|
Volcanoes
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions."Mid-ocean ridge tectonics, volcanism and geomorphology." Geology 26, no. 455 (2001): 458. https://macdonald.faculty.geol.ucsb.edu/papers/Macdonald%20Mid-Ocean%20Ridge%20Tectonics.pdf Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
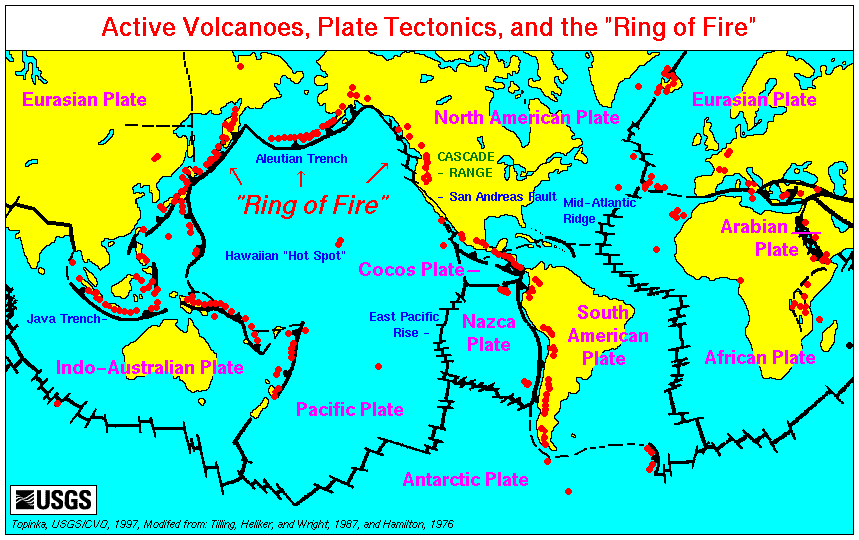
Ring Of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a tectonic belt of volcanoes and earthquakes. It is about long and up to about wide, and surrounds most of the Pacific Ocean. The Ring of Fire contains between 750 and 915 active or dormant volcanoes, around two-thirds of the world total. The exact number of volcanoes within the Ring of Fire depends on which regions are included. About 90% of the world's earthquakes, including most of its largest, occur within the belt. The Ring of Fire is not a single geological structure. It was created by the subduction of different tectonic plates at convergent boundaries around the Pacific Ocean. These include: the Antarctic plate, Antarctic, Nazca plate, Nazca and Cocos plate, Cocos plates subducting beneath the South American plate; the Pacific plate, Pacific and Juan de Fuca plate, Juan de Fuca plates beneath the North American plate; the Philippine Sea pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Volcano
An active volcano is a volcano that is currently erupting, or has the potential to erupt in the future. Conventionally it is applied to any that have erupted during the Holocene (the current geologic epoch that began approximately 11,700 years ago). A volcano that is not currently erupting but could erupt in the future is known as a dormant volcano. Volcanoes that will not erupt again are known as extinct volcanoes. Overview There are 1,350 potentially active volcanoes around the world, 500 of which have erupted in historical time. Many active volcanoes are located along the Pacific Rim, also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire. An estimated 500 million people live near active volcanoes. ''Historical time'' (or recorded history) is another timeframe for ''active''. The span of recorded history differs from region to region. In China and the Mediterranean, it reaches back nearly 3,000 years, but in the Pacific Northwest of the United States and Canada, it reaches back less tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
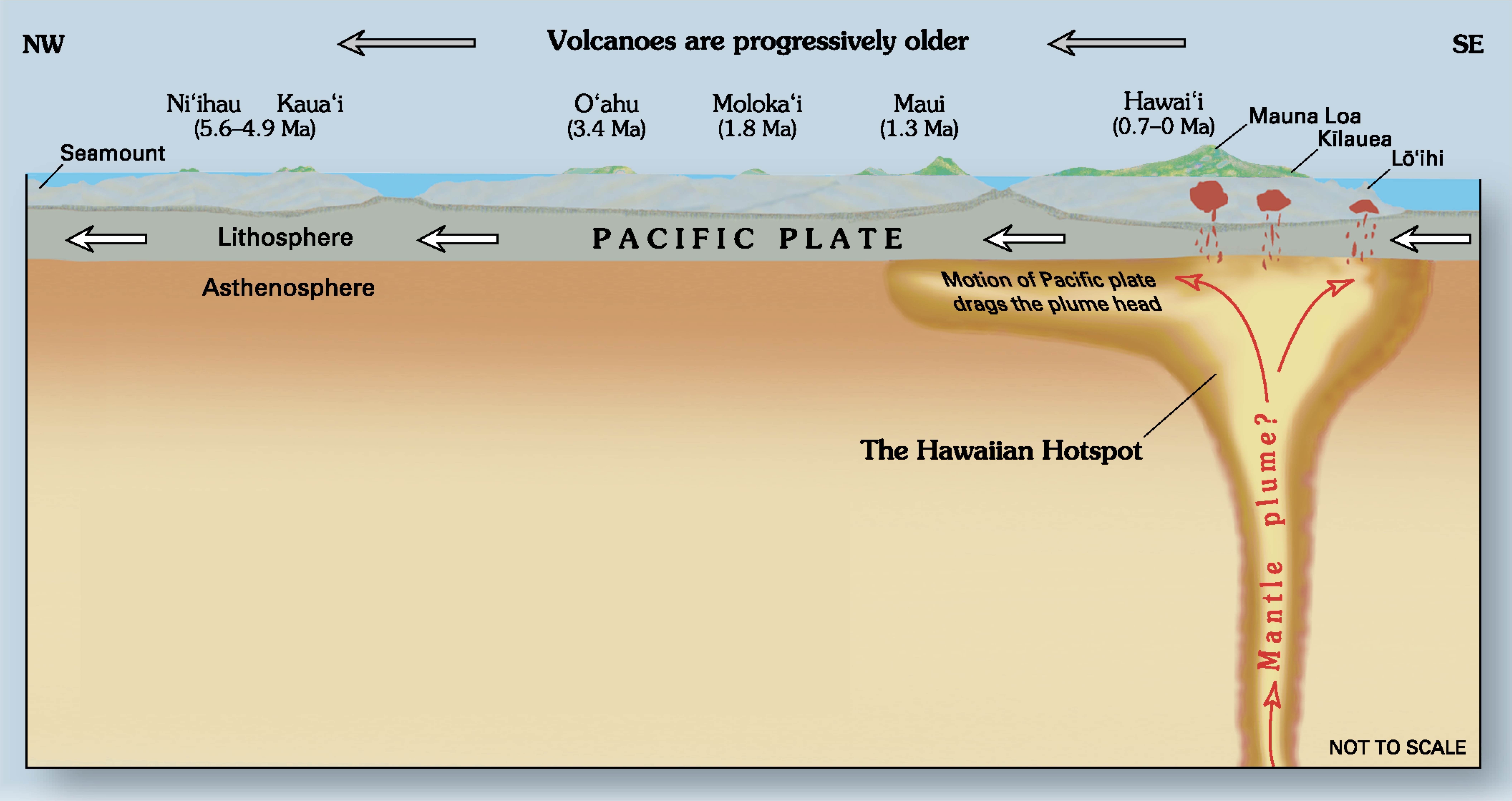
Hawaiian Hotspot
The Hawaii hotspot is a hotspot (geology), volcanic hotspot located near the namesake Hawaiian Islands, in the northern Pacific Ocean. One of the best known and intensively studied hotspots in the world, the Hawaii Mantle plume, plume is responsible for the creation of the Hawaiian – Emperor seamount chain, Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain, a mostly undersea volcanic mountain range. Four of these volcanoes are Volcano#Active, active, two are Volcano#Dormant, dormant; more than 123 are extinct volcano, extinct, most now preserved as atolls or seamounts. The chain extends from south of the island of Hawaii (island), Hawaii to the edge of the Aleutian Trench, near the eastern coast of Russia. While some volcanoes are created by geologic processes near plate tectonics, tectonic plate convergence and subduction zones, the Hawaii hotspot is located far from plate boundaries. The classic hotspot theory, first proposed in 1963 by John Tuzo Wilson, proposes that a single, fixed mant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wells Gray-Clearwater Volcanic Field
The Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field, also called the Clearwater Cone Group, is a potentially active monogenetic volcanic field in east-central British Columbia, Canada, located approximately north of Kamloops, British Columbia, Kamloops. It is situated in the Cariboo Mountains of the Columbia Mountains and on the Quesnel Highland, Quesnel and Shuswap Highlands. As a monogenetic volcanic field, it is a place with numerous small basaltic volcanoes and extensive lava flows. Most of the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field is encompassed within a large wilderness park called Wells Gray Provincial Park. This park was established in 1939 to protect Helmcken Falls and the unique features of the Clearwater River (British Columbia), Clearwater River drainage basin, including this volcanic field. Five roads enter the park and provide views of some of the field's volcanic features. Short hikes lead to several other volcanic features, but some areas are accessible only by aircraft. Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a Natural satellite, moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a Fissure vent, fracture in the Crust (geology), crust, on land or underwater, usually at temperatures from . The volcanic rock resulting from subsequent cooling is often also called ''lava''. A lava flow is an outpouring of lava during an effusive eruption. (An explosive eruption, by contrast, produces a mixture of volcanic ash and other fragments called tephra, not lava flows.) The viscosity of most lava is about that of ketchup, roughly 10,000 to 100,000 times that of water. Even so, lava can flow great distances before cooling causes it to solidify, because lava exposed to air quickly develops a solid crust that insulates the remaining liquid lava, helping to keep it hot and inviscid enough to continue flowing. Etymology The word ''lava'' comes from Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
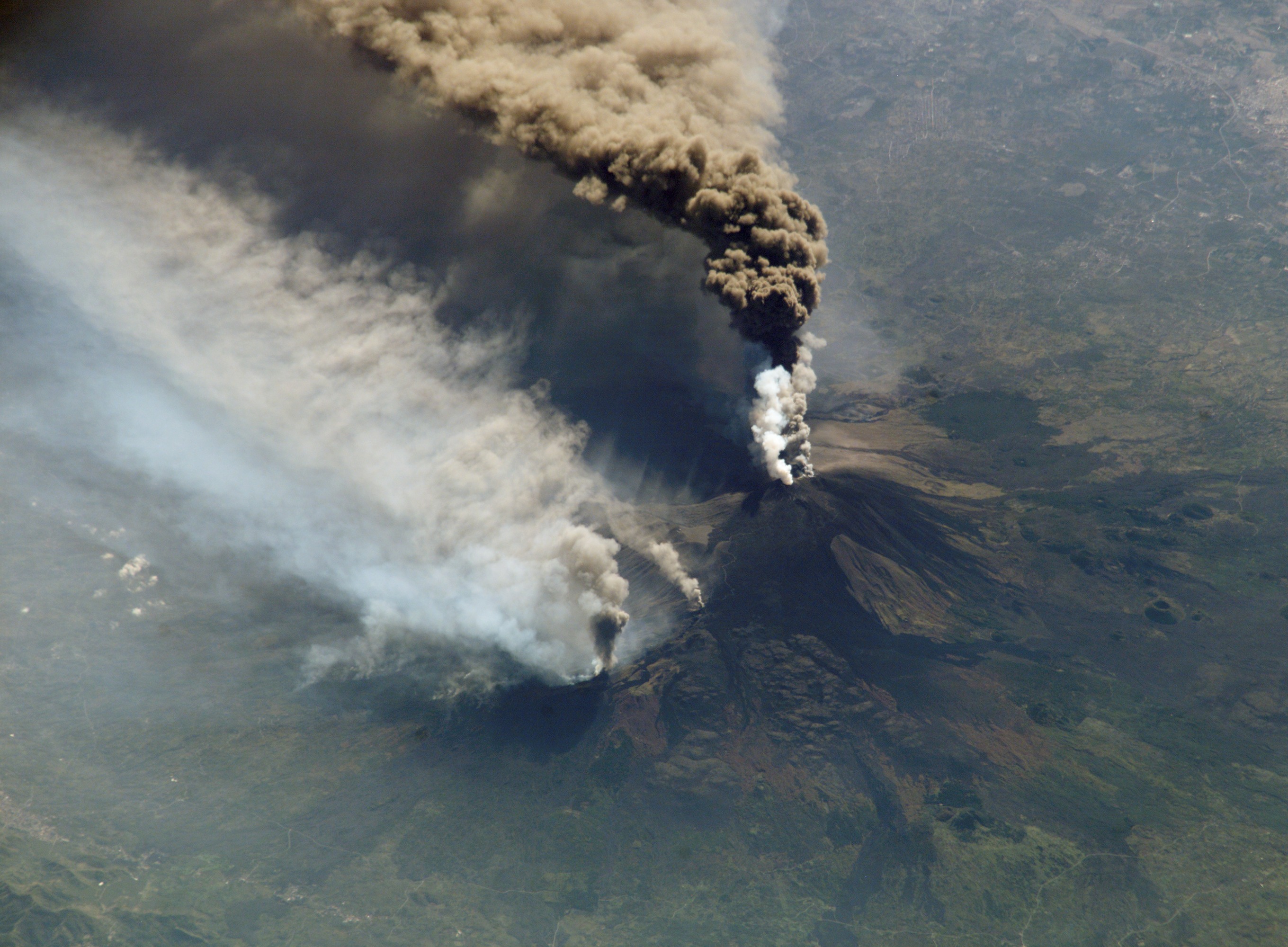
Volcanic Ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, produced during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer to all explosive eruption products (correctly referred to as '' tephra''), including particles larger than 2 mm. Volcanic ash is formed during explosive volcanic eruptions when dissolved gases in magma expand and escape violently into the atmosphere. The force of the gases shatters the magma and propels it into the atmosphere where it solidifies into fragments of volcanic rock and glass. Ash is also produced when magma comes into contact with water during phreatomagmatic eruptions, causing the water to explosively flash to steam leading to shattering of magma. Once in the air, ash is transported by wind up to thousands of kilometres away. Due to its wide dispersal, ash can have a number of impacts on society, including animal a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Gas
Volcanic gases are gases given off by active (or, at times, by dormant) volcanoes. These include gases trapped in cavities (Vesicular texture, vesicles) in volcanic rocks, dissolved or dissociated gases in magma and lava, or gases emanating from lava, from volcanic craters or vents. Volcanic gases can also be emitted through hydrothermal, groundwater heated by volcanic action. The sources of volcanic gases on Earth include: * primordial and recycled constituents from the Earth's mantle, * assimilated constituents from the Earth's crust, * groundwater and the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Substances that may become gaseous or give off gases when heated are termed volatile substances. Composition The principal components of volcanic gases are water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur either as sulfur dioxide (SO2) (high-temperature volcanic gases) or hydrogen sulfide (H2S) (low-temperature volcanic gases), nitrogen, argon, helium, neon, methane, carbon monoxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intraplate Volcanism
Intraplate volcanism is volcanism that takes place away from the margins of tectonic plates. Most volcanic activity takes place on plate margins, and there is broad consensus among geologists that this activity is explained well by the theory of plate tectonics. However, the origins of volcanic activity within plates remains controversial. Mechanisms Mechanisms that have been proposed to explain intraplate volcanism include mantle plumes; non-rigid motion within tectonic plates (the plate model); and impact events. It is likely that different mechanisms accounts for different cases of intraplate volcanism. Plume model A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection of abnormally hot rock within the Earth's mantle. Because the plume head partly melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hotspot (geology), hotspots, such as Hawaii hotspot, Hawaii or Iceland hotspot, Iceland, and large igneous provinces such as the Deccan Traps and Sib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotspot (geology)
In geology, hotspots (or hot spots) are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying Mantle (geology), mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Examples include the Hawaii hotspot, Hawaii, Iceland hotspot, Iceland, and Yellowstone hotspots. A hotspot's position on the Earth's surface is independent of plate boundary, tectonic plate boundaries, and so hotspots may create a chain of volcanoes as the plates move above them. There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins. One suggests that hotspots are due to mantle plumes that rise as thermal diapirs from the core–mantle boundary. The alternative plate theory (volcanism), plate theory is that the mantle source beneath a hotspot is not anomalously hot, rather the crust above is unusually weak or thin, so that lithospheric extension permits the passive rising of melt from shallow depths. Origin The origins of the concept of hotspots lie in the work of J. Tuzo Wilson, who postulated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Winter
A volcanic winter is a reduction in global temperatures caused by droplets of sulfuric acid obscuring the Sun and raising Earth's albedo (increasing the reflection of solar radiation) after a large, sulfur-rich, particularly explosive volcanic eruption. Climate effects are primarily dependent upon the amount of injection of SO2 and H2S into the stratosphere where they react with OH and H2O to form H2SO4 on a timescale of a week, and the resulting H2SO4 aerosols produce the dominant radiative effect. Volcanic stratospheric aerosols cool the surface by reflecting solar radiation and warm the stratosphere by absorbing terrestrial radiation for several years. Moreover, the cooling trend can be further extended by atmosphere–ice–ocean feedback mechanisms. These feedbacks can continue to maintain the cool climate long after the volcanic aerosols have dissipated. Physical process An explosive volcanic eruption releases magma materials in the form of volcanic ash and gases into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge (a Divergent boundary, divergent or constructive Plate tectonics, plate boundary) located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest mountain range in the world. In the North Atlantic, the ridge separates the North American plate, North American from the Eurasian plate and the African plate, north and south of the Azores triple junction. In the South Atlantic, it separates the African plate, African and South American plate, South American plates. The ridge extends from a junction with the Gakkel Ridge (Mid-Arctic Ridge) northeast of Greenland southward to the Bouvet triple junction in the South Atlantic. Although the Mid-Atlantic Ridge is mostly an underwater feature, portions of it have enough elevation to extend above sea level, for example in Iceland. The ridge has an average spreading rate of about per year. Discovery A ridge under the northern Atlantic Ocean was first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle Plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hotspots, such as Hawaii or Iceland, and large igneous provinces such as the Deccan and Siberian Traps. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, while others represent unusually large-volume volcanism near plate boundaries. Concepts Mantle plumes were first proposed by J. Tuzo Wilson in 1963 and further developed by W. Jason Morgan in 1971 and 1972. A mantle plume is posited to exist where super-heated material forms ( nucleates) at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle. Rather than a continuous stream, plumes should be viewed as a series of hot bubbles of material. Reaching the brittle upper Earth's crust they form diapirs. These diapirs are "hotspots" in the crust. In particular, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |