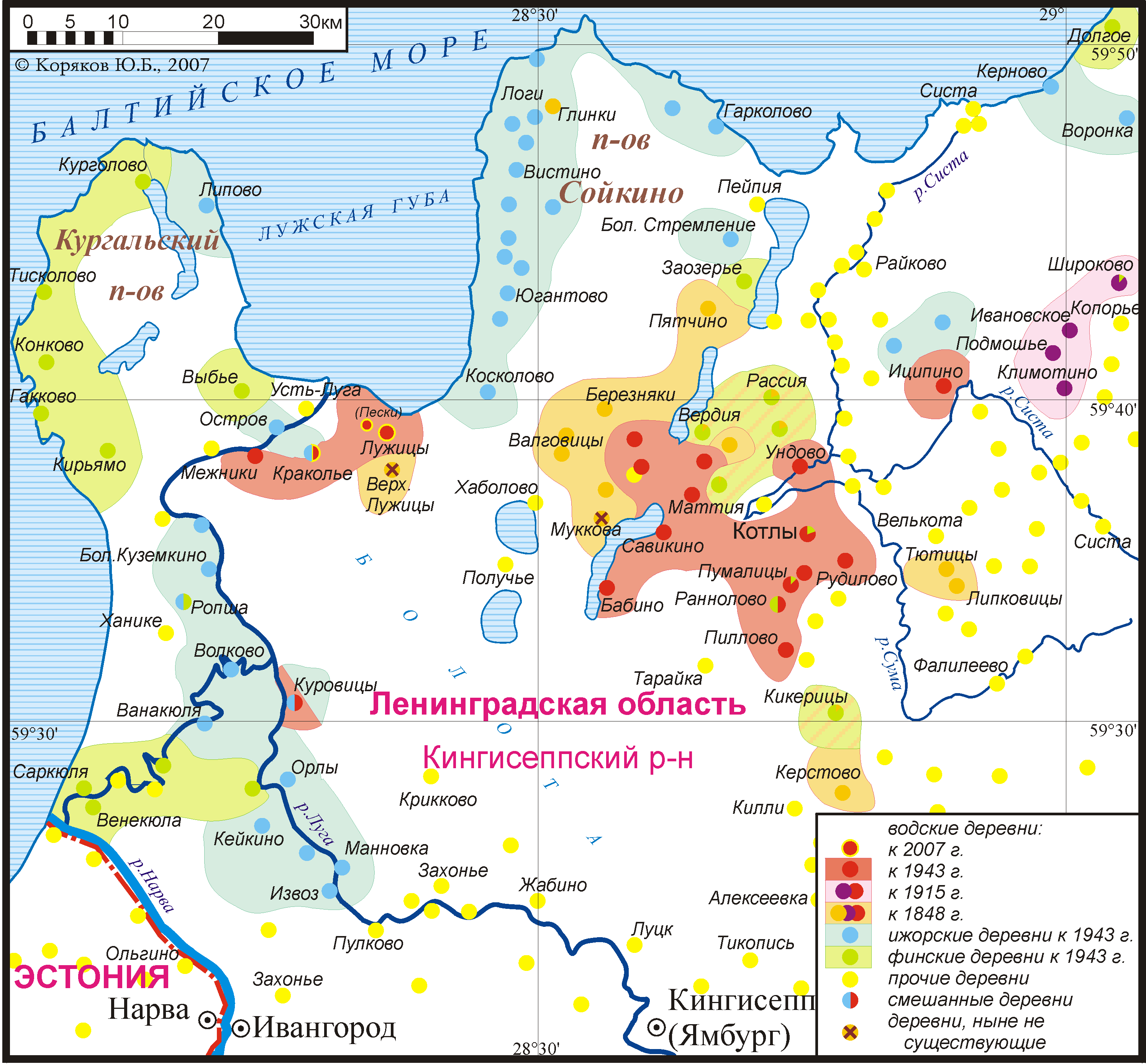
Vots, also referred to as Votes, Vods and Votians (, ''vađđalaizõd''; ; ; ) are a Baltic Finns, Finnic ethnic group native to historical Ingria, the part of modern-day northwestern Russia that is roughly southwest of Saint Petersburg and east of the Estonian border-town of Narva. The Finnic languages, Finnic Votic language spoken by Vots is close to Language death, extinction. The language is still spoken in three villages of historical Votia and by an unknown number of speakers in the countryside. The villages are ''Jõgõperä'' (Krakolye), ''Liivcülä'' (Peski), and ''Luuditsa'' (Luzhitsy).Eesti Rahva Muuseum: Vadjalased Archived In the Russian 2020 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingria
Ingria (; ; ; ) is a historical region including, and adjacent to, what is now the city of Saint Petersburg in northwestern Russia. The region lies along the southeastern shore of the Gulf of Finland, bordered by Lake Ladoga on the Karelian Isthmus in the north and by the Narva river on the current international border with Estonia in the west. The earliest known inhabitants of the region were indigenous Finnic peoples, primarily the ancestors of modern Izhorians and Votians, who converted to Eastern Orthodox Christianity during the late Middle Ages. They were later joined by the Ingrian Finns, descendants of 17th century Lutheran Finnish immigrants. At that time, Ingria, the Karelian Isthmus, Estonia, and what is now Finland were all part of the Kingdom of Sweden. Ingria as a whole never formed a separate state; however, North Ingria was an independent state for just under two years in 1919–1920. The inhabitants of Ingria cannot be said to have comprised a distinct n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Votic Language
Votic or Votian (, ) , is a Finnic language spoken by the Vots of Ingria, belonging to the Finnic branch of the Uralic languages. Votic is spoken only in Krakolye (now part of Ust-Luga) and Luzhitsy, two villages in Kingiseppsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. In the 2020–2021 Russian census, 21 people claimed to speak Votic natively, which is an increase from 4 in 2010. Arvo Survo also estimated that around 100 people have knowledge of the language to some degree. History Votic is one of numerous Finnic varieties known from Ingria. Votic shares some similarities with and has acquired loanwords from the adjacent Ingrian language, but also has deep-reaching similarities with Estonian to the west, which is considered its closest relative. Some linguists, including Tiit-Rein Viitso and Paul Alvre, have claimed that Votic evolved specifically from northeastern dialects of ancient Estonian. Votic regardless exhibits several features that indicate its distinction from Es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Votic Language Map
Votic or Votian (, ) , is a Finnic languages, Finnic language spoken by the Votians, Vots of Ingria, belonging to the Finnic languages, Finnic branch of the Uralic languages. Votic is spoken only in Krakolye (now part of Ust-Luga) and Luzhitsy, Kingiseppsky District, Leningrad Oblast, Luzhitsy, two villages in Kingiseppsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. In the 2020–2021 Russian census, 21 people claimed to speak Votic natively, which is an increase from 4 in 2010. Arvo Survo also estimated that around 100 people have knowledge of the language to some degree. History Votic is one of numerous Finnic varieties known from Ingria. Votic shares some similarities with and has acquired loanwords from the adjacent Ingrian language, but also has deep-reaching similarities with Estonian language, Estonian to the west, which is considered its closest relative. Some linguists, including Tiit-Rein Viitso and Paul Alvre, have claimed that Votic evolved specifically from northeastern d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601,911 residents as of 2021, with more than 6.4 million people living in the Saint Petersburg metropolitan area, metropolitan area. Saint Petersburg is the List of European cities by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in Europe, the List of cities and towns around the Baltic Sea, most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's List of northernmost items#Cities and settlements, northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As the former capital of the Russian Empire, and a Ports of the Baltic Sea, historically strategic port, it is governed as a Federal cities of Russia, federal city. The city was founded by Tsar Peter the Great on 27 May 1703 on the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Votic People
Vots, also referred to as Votes, Vods and Votians (, ''vađđalaizõd''; ; ; ) are a Finnic ethnic group native to historical Ingria, the part of modern-day northwestern Russia that is roughly southwest of Saint Petersburg and east of the Estonian border-town of Narva. The Finnic Votic language spoken by Vots is close to extinction. The language is still spoken in three villages of historical Votia and by an unknown number of speakers in the countryside. The villages are '' Jõgõperä'' (Krakolye), ''Liivcülä'' (Peski), and ''Luuditsa'' (Luzhitsy).Eesti Rahva Muuseum: Vadjalased Archived In the Russian 2020 census, 99 people identified as Votian. Vot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poluverniki
Poluverniki or poluvertsy () 'half believers' was a term used for a group of Estonian-Votian-Russian Christians in the 17th century, who mixed Orthodox traditions with Lutheranism. The Poluverniki were born as many Orthodox Christians in Eastern Estonia converted to Lutheranism in the East Viru Country as a result of assimilation into Estonian culture. Most Poluverniki were either converts with a Russian Russian(s) may refer to: *Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries *A citizen of Russia *Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages *''The Russians'', a b ... or a Votian background. The Poluverniks attended Lutheran congregations, however following many elements of Orthodoxy. The term "Poluvernik" was also used for the Setu people, but they are distinct from the Poluverniks of Northern Estonia. Despite later efforts to Russify the poluverniks, only a small portion of them remained R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Finns
The Baltic Finnic peoples, often simply referred to as the Finnic peoples, are the peoples inhabiting the Baltic Sea region in Northern and Eastern Europe who speak Finnic languages. They include the Finns, Estonians (including Võros and Setos), Karelians (including Ludes and Livvi), Veps, Izhorians, Votes, and Livonians. In some cases the Kvens, Ingrians, Tornedalians and speakers of Meänkieli are considered separate from the Finns. The bulk of the Finnic peoples (more than 98%) are ethnic Finns and Estonians, who reside in the two independent Finnic nation states—Finland and Estonia. Finnic peoples are also significant minority groups in neighbouring countries of Sweden, Norway and Russia, especially Karelia. Theories of origin According to the "Migration Theory" that was based primarily on comparative linguistics, the proto-Finns migrated from an ancient homeland somewhere in north-western Siberia or western Russia to the shores of the Baltic Sea around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kylfings
The Kylfings (Old Norse ''Kylfingar''; Finnic languages, Estonian ''Kalevid''; Hungarian language, Hungarian ''Kölpények''; Old East Slavic Колбяги, ''Kolbiagi''; Byzantine Greek Κουλπίγγοι, ''Koulpingoi''; Arabic ''al-Kilabiyya'') were a people of uncertain origin active in Northern Europe during the Viking Age, roughly from the late ninth century to the early twelfth century. They could be found in areas of Lapland (Sweden), Lapland, Russia, and the Byzantine Empire that were frequented by Scandinavian traders, raiders and mercenaries. Scholars differ on whether the Kylfings were ethnically Finnic languages, Finnic or Norsemen, Norse. Also disputed is their geographic origin, with Denmark, Sweden and the Eastern Baltic region, Baltic all put forward as candidates. Whether the name Kylfing denotes a particular tribal, socio-political, or economic grouping is also much debated. They are mentioned on the Viking runestones, the sagas of Icelanders (most notably in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setos
Setos (, , , ) are an indigenous Finnic peoples and linguistic minority that have historically lived in the borderlands between modern day Estonia and Russia. Setos have historically spoken the Seto language and been Orthodox Christians.Kalkun, A., Kupari, H., & Vuola, E. (2018). ''Coping with Loss of Homeland through Orthodox Christian Processions: Contemporary Practices among Setos, Karelians, and Skolt Sámi in Estonia and Finland''. ''Practical matters'', ''11''. http://practicalmattersjournal.org/2018/06/11/coping-with-loss-of-homeland-2/ The Seto language (like Estonian and Finnish) belongs to the Finnic group of the Uralic language family. Since the early 2000s, the Setos have sought greater recognition, rather than having their language considered a dialect of Estonian. Eastern Orthodox Christianity, with influences from local folk religions is widely practiced by the Seto peoples. The ancestral homes of many Setos can be found to the south of Lake Peipus, in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livonians
The Livonians, or Livs, are a Balto-Finnic people indigenous to the Livonian Coast, in northwestern Latvia. Livonians historically spoke Livonian language, Livonian, a Uralic language closely related to Estonian language, Estonian and Finnish language, Finnish. It was believed that the last person to have learned and spoken Livonian as a First language, mother tongue, Grizelda Kristiņa, died in 2013. In 2020, however, it was reported that newborn Kuldi Medne had become the only living person who speaks Livonian as their first language. As of 2010, there were approximately 30 people who had learned it as a second language. Historical, social and economic factors, together with an ethnically dispersed population, have resulted in the decline of Livonian identity, with only a small group surviving in the 21st century. In 2011, there were 250 people who claimed Livonian ethnicity in Latvia. History Prehistory The exact date of migration of Livonians to the region has been disputed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingrian Language
Ingrian (, ), also called Izhorian (, , ), is a Finnic language spoken by the (mainly Orthodox) Izhorians of Ingria. It has approximately 70 native speakers left, most of whom are elderly. The Ingrian language should be distinguished from the Ingrian dialect of the Finnish language, which became the majority language of Ingria in the 17th century with the influx of Lutheran Finnish immigrants; their descendants, the Ingrian Finns, are often referred to as Ingrians. The immigration of Lutheran Finns was promoted by Swedish authorities, who gained the area in 1617 from Russia, as the local population was (and remained) Orthodox. Dialects Four dialect groups of Ingrian have been attested, two of which are probably extinct by now: * Hevaha, spoken along Kovashi River and nearby coastal areas (†) * Soikkola, spoken on Soikinsky Peninsula and along Sista River * Ylä-Laukaa (Upper Luga or Oredezhi), spoken along Oredezh River and the upper Luga River (†) * Ala-Laukaa (Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chud
Chud or Chude (, , ) is a term historically applied in the early East Slavic annals to several Baltic Finnic peoples in the area of what is now Estonia, Karelia and Northwestern Russia. It has also been used to refer to other Finno-Ugric peoples. Etymology There are a number of hypotheses as to the origin of the term. ''Chud'' could be derived from the Slavic word ''tjudjo'' ('foreign' or 'strange'). Another hypothesis is that the term was derived from a transformation of the Finno-Ugric name for the wood grouse. Yet another hypothesis contends that it is derived from the Sami word ''tshudde'' or ''čuđđe'', meaning an enemy or adversary (). This, however, would have required prominent Sami presence in trading centers around Lake Ladoga. Attestation in Slavonic sources Arguably, the earliest attested written use of the word "Chuds" to describe Baltic Finnic peoples (presumably early Estonians) was 1100, in the earliest Rus' chronicles in the Old East Slavic language. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |